Heap Leaching Economics
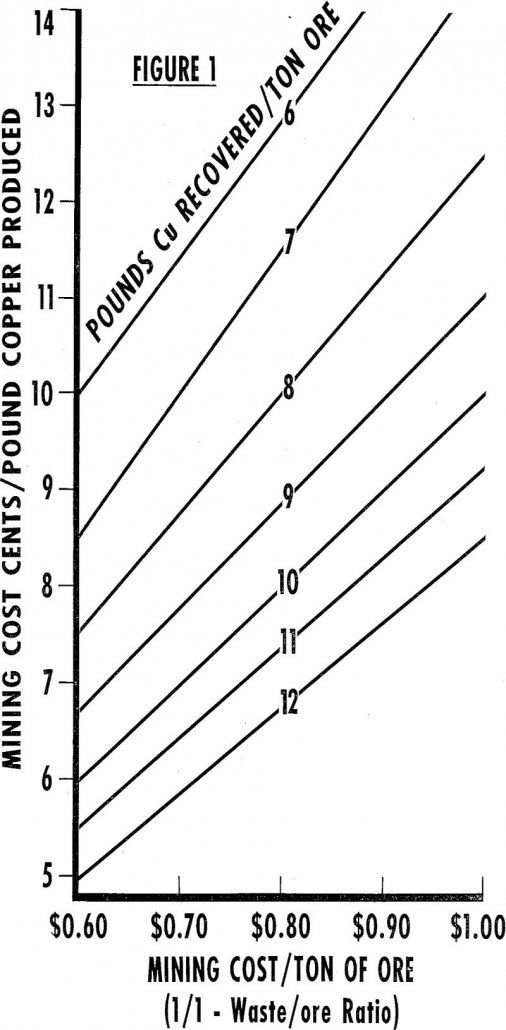
Expanded markets for copper in the past few years and a consequent search for new ore bodies have revitalized the widely known but seldom applied method of producing copper called heap leaching. This term should be differentiated from dump leaching in that the latter is applied to dumps of mixed oxide and sulfide ores (although […]
Leaching of Copper by Fungi
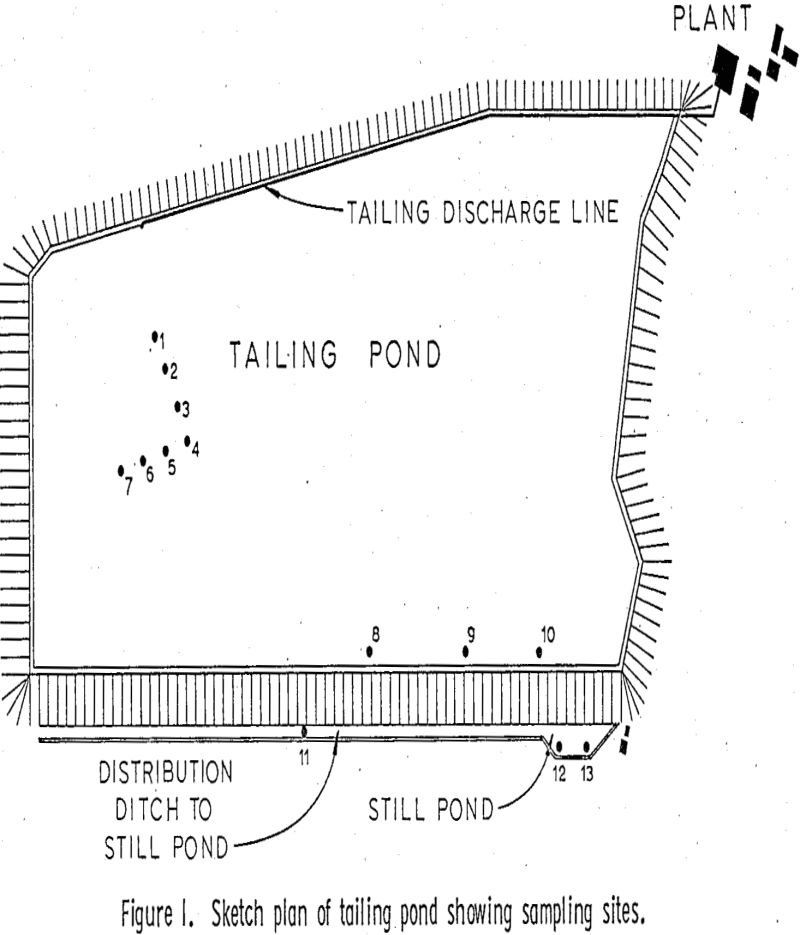
Bacterial and fungal populations were observed in samples taken from the White Pine Copper Company tailing pond and mine, and isolates were prepared of the dominant species. The isolates were then screened for solubilization of copper from tailing, ore, and concentrate during incubation in a carbon and nitrogen supplying medium. Certain Penicillium fungi solubilized significant […]
Heap Leaching of Gold Ores in Northeastern Nevada
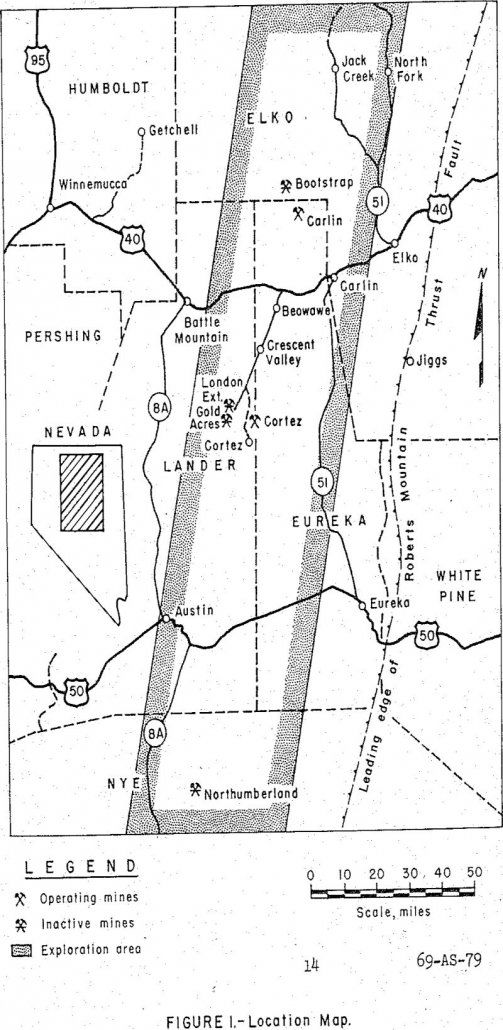
Heap leaching shows promise of being an attractive method for treating large tonnages of oxidized gold ores from the sedimentary beds of northeastern Nevada which are not economically amenable to treatment by conventional milling methods. The ores are unique, with the gold occurring as sub-micron particles in a porous host rock. The preliminary test work […]
Impermeable Dump Leaching Chemistry
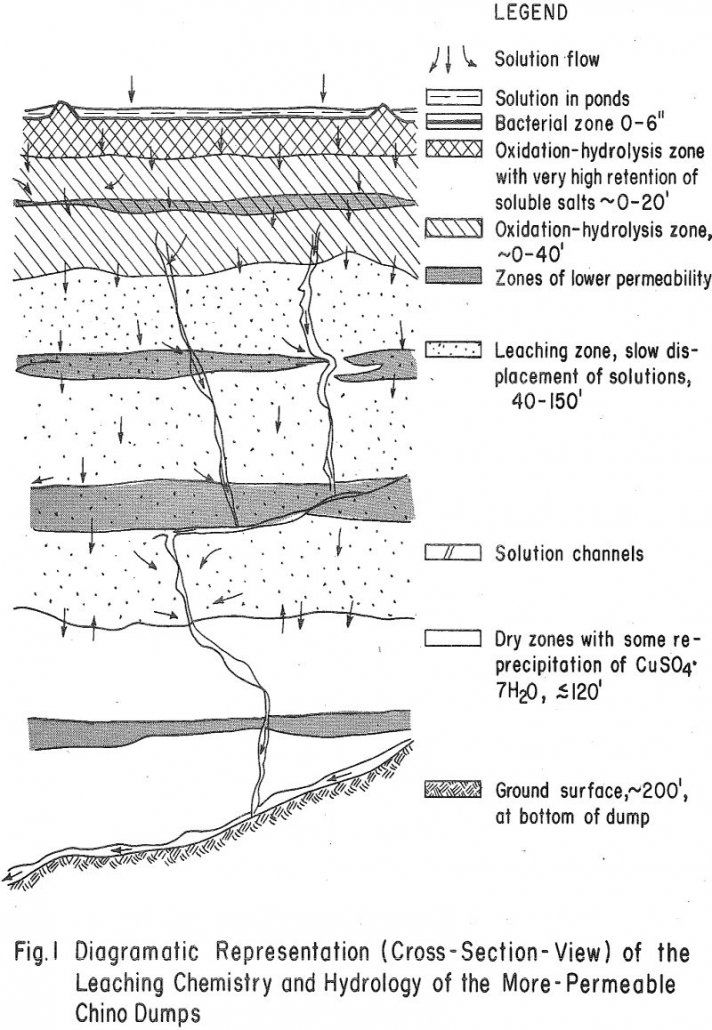
A series of tests were run on fresh Becker drill samples from a drill hole in Kennecott’s Chino “J” dump, near Silver City, New Mexico, to obtain data on the leaching chemistry of a relatively impermeable sulfide copper waste dump. Vertical profiles were made of the moisture and soluble-salt content; the content of Fe+³, Fe+², […]
Selection of a Leach Dump Test Area
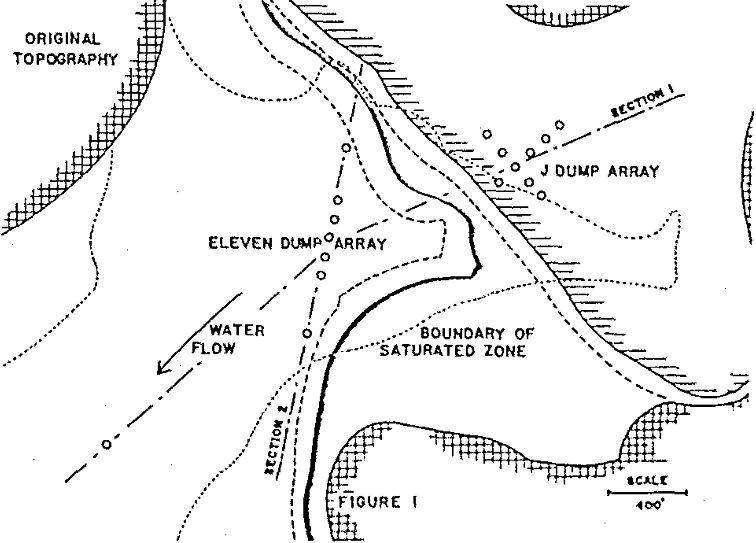
Leaching of waste material at Kennecott’s Chino Mines Division at Santa Rita, New Mexico, has been accompanied by increasing difficulty in circulating leach solutions through the dumps. As a means of recognizing existing problems and considering alternative applications of the leaching concept, a leaching research program was proposed which could be applied to a specific, […]
Laboratory Extraction of Copper by Roasting and Smelting
In a broad sense, sulfide copper pyrometallurgy is a batch sequence in three separate vessels, i.e., reverberatory furnace to yield “matte copper,” a converter to produce “blister copper,” and another reverberatory furnace to produce fire-refined copper. Matte smelting is relatively unchanged since it became universal practice some 50 to 60 years ago. It is now […]
Heap Leaching Oxide and Sulfide Copper Ores
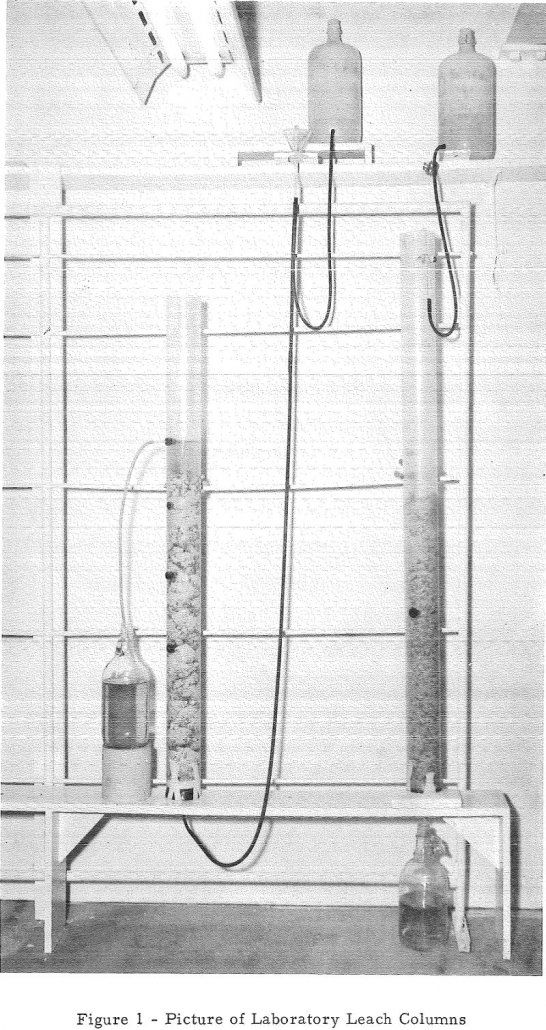
Heap leaching is a simple means of recovering copper from oxide and oxide-sulfide ores. Although this method requires relatively low capital investment, it suffers from low copper recoveries and relatively high acid consumption. The objectives of this study were (1) to determine what factors influence these shortcomings, and (2) to establish a basis of correlation […]
Using Platinum Electrodes to Indicate Redox Potential
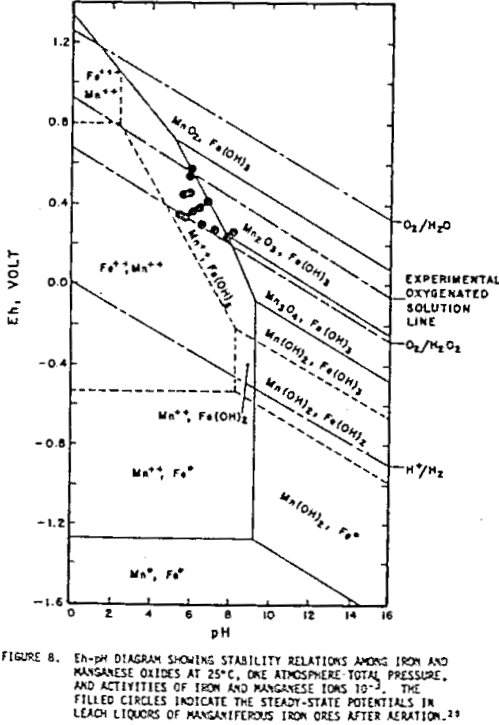
Platinum electrodes are not inert as originally thought to be. The reactivity of platinum electrodes can explain their erratic behavior in many electrochemical measurements of metallurgical interest, e.g., in flotation systems, streaming potential measurements, contact-angle measurements, and in leaching systems. Experimental Procedure A rotating platinum electrode was used in many of the measurements to study […]
Large Scale Mixer Settlers Design
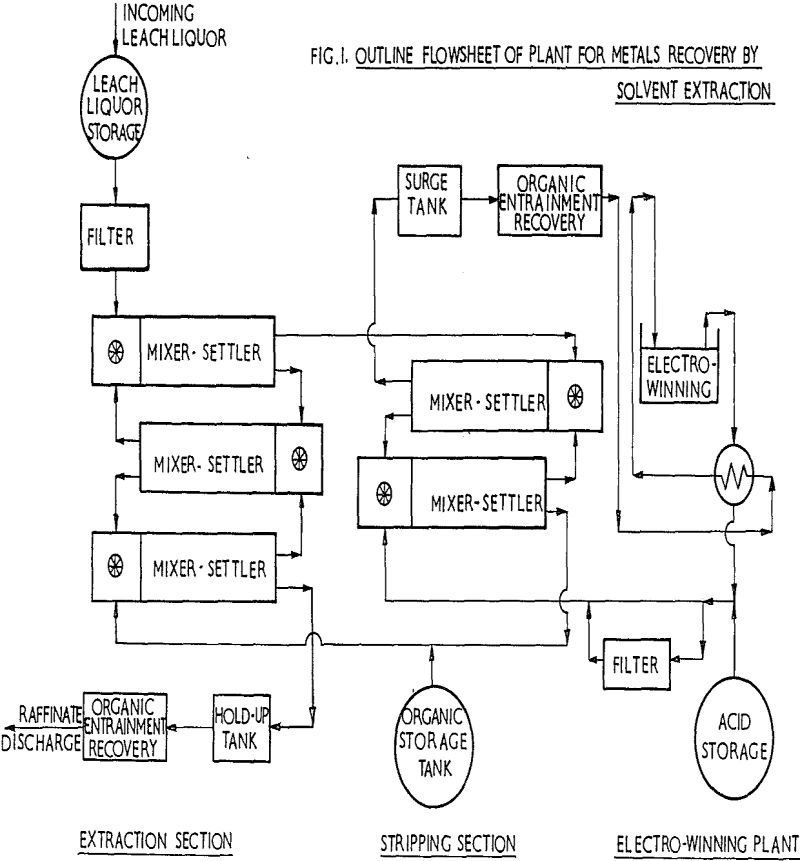
This paper outlines the physical and mechanical factors which must be taken into account when designing mixer-settler systems for large scale solvent extraction plants. The performance of the equipment will also be dependent upon the chemistry of the system, including the kinetics and thermodynamics of the ion exchange reaction itself, the effect of impurities flocculants, […]
Nitric Acid Processing Copper Concentrates
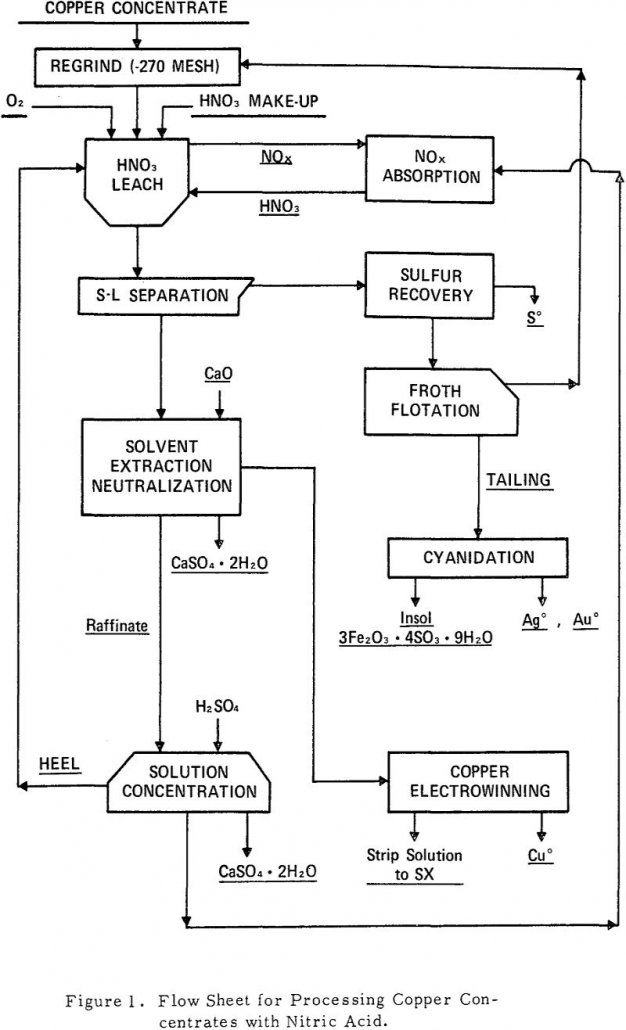
The process parameters for effective utilization of nitric acid as an oxidant for copper-iron sulfides have been developed. Leaching variables found to be important were acid concentration, temperature, time, atmosphere, pressure, mineral type, particle size, and percent solids. Particular attention was devoted to analysis and control of fumes evolved during the oxidation. Numerous references have […]
