Why Oxygen is Important in Cyanidation
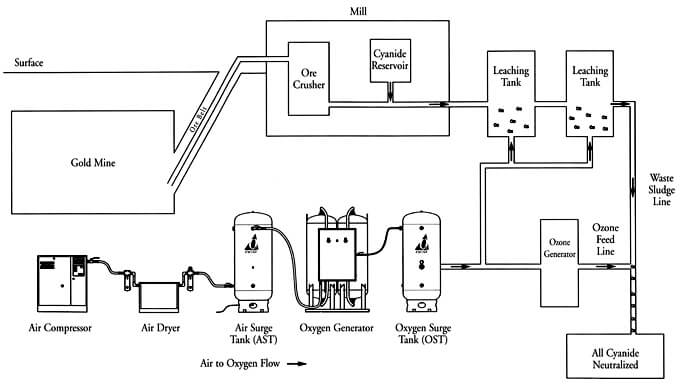
The Rule and Function of Oxygen in Cyanidation.—Oxygen appears to be an indispensable factor, either directly or indirectly, in the dissolution of gold and silver by cyanide solutions, except in the case of the haloid compounds of silver. Whether the action of oxygen in the dissolution of gold be a direct one, as illustrated by the […]
Hydrochloric Acid & Sodium Cyanide

Even a small concentration of hydrochloric acid in the air irritates the membranes of the respiratory tract making it easily detectable in amounts below the Threshold Limit Value of five parts per million. One to five parts per million can be detected by smell, while five to ten parts become disagreeable. In addition hydrochloric acid […]
Lead Nitrate Safety

Lead nitrate is used in small quantities in the gold recovery circuit. Lead is extremely toxic. It is a cumulative poison and so a dangerous exposure level would not necessarily show an immediate result, but continuous exposure at this level would maybe show as serious problems after a month. View a lead nitrate MSDS. Ingestion of […]
Sodium Cyanide Safety – Poisoning – HCN Vapor

Almost all solutions in the plant contain cyanide, and in the absence of any other information it should be assumed that all solutions contain cyanide. Because of the toxicity of sodium cyanide, it is important that all persons coming in contact with it be completely familiar with and observe the established safety practices. Sodium cyanide […]
Effect of Cyanide on Steel and Iron Minerals Leached by Cyanide

The corrosion of black rolled mild steel in sodium cyanide solution is negligible. A piece of steel suspended in a sodium cyanide solution maintained at 0.05% NaCN and 0.001% CaO, in the presence of air, lost 0.002% of its weight in two weeks, this was equivalent to a penetration of 0.76 micron per year.Oxidized iron minerals […]
Flotation Oils

The work of the past two years at many mills in the United States, Mexico, and South America, has done much to prove the suitability of flotation processes to the recovery of the sulphide ores of copper, and to indicate the best reagents. In a general way, it may be said that oils of mineral […]
Gravity Borax Method GBM Mercury Free Gold Recovery

The Gravity-Borax Method GBM is still unknown to most Artisanal and small-scale gold miners (ASGMs) worldwide as most still use mercury to extract gold. “Whole-ore amalgamation” is a technique that requires the use of 10–25 g of mercury to produce 1 g of gold. Within the last eight years, it has become evident that this technique is more […]
Cyanide Leaching and Decomposition of Pyrrhotite

Research on cyanidation methods brought considerable discussion on the reactions involved in the leaching and decomposition of pyrrhotite in cyanide solutions. Pyrrhotite has one loosely held sulphur atom which readily reacts with cyanide to form thiocyanate: Fe5S6 + NaCN = NaCNS + 5 FeS The ferrous sulphide oxidizes rapidly to the sulphate which reacts with cyanide to […]
Eliminating Copper from Gold Ore
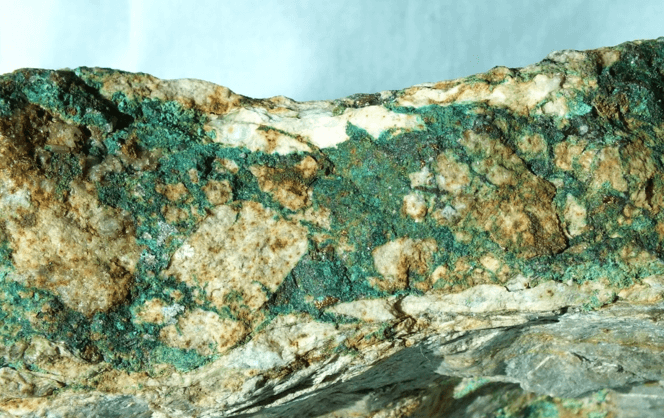
When reviewing Methods of Eliminating Copper from Gold Ores we see that several methods have been suggested to eliminate copper from ores prior to cyanidation. Preliminary extraction of the copper with sulphuric or sulphurous acids may be applicable to ores containing oxidized copper minerals such as malachite, azurite and chrysocolla but these acids have but little […]
Pyrite Depression in Copper Flotation
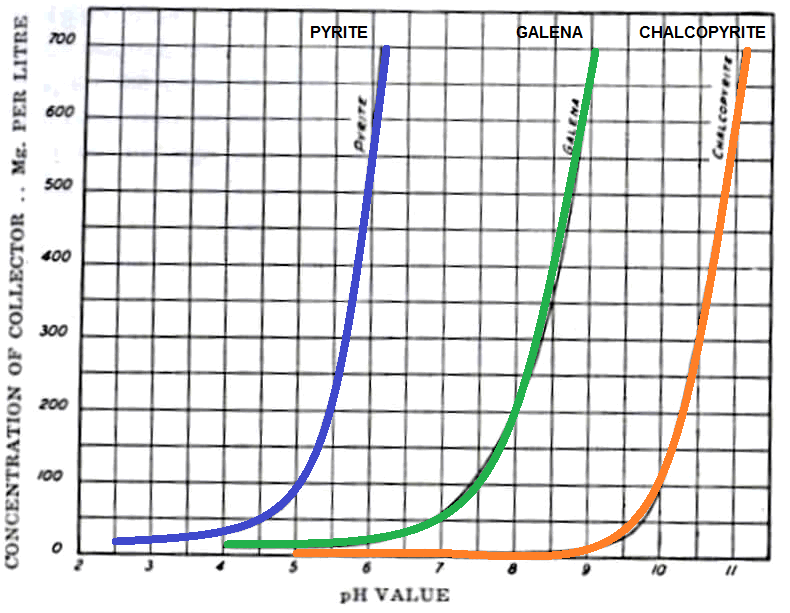
The Pyrite Depression in a Copper Only Flotation circuit is simple enough. If your froth flotation system only tries to recover chalcopyrite-copper, you need to bring the plant’s pH up to the other side (right side) of the PYRITE curve. The more flotation collector you have on, the higher you will need to increase that pH […]
