Zinc Electrowinning from Chloride Electrolyte
Chemical and electrochemical leaching processes using chloride solutions (FeCl3, HCl, CuCl2) and dry chlorination with Cl2 gas followed by leaching of the resultant chlorides are some of the methods considered for treating fine-grained Zn-Pb-Cu-Fe sulphide ores and concentrates. These processes eventually result in an impure zinc chloride liquor which, after purification using either solvent extraction […]
Uranium Precipitation by Hydrogen Peroxide
Uranyl peroxide precipitation offers two advantages over other precipitation methods, product purity and product handling. However, since it is a less well known process than ammonia, caustic or Mag-Ox precipitation, it is helpful to demonstrate the advantages of hydrogen peroxide by comparing its performance with the widely known and used ammonia precipitation process. First, product […]
Recycling Chrome Refractory Waste
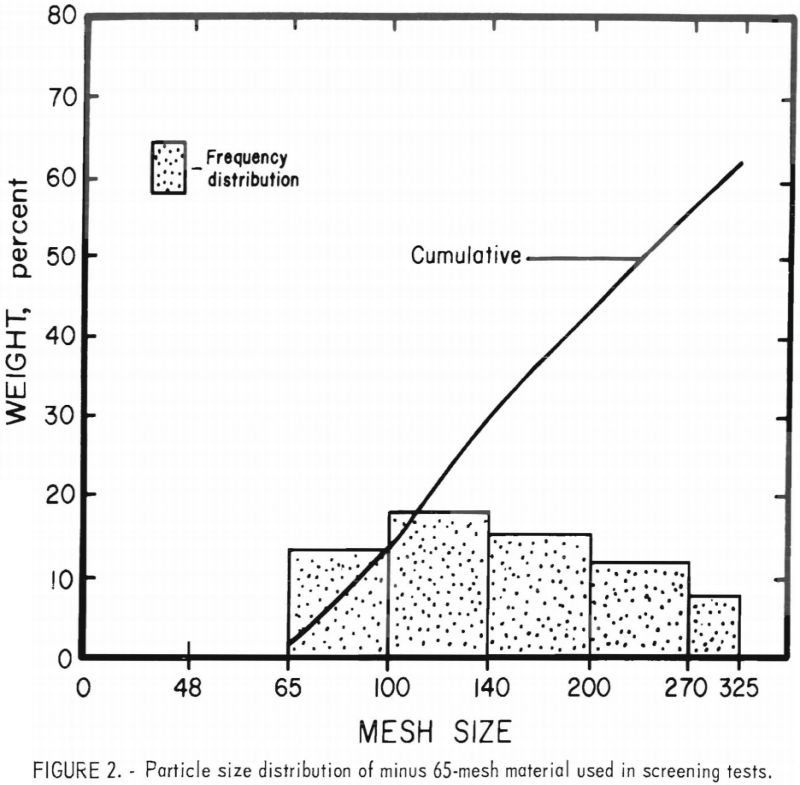
Chromite ore in combination with various quantities of magnesia is used in basic refractories. Refractories of this type are used as linings in steelmaking and copper smelting furnaces, rotary cement calciners, and glassmaking tanks. However, most of the consumption is by the copper and steel industry. Approximately 20 percent of the chromite consumed in the […]
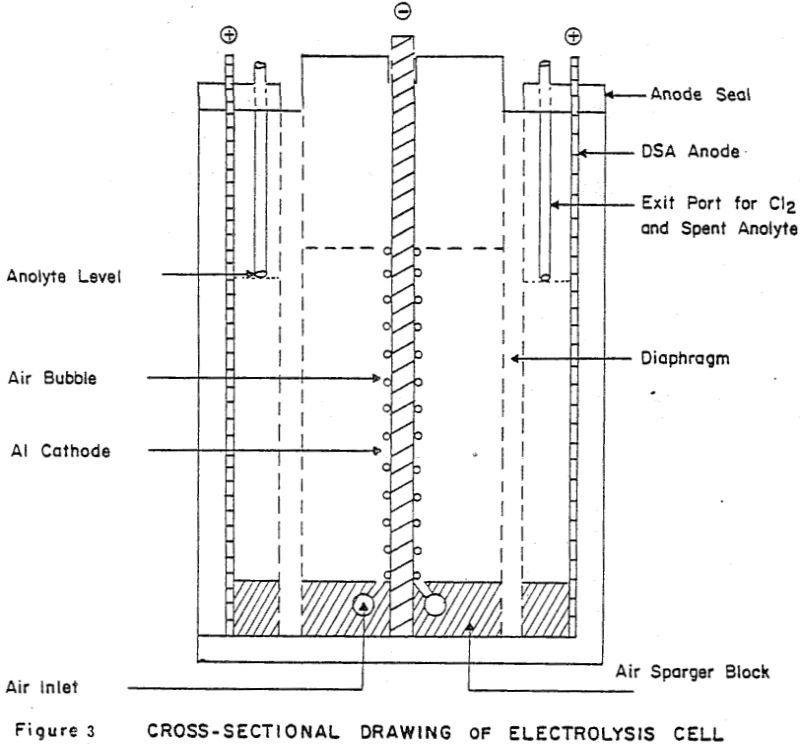
Chloride Leaching of Silver and Precipitation Recovery of Ag
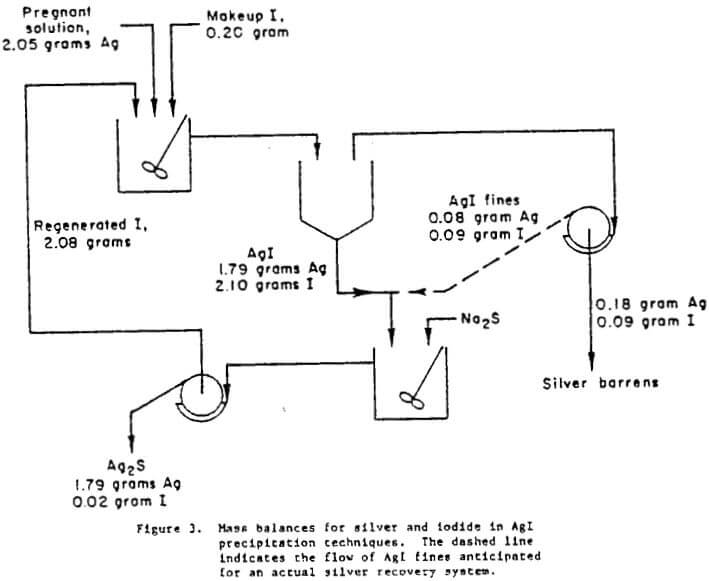
As part of the U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines, mission to assure a viable domestic minerals and materials economy, research is being conducted to investigate methods for recovering accessory elements from solutions resulting from hydrometallurgical processing of base-metal sulfide concentrates. These types of sulfide concentrates have traditionally been treated by smelting procedures […]
Ferrochromium Alloys Manufacturing
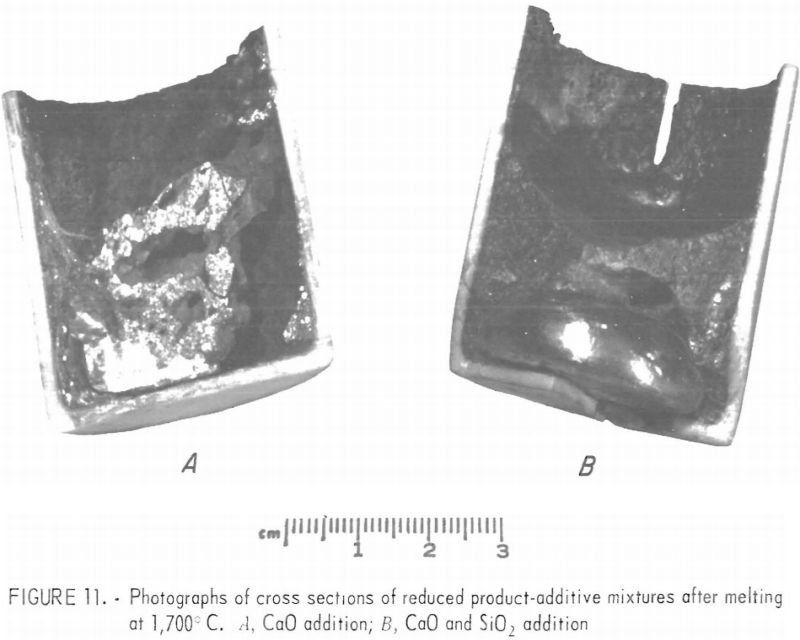
As part of its effort to reduce the need for strategic minerals through conservation and to reduce the capital and energy requirements of mineral processing, the Bureau of Mines has investigated a method for preparing ferrochromium alloys containing less than 2 percent carbon. This method will conserve chromium and should reduce the capital and energy […]
Extracting Lithium
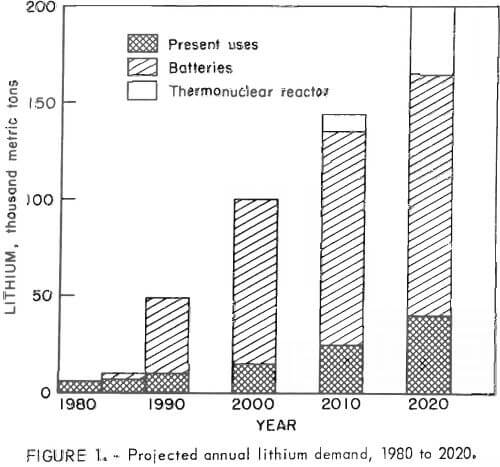
The Federal Bureau of Mines investigated extraction of lithium from non-conventional resources in keeping with its goal of maximizing minerals and metals recovery from domestic resources in order to assure an adequate supply of minerals to meet national economic and strategic needs. This report describes the results of bench-scale studies on the processing characteristics of […]
Electrolytic Reduction using Coke Electrodes
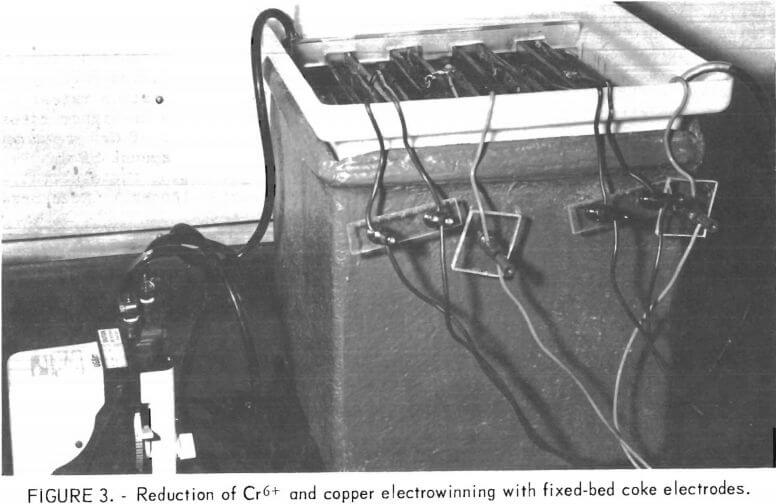
The objective of this investigation was to reduce toxic Cr6+ in various waste processing liquors to less toxic Cr3+ while simultaneously removing copper. In addition to recovering a valuable copper product, removal of copper and reduction of Cr6+ in these liquors will substantially decrease the chemical demand and increase efficiency in waste treatment operations associated […]
Electric Arc Furnace Operation
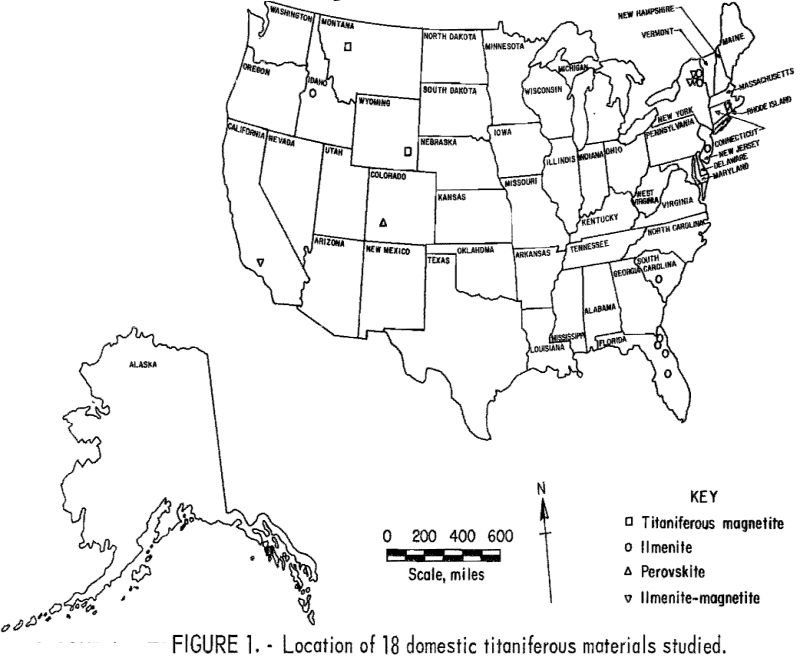
The lack of domestic reserves of rutile and high-grade ilmenites to accommodate the projected increased demand for TiO2 has prompted the Bureau of Mines to investigate methods for recovering titanium from lower grade deposits. In addition, rapid depletion of domestic high-grade iron ore deposits constitutes a growing problem. The United States is well endowed with […]
Roasting of Copper Smelter Feed
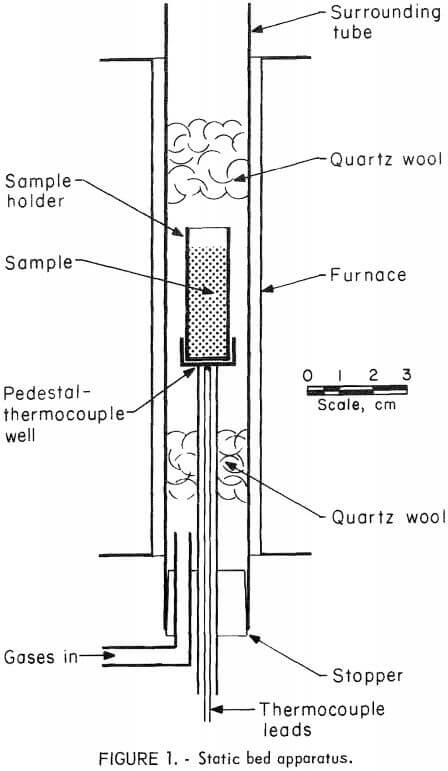
Arsenic is produced in the United States as a byproduct from base metal ores. Although this production supplies only about one-half of the national demand, arsenic is generally not recovered but is treated as a troublesome impurity. Its complete recovery in domestic metallurgical plants could nearly supply the country’s arsenic needs, but complicated and inefficient […]
Titanium Oxide or Titania Pigment by Ilmenite
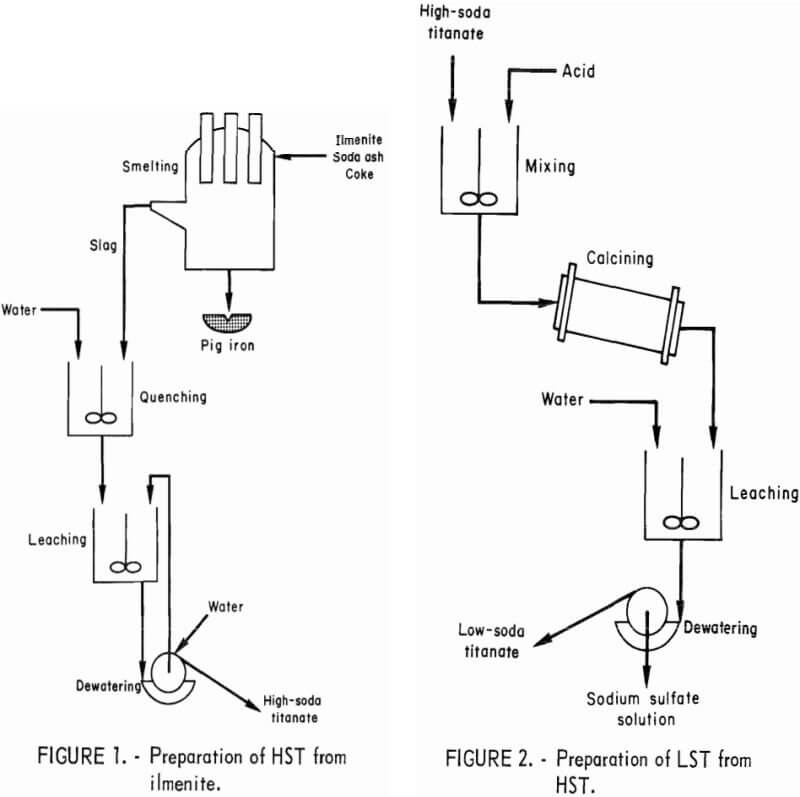
Titanium dioxide or titania pigment is prepared commercially from ilmenite, an iron-titanium oxide mineral, by the sulfate process. Ilmenite is digested with H2SO4 to yield a titanium sulfate solution. Subsequently, the solution is hydrolyzed to yield a hydrous titania precipitate that is calcined to produce pigment. A major problem associated with the process is the […]
