Waste Chromic Acid – Sulfuric Acid Etchants Regeneration

Two of the missions of the Bureau of Mines are to conserve scarce, costly metals and to reduce pollution. In accordance with these missions, the objective of this investigation was to develop a method of recycling spent chromium etching solutions that are now discarded as wastes. Solutions containing hexavalent chromium (as chromic acid or sodium […]
Aluminum Dross Furnace Salt Slags Processing

Disposal of the salt slag produced during the processing of aluminum dross and scrap is of particular interest to the secondary aluminum industry. Melting of these materials is carried out under a salt flux cover to dissolve the contaminants, mostly aluminum oxide, and to optimize the recovery of aluminum metal. Typically, dross and low-grade scrap […]
Hot Rolling Metals in Vacuum
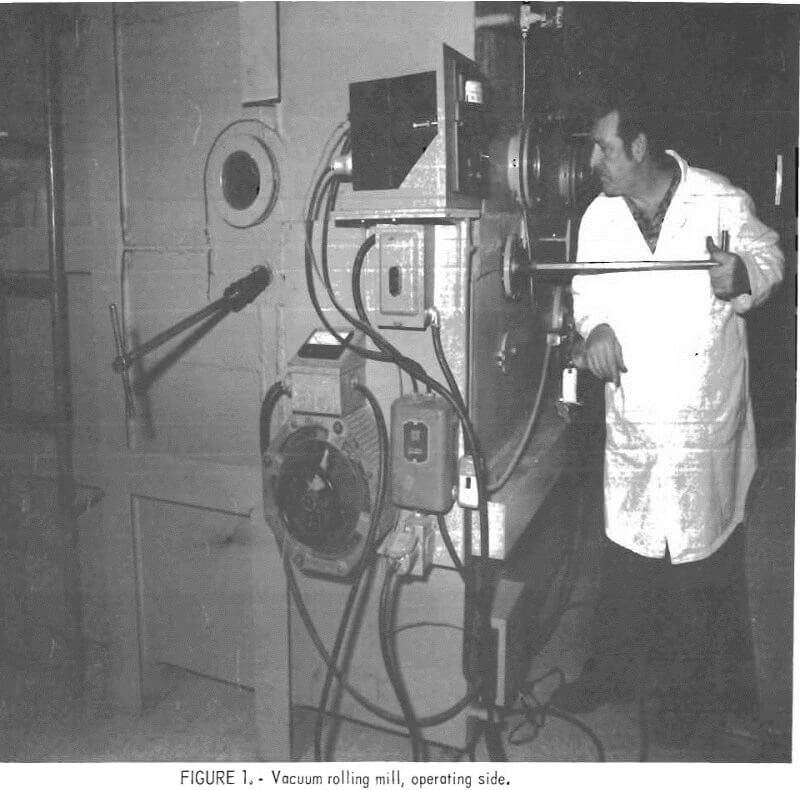
Among the significant technological accomplishments of the third quarter of the 20th century was the wide application of vacuum-to-metal melting. Many of the more common metals, as well as superior alloys of steel, have benefited from vacuum degassing, and the production of reactive and refractory metals leans heavily on vacuum-melting techniques. Fabrication and other forming […]
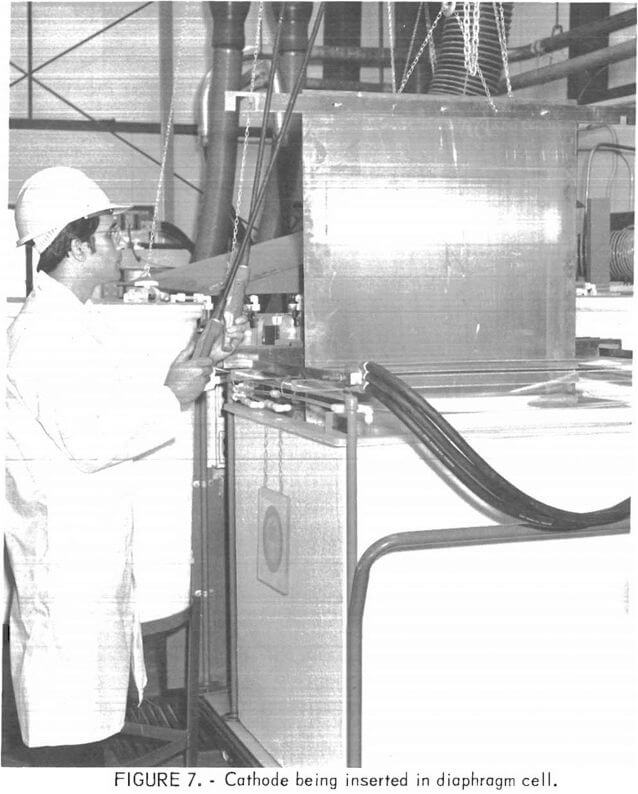
Zinc Electrolysis
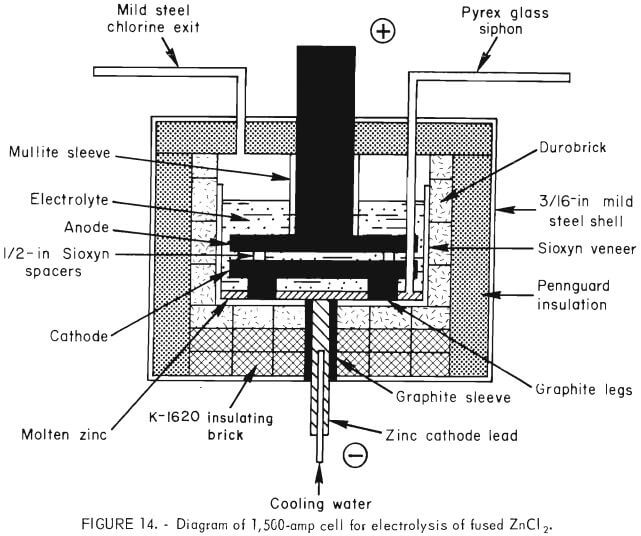
Zinc Electrolysis was studied to help maintain an adequate domestic minerals base, the Bureau of Mines is investigating an aqueous chlorine-oxygen leaching procedure to produce ZnCl2 from sulfide concentrate and is also studying a fused-salt electrolytic technique to produce zinc metal from ZnCl2. Several chlorine leach/electrolysis methods for treating zinc ores and concentrates have been […]
Electroslag & Electric Arc Furnace Processes

Demand for pressure vessel steels for use in power generation and energy transport applications is increasing in the United States. Coupled with the increased demand is the requirement for higher quality steels that are better able to withstand temperature extremes and mechanical stresses, and that possess greater tensile ductility, impact strengths, and isotropy. One important […]
Electrorefining Copper
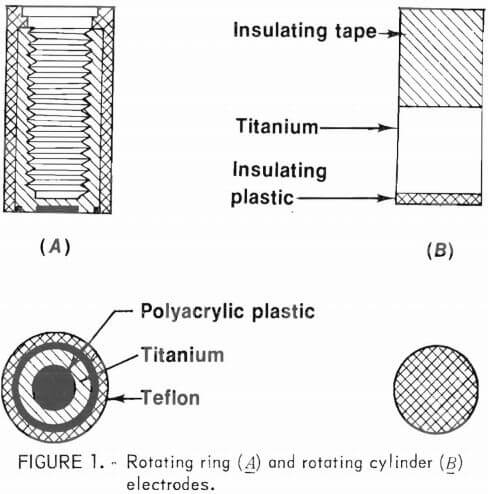
This report discusses Electrorefining Copper research conducted to increase the rate, deposit purity, and overall efficiency in industrial processes used to electrodeposit and purify metals by increasing substantially the operating current density range and optimizing the deposition process. Traditionally, copper refineries operate electrolytic cells at a current density of 20 amp/ft². At this current density, the […]
Cristobalite in Fire Clay Calcines
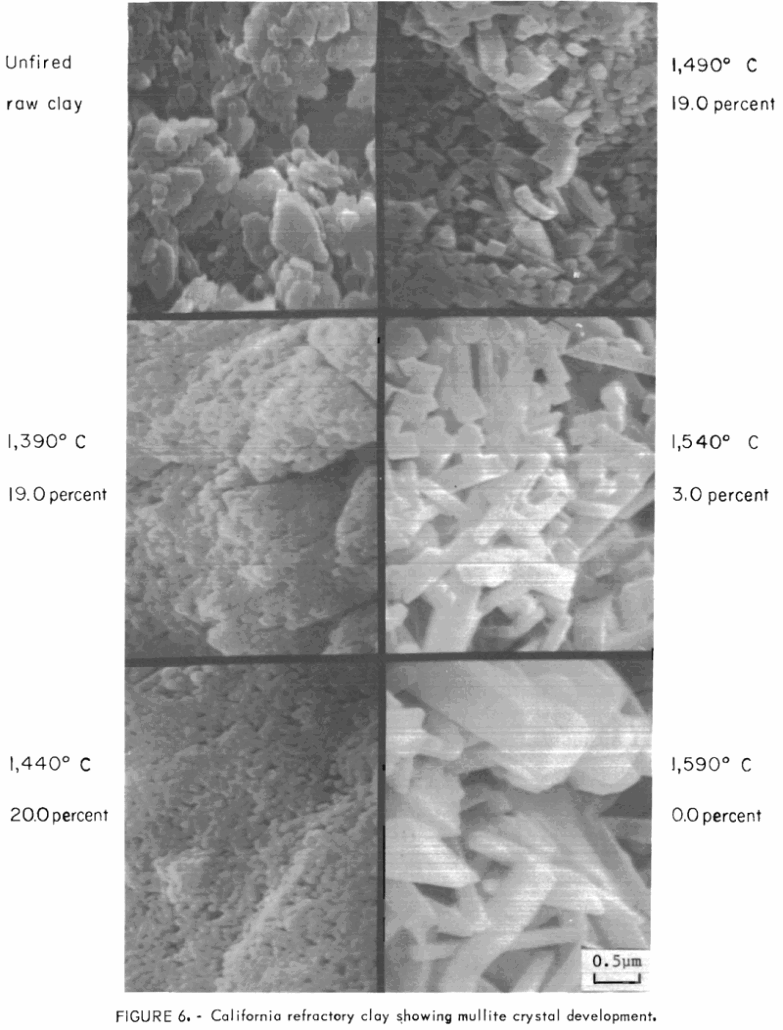

One goal of the Bureau of Mines is to conserve the Nation’s mineral resources by developing improved performance materials. Consistent with this goal, the Bureau conducted studies on the formation of undesirable cristobalite in seven different fire clays used as refractories. The studies employed scanning electron micrography, chemical and X-ray analyses, and pyrometric cone equivalent […]
Remove SO2 from Lead Smelter by Citrate Process
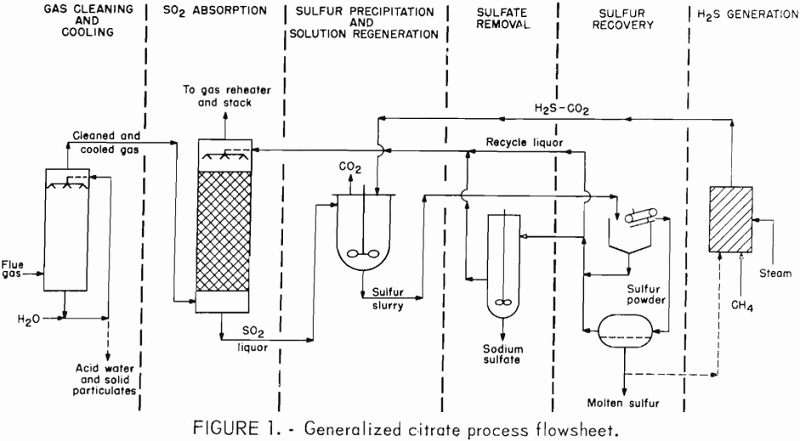
The Federal Bureau of Mines has developed a flue gas desulfurization (FGD) process that uses a carboxylate solution, such as citric acid, to absorb sulfur dioxide (SO2) from industrial waste gases. The absorbed SO3 is subsequently reacted with hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to precipitate sulfur and regenerate the solution for recycle. This process is known as […]
Electric Smelting Furnace of Ore
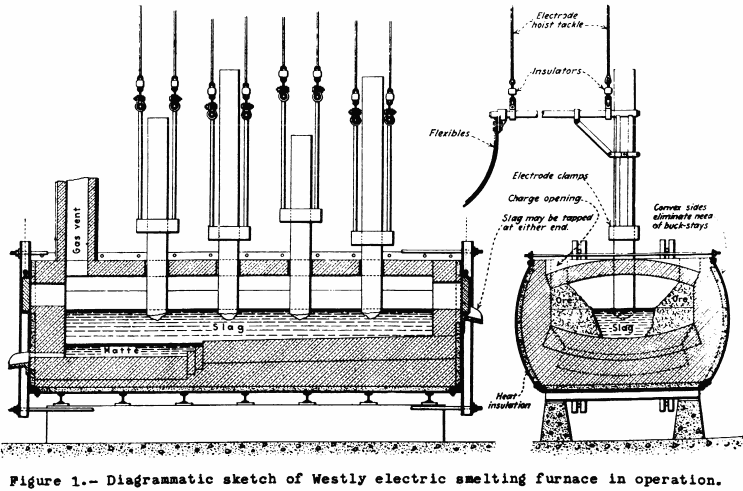
The possibility of cheap electric power for a number of mining areas in this country has suggested to many the idea of electric smelting of nonferrous ores in small units at or near the mines. The electric smelting of nonferrous ores was tested fairly thoroughly 20 years ago by United States Bureau of Mines and […]
Steel Chimney Lining of Copper Smelting Plants
In the Southwest a number of large steel chimneys discharge the gases from the copper smelting furnaces. Some of these chimneys show no deterioration after twenty years, others show serious deterioration after four years service. A steel stack 20 ft. 7½ in. (6.3 m.) in diameter by 279 ft. (85 m.) high, Fig. 1, used […]
