Titration of Cyanide Solutions

Titration of Cyanide Solutions Containing Dissolved Zinc: Sodium zinc cyanide reacts with silver nitrate to precipitate zinc cyanide: Na2Zn(CN)4 + AgNO3 = Zn(CN)2 + NaAg(CN)2 + NaNO3 In the presence of an alkali, considerably more silver nitrate must be added to sodium zinc cyanide before a precipitate is formed. Many investigators have claimed that this […]
Zinc Cyanide & Silver Gold Precipitation
In cyanidation, zinc (the Merrill-Crowe Process) is practically the universal precipitant for precious metals dissolved in cyanide solutions although for specific reasons aluminium and charcoal have been used. During the reactions involved in precipitation, the greater part of the zinc dissolves in the cyanide solution and forms various cyanogen complexes such as sodium or calcium […]
Effect of Temperature on Gold Cyanidation

When heat is applied to a cyanide solution containing metallic gold, two opposing factors affect the rate of dissolution. The increase in temperature would be expected to increase the activity of the solution and thus increase the rate of dissolution of gold. At the same time the amount of oxygen in the solution would decrease […]
Effect of pH Alkalinity on Gold Leaching

The role pH has in affecting gold leaching rates by cyanide and the functions of calcium hydroxide in cyanidation are as follow: 1. For safety and to prevent loss of cyanide by hydrolysis. 2. To prevent loss of cyanide by the action of carbon dioxide in the air. 3. To decompose bicarbonates in mill water […]
Effect of Oxygen on the Dissolution of Gold

In discussing the effect of oxygen on the gold dissolution, one can understand the use of oxygen or an oxidizing agent is essential for the dissolution of gold under normal conditions of cyanidation. Such oxidizing agents as sodium peroxide, potassium permanganate, bromine, chlorine have been used with more or less success in the past; but […]
Effect of Gold Particle Size on Rate of Dissolution

When coarse free gold occurs in ores, the usual practice is to remove it by means of gold traps, jigs, blankets, etc. ahead of cyanidation. Otherwise, these coarse particles might not be completely dissolved in the time available for cyanidation. Another practice which reduces the size of the gold particles going to cyanidation is the […]
Gold & Silver Dissolution and Cyanide Concentration

By far the most important cyanides used in cyanidation are sodium cyanide and calcium cyanide. The latter product is sold in an impure form analyzing close to 50% NaCN equivalent. The former is sold in various grades from 85 to 98% NaCN. In comparing the dissolving effects of the cyanides of ammonium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, […]
Arsenic and Antimony Sulphide Minerals in Cyanidation

The successful cyanidation of gold ores containing appreciable amounts of arsenic or antimony sulphide minerals such as orpiment, realgar, and stibnite is usually difficult or even impossible. Extractions are low and the solutions soon become ‘foul.’ The gold in such ores could be free and uncoated, and no trouble in dissolving it in clean cyanide […]
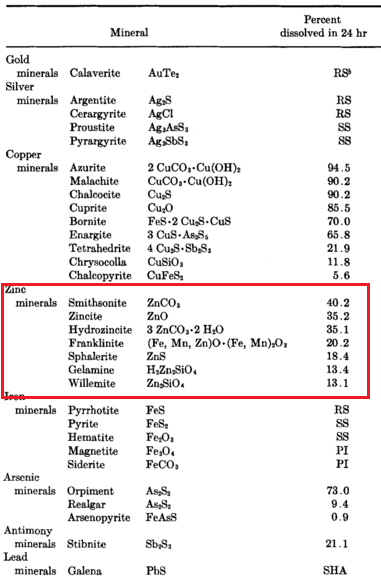
How Copper Affects Cyanidation & Leaching
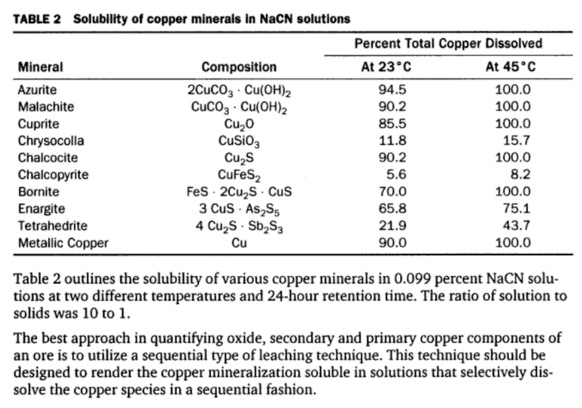
Many precious metal ores contain copper minerals in various amounts. These copper minerals dissolve in cyanide solutions to a greater or lesser degree depending on the particular copper mineral or minerals present, their fineness, and the dissolving effect of the cyanide solutions. In the process of dissolution the copper combines with, or as it is […]
Process of Cyanide Gold Extraction

Here I present an Process EXAMPLE of Gold Extraction Cyanide in which the cyanidation feed consists of a pyrite concentrate floated after the selective flotation of a copper-gold concentrate. The pyrite concentrate is reground to 90% minus 325 mesh and aerated in a high-lime solution prior to cyanidation. It contains 99% sulphides of which 10 to […]
