How pH Affects Cyanide Decomposition & Use Alkalinity to Preserve Cyanide
Since acidity of the ore causes decomposition of the cyanide, an obvious method of reducing the loss is to add alkali in some form. Before doing this, the free sulphuric acid and soluble salts may be removed by leaching with water, and then a solution of caustic soda or lime is run on to the […]
How to Prepare and Storage of Cyanide Solution
The cyanide is usually dissolved in a little water before being added to the stock solution, as the amount of KCy present is more easily determined in a strong solution than in any other form. A special dissolving vat of small size is often provided and is placed at a higher level than the large […]
Gold Chloride
Gold Monochloride or Aurous Gold Chloride “AuCl” is a salt is prepared by heating the trichloride to 185° in air for twelve hours. It is non-volatile and unaltered at ordinary temperatures and pressure by dry air, even when exposed to light, but begins to decompose at temperatures above 160°, and the decomposition is complete if it is […]
Flotation Conditioning

Flotation Conditioning is often necessary as it is not sufficient merely to make the addition of the various reagents to the pulp and then to proceed with flotation. Intimate admixture is essential in order not only to bring about their even dissemination throughout the pulp but also to ensure that the millions of particles of […]
Assay gold and silver in cyanide solutions
In the assay of gold and silver in cyanide solutions the degree of accuracy and the speed desired are the governing factors in the choice of methods used and the quantity of solution taken for the determination. Evaporation {Litharge) Method To an evaporating dish add about 50 grams litharge and 146 to 292 cc cyanide solution. […]
Assaying for Zinc in Cyanide Solution
Zinc usually occurs in cyanide solutions as the double cyanide, but under certain conditions, e.g., in dilute solutions, a portion of the zinc may be present as zinc cyanide. It is possible that some may also exist as an alkaline zincate. Procedure To 500 cc of solution add 10 cc HCl, 10 cc HNO3, and […]
Ferrocyanide Assay Determination
The most reliable method of determining ferrocyanide in a cyanide solution is to determine the total iron and calculate to ferrocyanide. Volumetric Method Procedure To 200 to 500 cc solution, depending upon the quality of ferrocyanide thought to be present, add 10 cc HCl and 5 cc HNO3, and evaporate to about 50 cc. Add […]
Measure the Oxygen Content of Cyanide Solutions
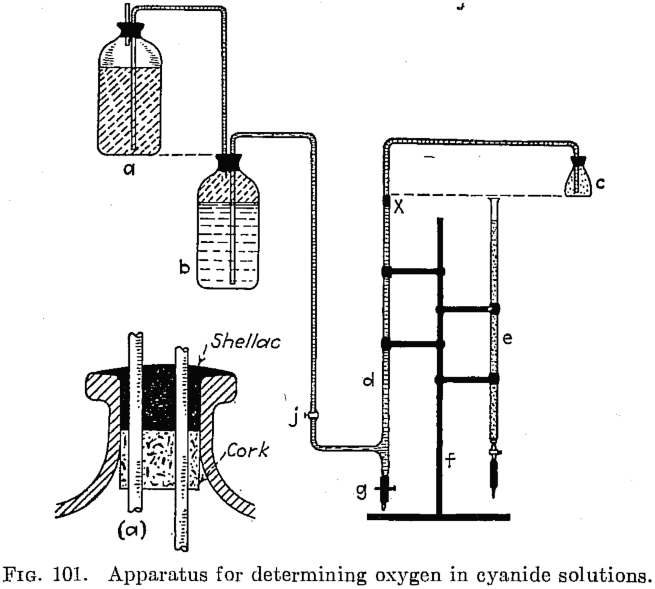
Two methods for determining the oxygen content of cyanide solutions are offered as being simple and accurate. White’s method is a colorimetric one, depending on the degree of coloration imparted to a solution of pyrogallic acid in the presence of caustic soda. Weinig and Bowen’s method, a modification of that of Schutzenberger, depends on the reducing […]
Free Lime CaO Determination Protective Alkalinity
It is important to know the free, or available, CaO in burnt or hydrated limes, especially for the laboratory determination of lime consumption in cyanide tests. The so called sugar method is a convenient one and is widely used. It is based on the solubility of the CaO present in sugar solution. The carbonates and […]
MIBC Frother Pump

I once had to conduct an MIBC frother test to confirm if it could give me better flotation results than the glycol frother my client was using. The technical/metallurgical problem we had in the plant was best described in the video below as well as a poor concentrate grade. My “challenge” was that since MIBC […]
