List Native Elements Minerals

Here is a List Of Native Elements Minerals & Naturally Occurring Metals In Pure Form are subdivided into two classes, metals and nonmetals, to accord with similar divisions in chemistry. Gold Symbol, Au.; color, yellow, but paler when mixed with silver, which is usually present in native gold; H = 2.5 to 3; G = 19.33 […]
Major Mineral Groups
The great majority of minerals are compounds of two or more elements, though a few are native elements, i. e., elementary substances, as gold, silver, platinum, copper, carbon, and sulphur, which are found naturally. Minerals may be conveniently divided into the following eight Major Mineral Groups, and the descriptions will be in accordance with this […]
Wet Metal Assay Techniques

Wet Metal Assay Techniques include a method by which the “ore” is turned into powder and thoroughly dissolve it in some liquid, usually an acid, or mixture of acids, and then to recognise the presence of some known metal or metals by the peculiarity of the precipitate produced, when a reagent has been added to the […]
How to Determine the Elemental Composition of Minerals
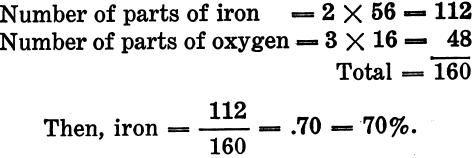
Pure Minerals always Have same Composition A pure mineral, one that is not mixed with any other mineral, is always of the same composition (certain exceptions). For example, iron pyrites is composed of iron and sulphur, in the proportion of 46.67% of iron and 53.33% of sulphur; and any specimen of the pure mineral will, […]
How Crystals are Formed

Minerals have taken their place in the earth’s crust by becoming solid from an originally liquid or, sometimes, gaseous condition, either melted rock matter (magma) or dissolved in water or other solvents. When the change from a liquid to a solid has been slow enough and undisturbed, the minerals have grown as crystals, which are […]
Tin Minerals

When a tin-bearing mineral is heated before the blowpipe with carbonate of soda or charcoal, white metallic tin is yielded. By dissolving this in hydrochloric acid and adding metallic zinc, the tin will be deposited in a spongy form. In the blowpipe assay, tin leaves a white deposit behind it, which cannot be driven off […]
How to Identify Precious Stones
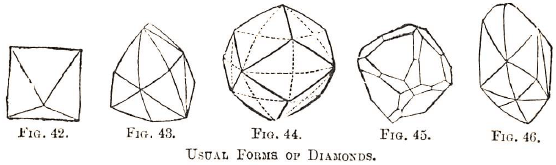
Most precious stones belong to such formations as granitic, gneissic, porphyritic rocks, and are generally found in the débris of such; and although certain diamond-bearing soils may be of a comparatively recent age, they are for all that made up of the constituents of the older rocks. Corundum, sapphire, and ruby are found in gneiss, […]
Silver Rocks and Minerals
Silver ores, Silver Rocks and Minerals are easily fused before the blowpipe flame, either with or without carbonate of soda. The resulting globule of metal, of its characteristic white colour, can be readily hammered out or cut by a knife. If the powdered mineral, supposed to contain silver, be dissolved in nitric acid and the solution […]
Nickel Ores and Minerals

To test the presence of nickel in a mineral, by means of the blowpipe, requires great care. If heated on charcoal, together with carbonate of soda in the inner flame, a grey metallic powder, attractable by the magnet, is formed. If heated with borax on platinum wire in the outer frame, a hyacinth red to […]
Characteristics of Common Minerals

As mentioned before, in the last chapter, any one who searches for useful minerals is chiefly attracted by their colour; the lustre, and perhaps streak, may assist him in the determination of their nature. Still, doubts may suggest further investigation. The hardness and the specific gravity may guide him, though it must be confessed, in […]
