Solvent Extraction Electrostatic Coalescence
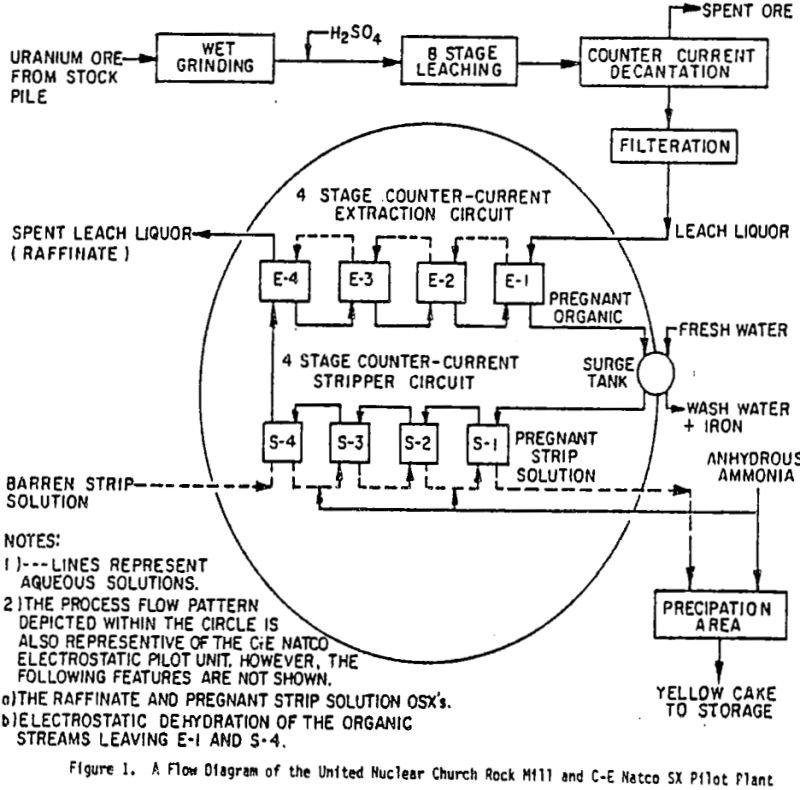
The solvent extraction unit of both systems contained four extraction and four stripping stages through which aqueous and organic phases flowed continuously and counter-currently. Each stage of the United Nuclear system consisted of a conventional mixer-settler. Each stage in the extraction circuit of the C-E Natco SX pilot utilized a throttled centrifugal pump for fluid […]
How to Build a Clay Heap Leach Pad – Construction
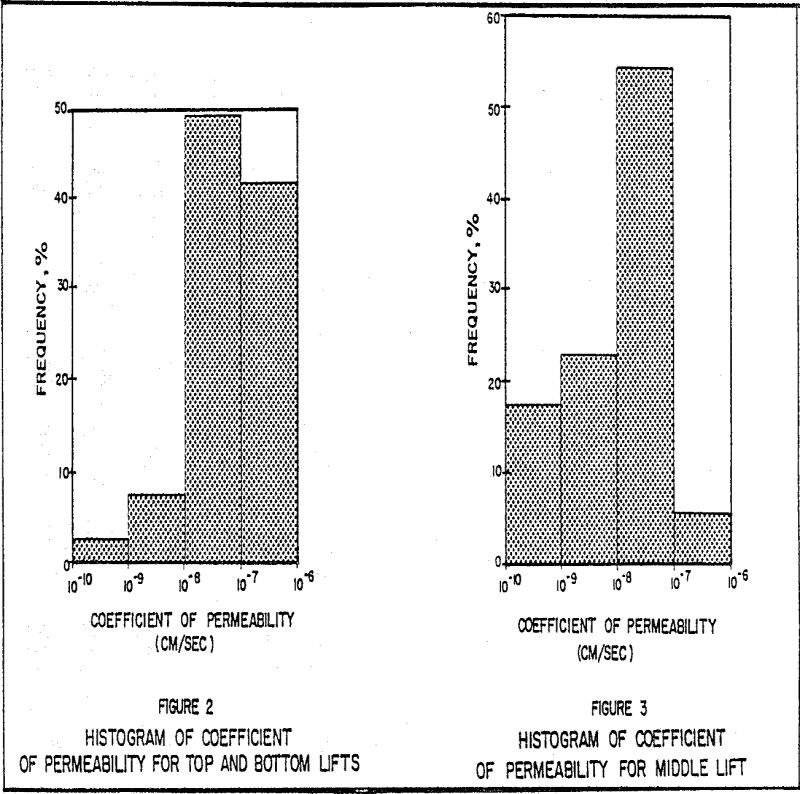
Natural materials can be used successfully in the construction of heap leach pads. The use of these materials usually result in the least expensive approach for such facilities. Sufficient geotechnical experience has been gained in the design and construction of clay heap leach pads so that they can be used with confidence. Requirements of Pad […]
Design CIL Circuit
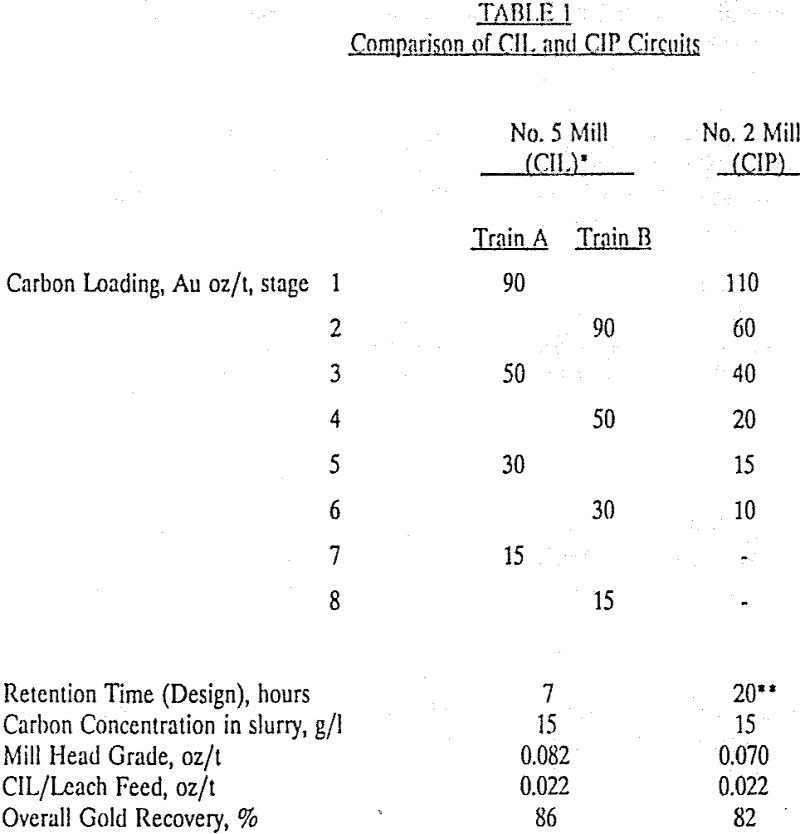
Carbon-in-Leach (CIL) is conventionally used in gold processing operations when preg robbing components are present in the ore. CIL process is becoming attractive even in other situations when preg robbing is not a factor. This paper discusses the situations in which the CIL circuit can be applied. CIP or CIL Conventionally, a carbon-in-leach (CIL) circuit […]
Treatment of Gold Tailings in High Rate Thickeners
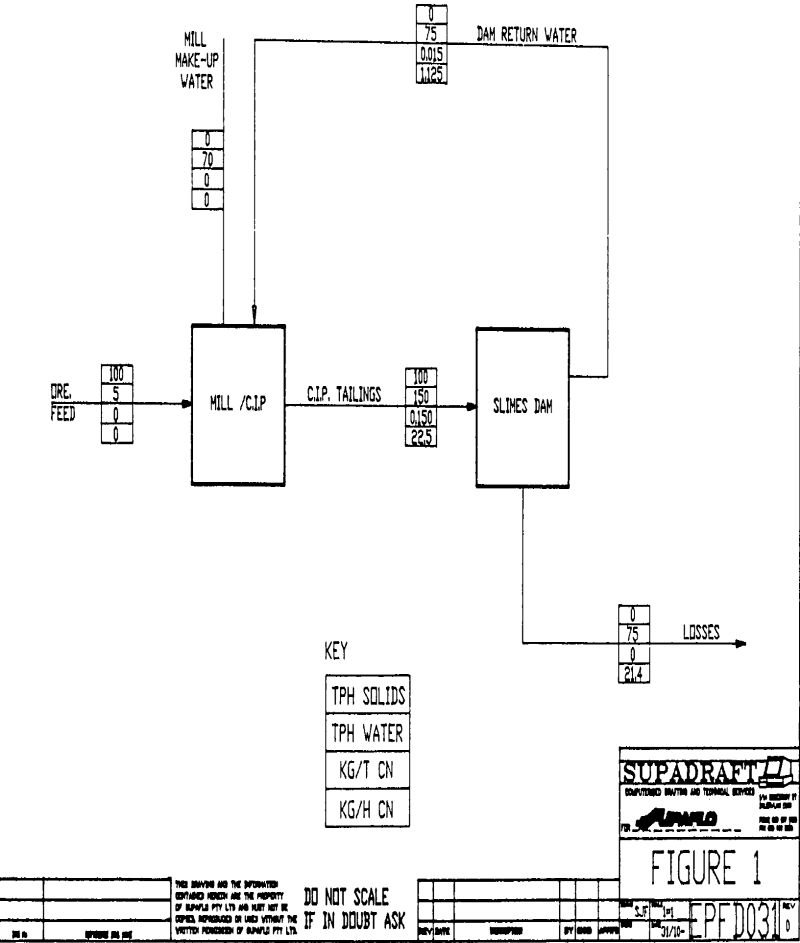
Degradation of cyanide occurs in the tailings water discharge to slimes dams. The degree of degradation or cyanide loss in the water recovered depends on a number of factors, but is usually assumed to be about 90%. The most important mechanisms of CN loss are through HCN losses and oxidation by oxygen in the air, […]
Bacterial Oxidation of Refractory Ores

The bacterial oxidation (BIOX) process for the pre-treatment of refractory ores for gold recovery was developed by the Genmin Process Research laboratory. Early work started in the late 1950’s when the bacteria strain, “Thiobacillus ferrooxidans” was isolated from effluents pumped from the West Rand Consolidated underground mine but at this stage the focus was on […]
Heap-Leaching Pad Volume Calculations
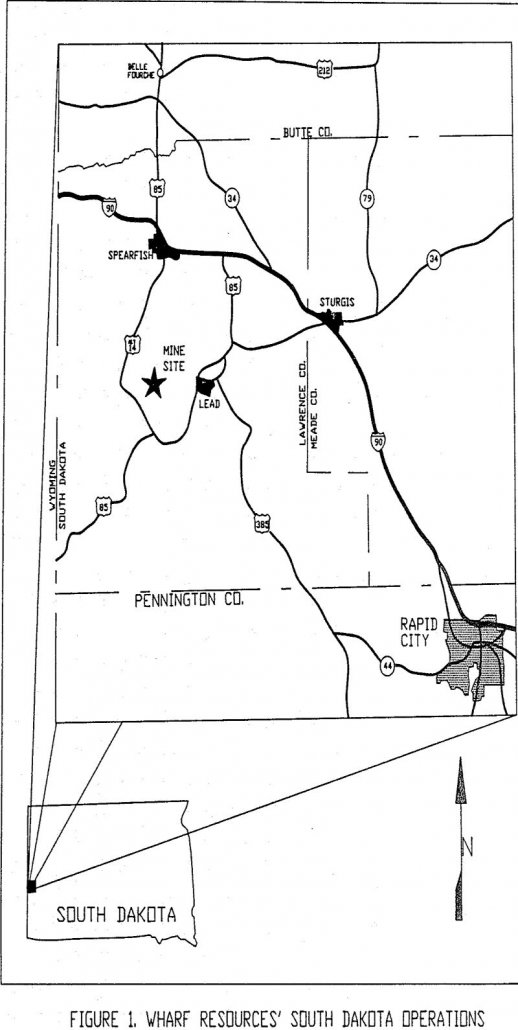
The estimating of volumes is a routine practice in an open pit-heap leaching operation. Until recently, the conventional cross-section manual method has been used at Wharf Resources’ South Dakota operation for the estimate of material mined from the pits, crushed ore delivered to the heaps, unload spent ore, ore and topsoil stockpiles, waste dumps and […]
Cellular Heap Leaching & Cyanide Regeneration
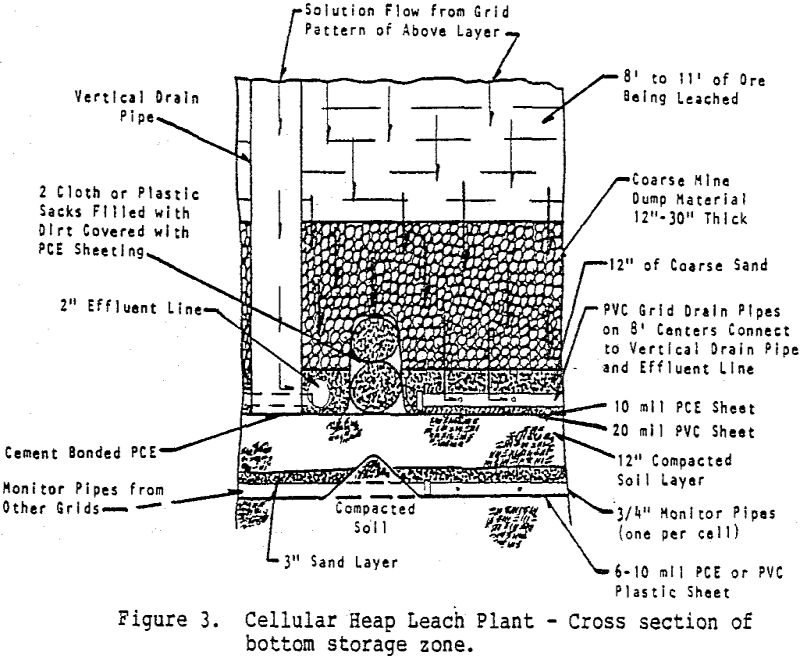
In conventional gold and silver heap leaching systems, crushed or uncrushed ores are generally placed in a large rectangular pile on a pad surface and sprinkled with weak cyanide leach solutions. The solutions leach the ore particles in their downward migration through, the heap. Effluent solutions are usually stored, sent to a metal recovery system […]
Gold & Silver Leaching Methods

Climbing gold and silver prices during the 1970’s awakened dormant interest in mining these metals in many districts. Since gold and silver deposits frequently can be profitably mined by small operators, a mix of mining activity has been created, comprised of large and small companies, both experienced and unexperienced. A key factor in the profitability […]
Ferric Sulfate Leaching
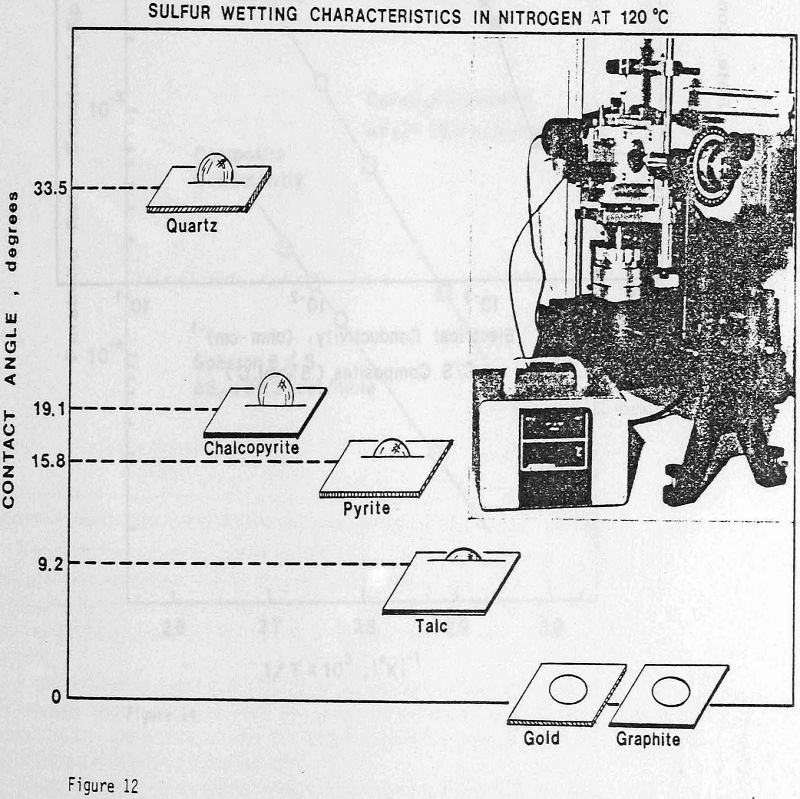
Acid ferric sulfate solution has been used for heap and dump leaching of low-grade chalcopyrite ores and is being considered as a possible lixiviant for the hydrometallurgical processing of copper sulfide concentrates. For many years, researchers have attempted to explain the leaching behavior of chalcopyrite, since the reaction rate kinetics are extremely slow and seem […]
Dump and Heap Leaching Permeability Solution
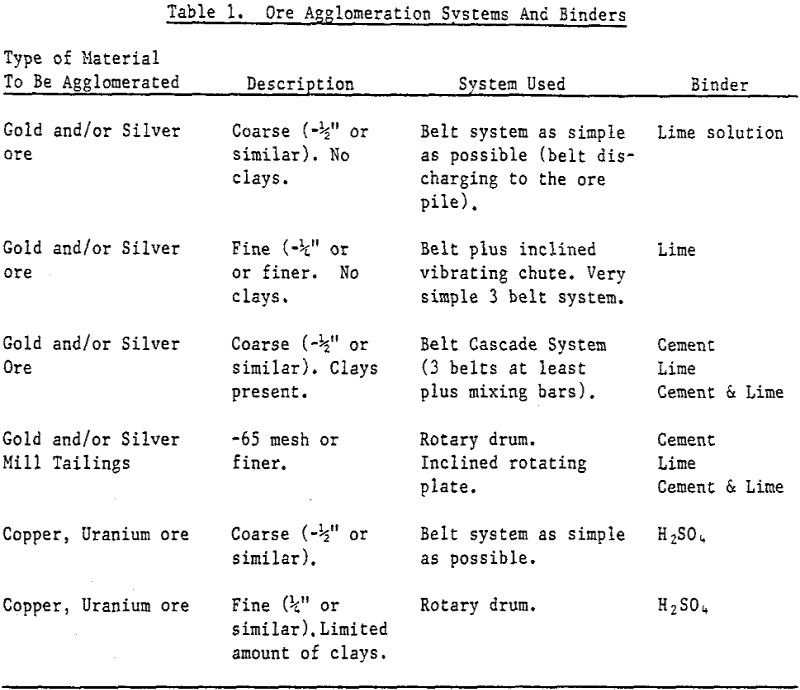
The basic condition controlling the choice of a dump or heap leaching process versus a fine grinding-agitation leaching process is the grade and tonnage of the ore body. Low grade ore and small tonnages are best treated by a low-cost method such as dump or heap leaching. The permeability of the material in a dump […]
