Emulsion Polymers -Mixing Procedure

Emulsion polymers are polymer in oil emulsions and are designed to “break” out of this emulsion into a water solution at 0.5 to 1.0% concentration. If water is allowed to get into the bulk storage tank, either by backing up in the feed line or by condensation, gels will form. They may take the […]
Preparation of Solution Polymers
Here is a Procedure for the Preparation of Solution Polymers: Solution polymers can be made down to any convenient concentration for laboratory testing. Suggested solution concentrations should be based on the expected dosage, ie: For raw water clarification 0.05 to 0.10% or for use in sludge dewatering at 1.0 to 5.0%. Use the same water for […]
Iron in Cyanidation -Ferrocyanide Compounds

Practically all ores treated by the cyanidation process contain iron minerals. In addition, the equipment in cyanidation plants with which cyanide solutions come in contact is made largely of iron and steel. Fortunately, cyanide solutions have very little action on metallic iron and most iron minerals, otherwise the cyanidation process would be impractical for die […]
Copper – Lead Separation by Lead Depression
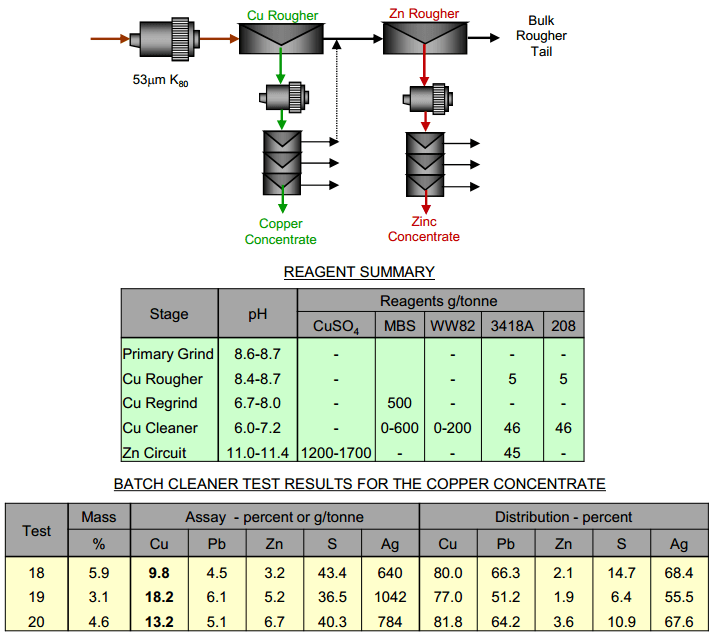
Another method to separate Pb from Cu is in depressing the lead away from the copper to float. Here, three batch cleaner tests were performed with additional depressants to reject more lead from the copper flotation concentrate. The baseline test utilized no MBS depression in the rougher circuit to maximize copper recovery, but MBS depression in the copper […]
How to Separate Copper from Lead by Cu Depression
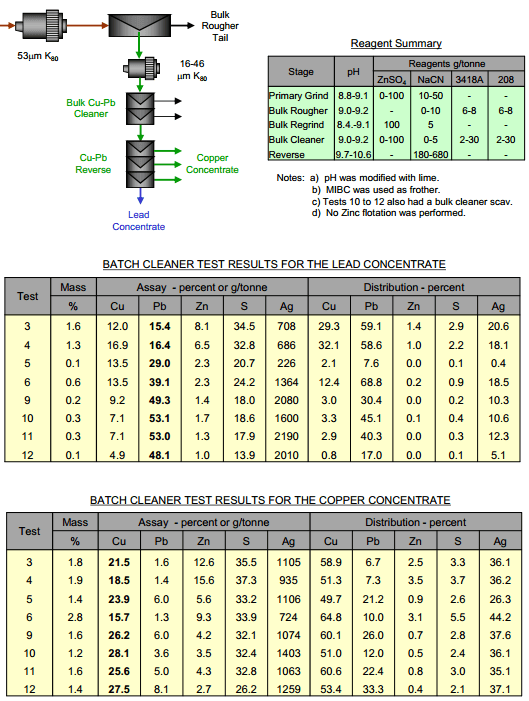
How you separate Pb from Cu depends on how much of each metal is present. You best depress the metal that’s the most present, the metal you have the most of & you float the metal you have the least of. In this case, flotation of a small amount of lead from the copper concentrate would […]
Silver & Gold Cyanide Leaching of Copper Ore

Much work has been done on the effect of copper in cyanide solutions on the leaching of gold. It is generally accepted that copper in cyanide solutions can form complex ions such as Cu(CN)2-, Cu(CN)3=, and Cu(CN)4=-, although Cu(CN)3= is considered the most probable of these. According to leach scientists, the complex having an empirical formula […]
Free Cyanide Titration: Pyrrhotite & Sodium Sulphide, Thiosulphate, Thiocyanate, Ferrocyanide

When cyaniding a precious metal ore containing pyrrhotite, various compounds such as, thiosulphate, thiocyanate, ferrocyanide and soluble sulphide are formed and found in the cyanide solution. Soluble sulphides, if present at all, are found only in relatively small amounts; on the other hand thiosulphate, thiocyanate and ferrocyanide have been found in solutions in amounts of […]
GOLDIX
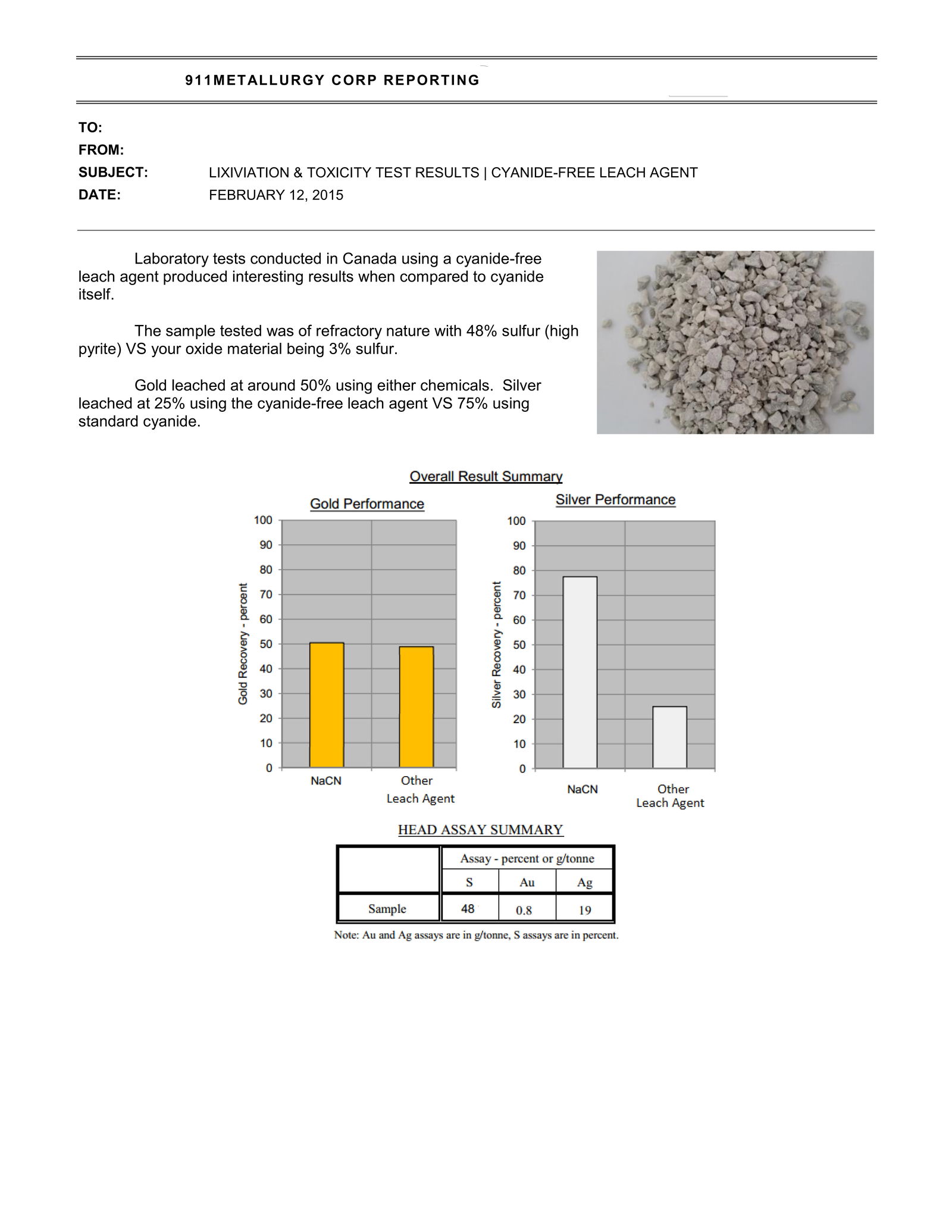
Discuss Goldix 1, 2 and 3
Gold/Silver Leaching with Sodium Zinc Cyanide

Dissolution of Precious Metals in Sodium Zinc Cyanide: The dissolving effect of sodium zinc cyanide on precious metals has been the subject of much discussion. According to one researcher, pure K2Zn(CN)4 in the presence of oxygen dissolves gold with the formation of gold potassium cyanide and zinc oxide. Another researcher compared the dissolving effects of KCN and […]
Titration of Cyanide Solutions
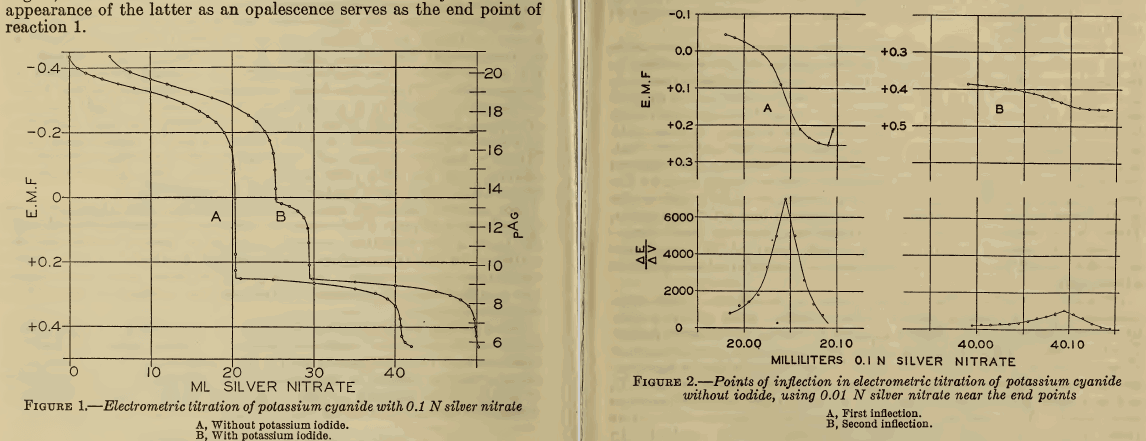
Titration of Cyanide Solutions Containing Dissolved Zinc: Sodium zinc cyanide reacts with silver nitrate to precipitate zinc cyanide: Na2Zn(CN)4 + AgNO3 = Zn(CN)2 + NaAg(CN)2 + NaNO3 In the presence of an alkali, considerably more silver nitrate must be added to sodium zinc cyanide before a precipitate is formed. Many investigators have claimed that this […]
