Loading railroad car, truck, or barge
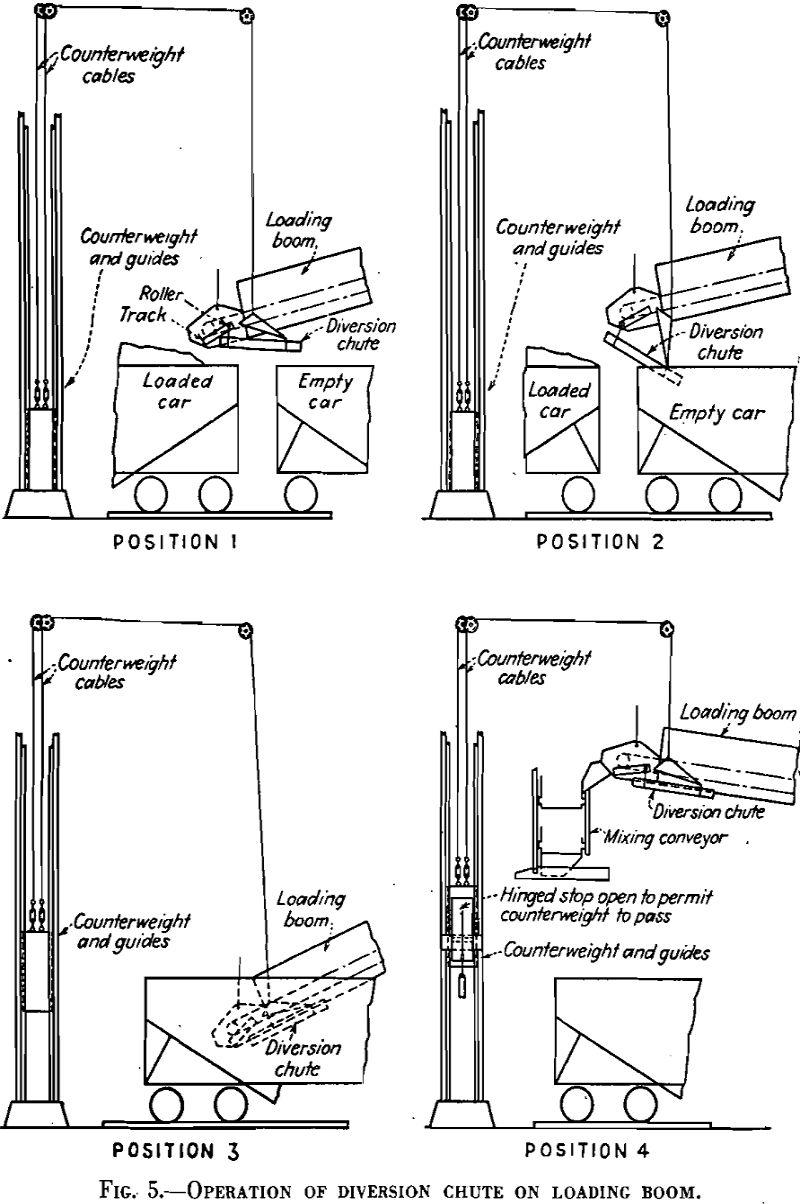
The primary purpose of the loading plant is to transfer the finished product from the preparation machines to the railroad car, truck, or barge in which it is to go to market. Secondary purposes of the loading plant are: to prevent excessive degradation of sizes during loading, to reduce segregation as much as possible, and […]
Shaft Sinking
In shaft sinking for coal mines, the cost item greatly influences the method adopted. This holds true especially when soft material must be traversed. The average life of a coal mine is short. This is due either to the limited area of the coal basin or to the great expense of maintenance and haulage underground […]
Potash Mining Methods
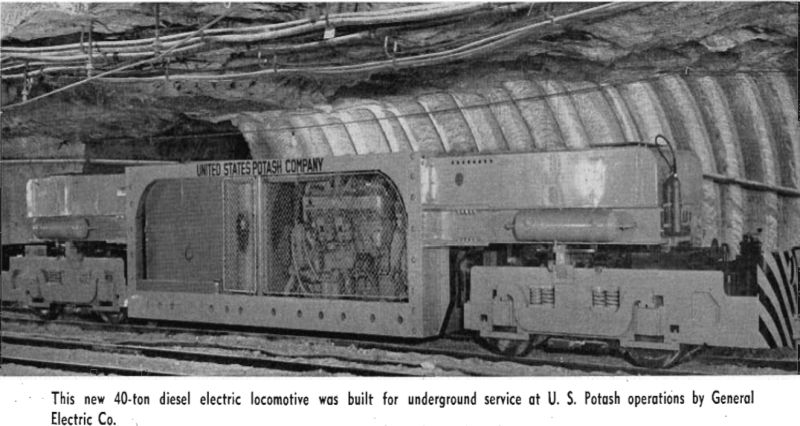
Commercial beds of sylvite ore were discovered by the Snowden & McSweeney Co. while drilling a wildcat oil well some 25 miles northeast of Carlsbad, N. M., in 1925. After a preliminary core drilling program the U. S. Potash Co. sank a 1060-ft shaft within 4 miles of the original discovery. This shaft was in […]
Belts and Concrete Ore Passes
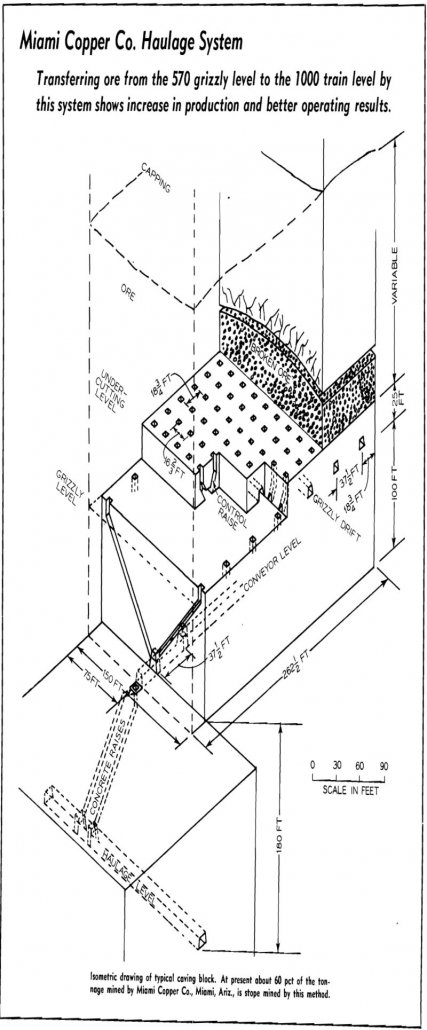
Conveyors were first used underground at Miami Copper Co., in the latter part of 1947. At that time some of the stoping area was too heavy and too close to the haulage level to use conventional haulage. To get the haulage drifts out from under the stoping area belt conveyors were used for the additional […]
Sublevel Stoping in Small Mines
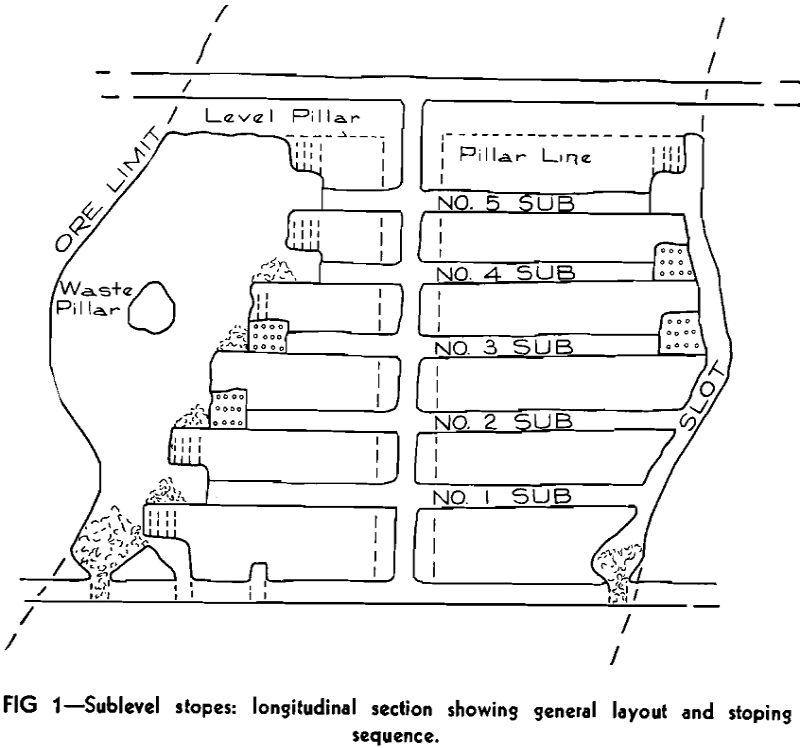
Sublevel stoping was first developed in the Michigan iron mines many years ago. Since that time this method, and modifications with long hole drilling, have been used in a number of non-ferrous mines and have been described in various papers and articles. With a few exceptions, the operations where sublevel methods have been applied are […]
Mining Face Preparation

Anthracite Although the unmined anthracite will last for approximately 150 years, most of the thicker and cleaner coal beds have been almost entirely first-mined and pretty well robbed, leaving much of the present and future production to come from thin and dirtier beds. Herewith is a section of one of the dirty beds being mined […]
Placing Concrete in a Deep Mine
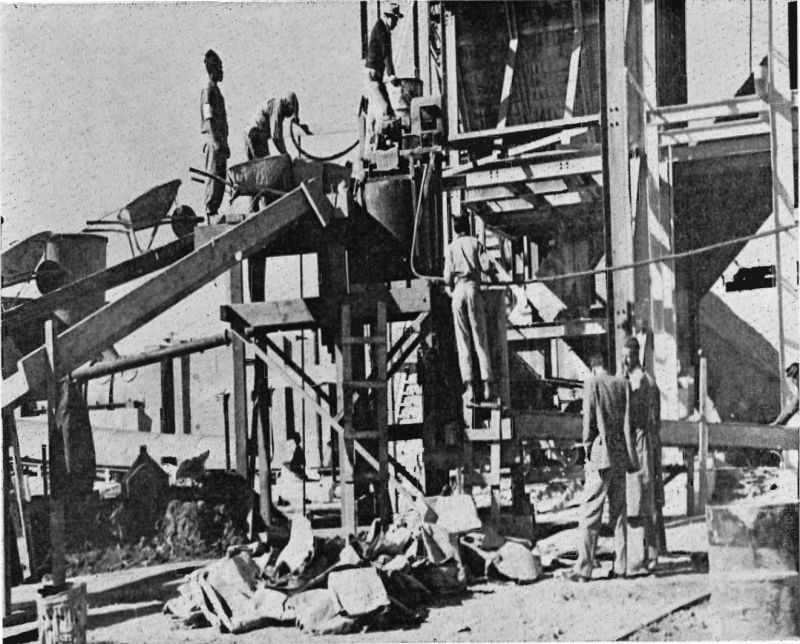
In U. S. underground mines concrete work is not widely used. Timber and steel are cheaper, and there are few serious water problems. But in the Union of South Africa men dig deeper, more persistently, and probably more profitably than anywhere else on earth. Some gold mines near Johannesburg are below the 10,000 level and […]
Mine Ore Mining Methods
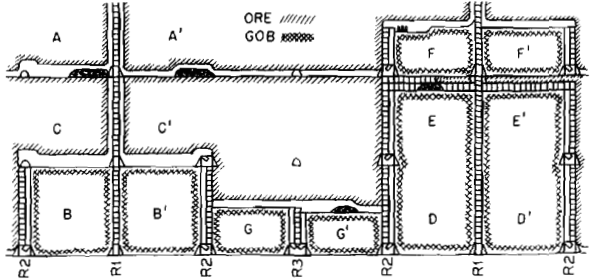
Iron king mine, producing gold-silver-lead-zinc ore, is 10 miles east of Prescott, Ariz. At present the 1806 level is being developed. The echelon pattern of ore deposit continues at depth but is less pronounced, and the orebody is now more or less continuous over 2600 ft of strike length, with widths 5 ft to as […]
Analyzing Ore Reserves: Statistical Method of Calculating

There are certain data handling techniques used by statisticans that can help one to calculate the size of an orebody and to develop some of the relationships between size, cutoff grade, average grade, mining cost, and profit. Knowing the relationships amongst these factors can help determine the most desirable operating conditions. A statistical technique that […]
Block Caving Mining Method
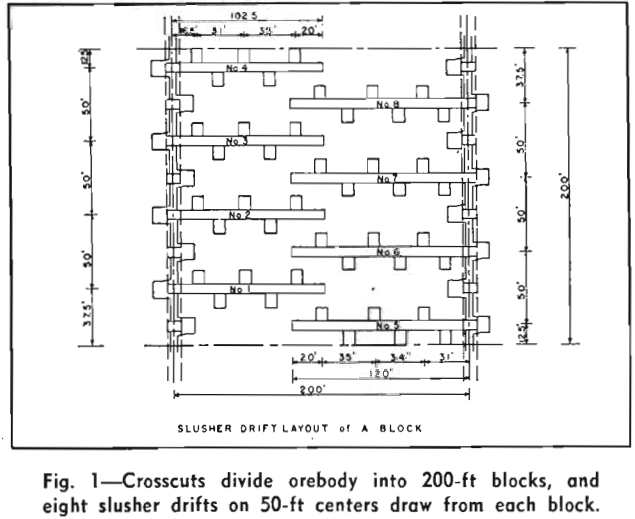
Block Caving has been developed to a high degree of efficiency in the last two decades and more particularly since World War II. At the Jeffrey mine of Canadian Johns-Manville Co., in the Eastern Townships of Quebec, several innovations have increased production and decreased costs. Asbestos ore is produced at the rate of 10,000 tpd […]
