Reagent Distribution Systems and Feeders
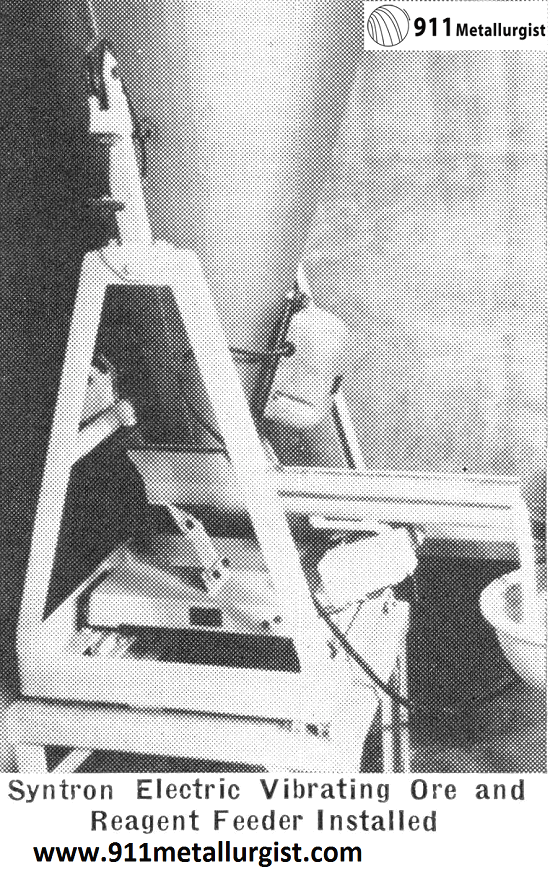
Electric Vibrating Feeder The Syntron Electric Vibrating Feeder is built on the same simple and strong principles as the Syntron Electric Vibrator. The vibrating trough is carried on two leaf springs and vibrated through the pulsating current of an electro-magnet. The speed of this magnet is controlled by a separate electric controller, which is furnished […]
Reagent Emulsifier
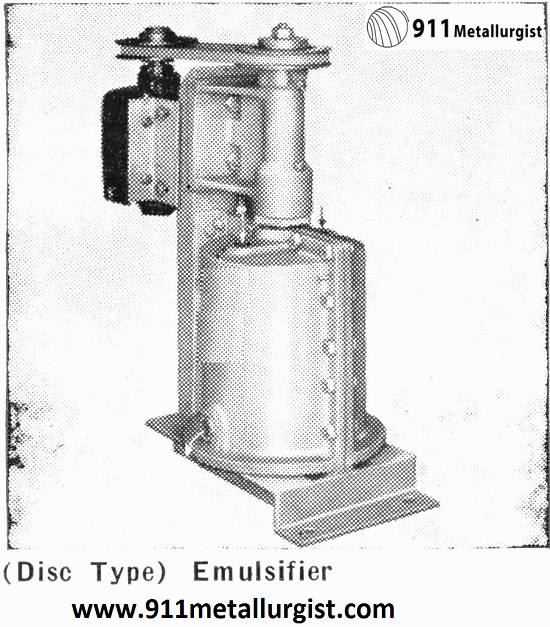
The (Disc Type) Reagent Emulsifier is used to emulsify flotation reagents with water before introducing them into the cells. By using this unit greater efficiency is attained from reagents, decreasing the amount necessary to produce the best flotation results. The unit consists of a sturdily constructed tank and impeller, together with the driving motor, on […]
Slurry Agitator Mixer & Flotation Conditioner
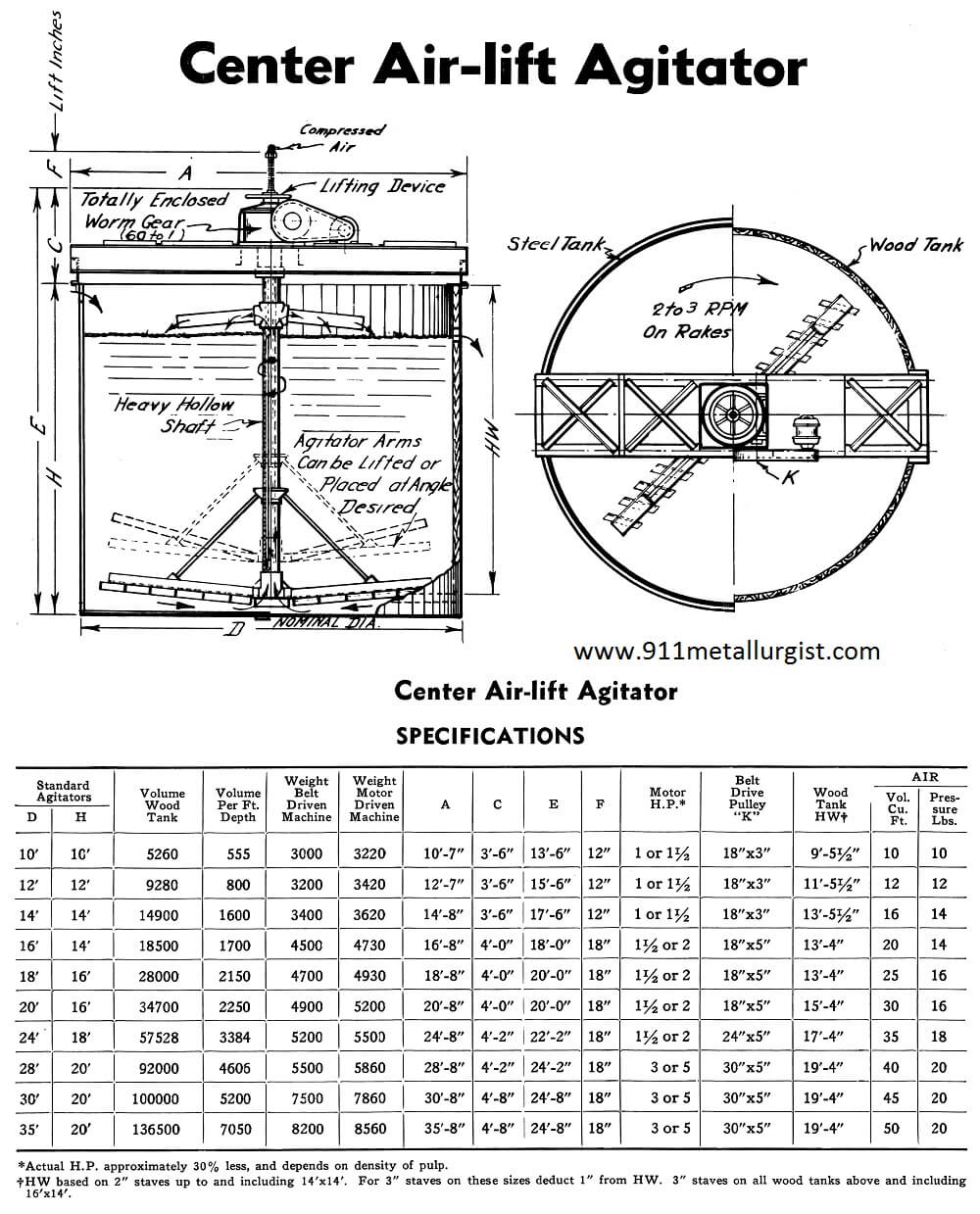
Any Air-lift Agitator is readily convertible from one to another of three general types. Center Air-lift, Side Air-lift or combined Side and Center Air-lift. Each type has its own advantages and application. No matter which type of Air-lift Agitator you have, it is the basis for any of the three general types, for each type […]
Electrolytic Oxygen in Cyanide Solutions
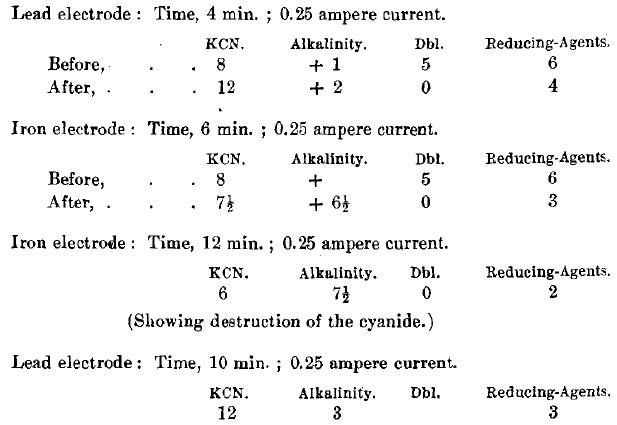
There are two conditions generally prevailing upon the earth—those within atmospheric influence, tending towards oxidation, and those away from atmospheric influence, tending towards reduction. Practically all mineral substances from mines of any depth are in a reducing condition. Since the cyanide process, in order to dissolve silver or gold, requires that the prevailing conditions under […]
Counter Current Decantation Cyanide Gold Leaching
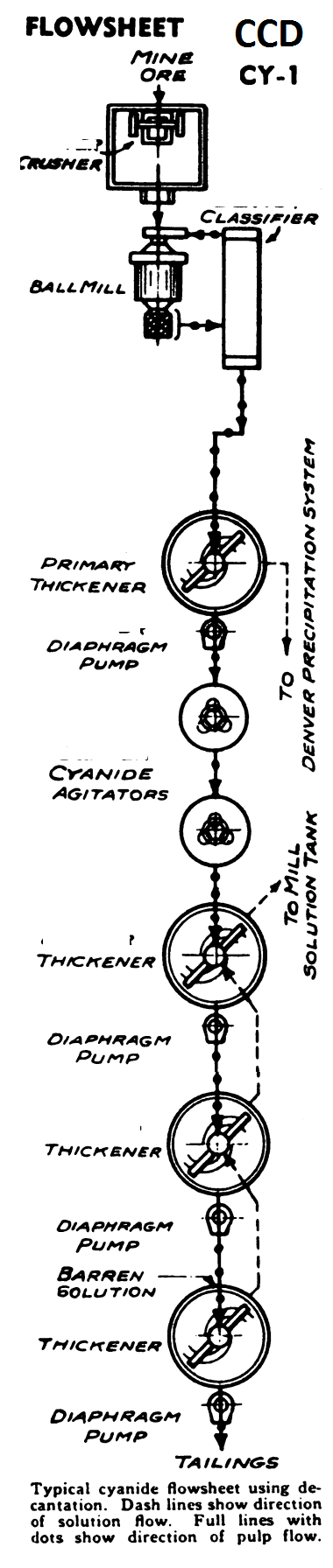
The Process Flowsheet CCD CY-1 shows (below) the continuous counter-current decantation system, in which all the ore is first reduced to a very fine state in the grinding mill-classifier circuit, in a cyanide solution. The slime overflow of the classifier, usually 70%—200 mesh, or finer, is sent to the first thickener, known as the primary thickener. […]
Fine Grinding in Cyanide Plant

This plant, near Marysville, Montana, was planned to treat the ore from the Piegan and Gloster mines, the latter being one of the early and famous producers of the Marysville district. When the mill was closed, treatment consisted of stamp milling, followed by pans and settlers for pan amalgamation. The extraction was evidently poor, because, a […]
Estimation of Free Cyanide using Iodine and Potassium

The process of estimating free cyanide depends upon the fact that when a solution of iodine in potassium iodide is added to a solution of a simple cyanide, the reddish-brown color of the iodine solution disappears so long as the cyanide is in excess, since the reaction results in the formation of an iodide of […]
Preparing Flotation Reagents

The following flotation reagent mixing system is typical for the flotation reagent mixing systems: A-208, Xanthate and Sodium Silicate. The reagent mix tanks, for the above mentioned reagents, are located on the basement floor. Feed chutes from the main operating floor carry dry or wet reagents to each mix tank. Either reclaim or fresh water is […]
Lime Addition System
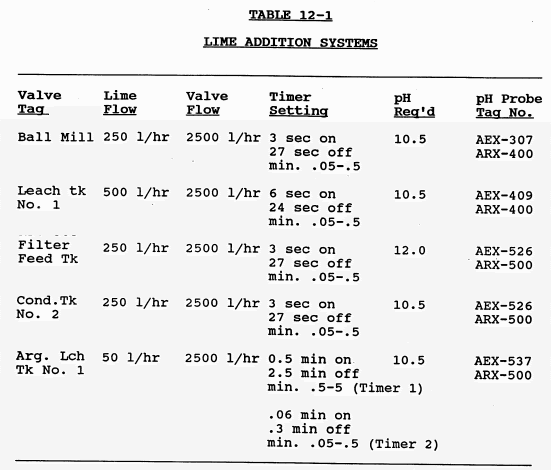
The lime system is a packaged unit which operates automatically and continuously. The equipment provided in the package includes the lime silo, rotary feeder, lime slaker and lime slurry mix tank and agitator. The lime system is equipped with its own PLC which automatically provides lime slurry for the process. Hydrated lime is stored in a […]
Silver Flotation Concentrate Leaching and Filtration Circuits

Producing a Silver Flotation concentrate from this EXAMPLE Argentite (cubic silver sulfide (Ag2S)) Flotation Circuit enters the first of four successive Argentite leach tanks. The purpose of this leach circuit is to dissolve the silver and gold recovered in the Flotation Circuit. A high strength solution of sodium cyanide, air, and lime are added to the […]
