Design of Mixer Settlers in Solvent Extraction
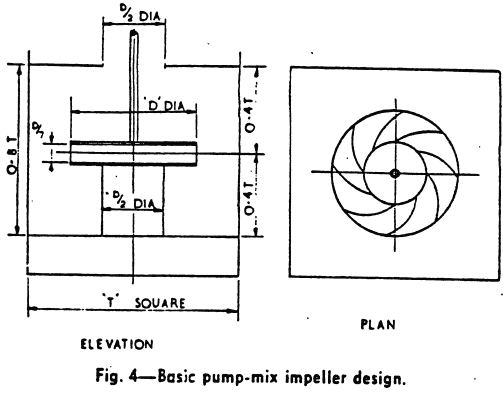
The development of solvent extraction processes over recent years has led to their application on an increasing scale in metal extraction plants. The author’s company has recently been awarded a contract for the design of the world’s largest solvent extraction plant based on pump-mix mixer-settlers. The plant is designed to extract copper from a leach […]
Copper Recovery by Solvent Extraction Techniques
Development of Suitable Reagents was Vital Key: Solvent extraction techniques were first applied to the recovery of metals for atomic energy projects in the decade 1945-55. They were subsequently applied to the large scale production of such refractory metals as hafnium and zirconium. Since then the technique has been applied to the recovery of the rarer […]
Solvent Extraction Glossary of Terms
Some of the more important technical terms used in this World Mining article and in other solvent extraction literature. Contactor Device for dispersing and disengaging immiscible solutions; extractor. May be single stage, as in a mixer-settler, or multiple stage, as in columns and certain centrifuges. Countercurrent extraction Multistage extraction in which the aqueous and organic solutions […]
SX Solvent Extraction Process Principles Theory

An increasing demand for metals in general, and higher purity metals in particular, decreasing ore grades and more stringent environmental regulations have driven, and will continue to drive, research into finding more effective and efficient methods for processing the ores available to us, and recycling previously used metals. Hydrometallurgy has provided, and will continue to […]
Solvent Extraction Plants: Thiele Diagram & Theoretical Design Aspects
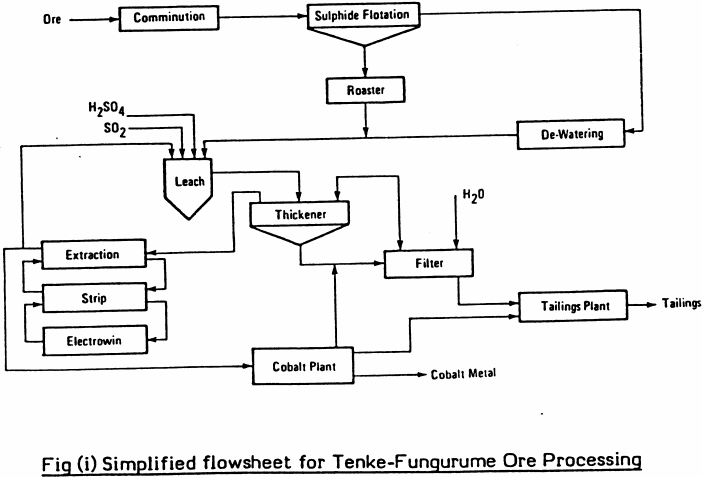
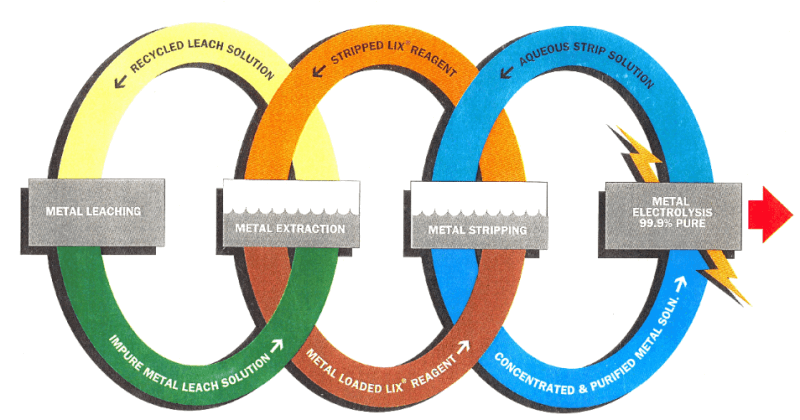
It has been explained in an earlier talk that solvent extraction in the copper industry is used to convert impure, and frequently very dilute copper solutions into very pure and concentrated solutions from which pure copper can be extracted by a variety of means, usually electrochemical. These impure solutions emanate from in-situ leaching, dump leaching, […]
Solvent Extraction Process SX: Hydrometallurgical Extraction of Copper
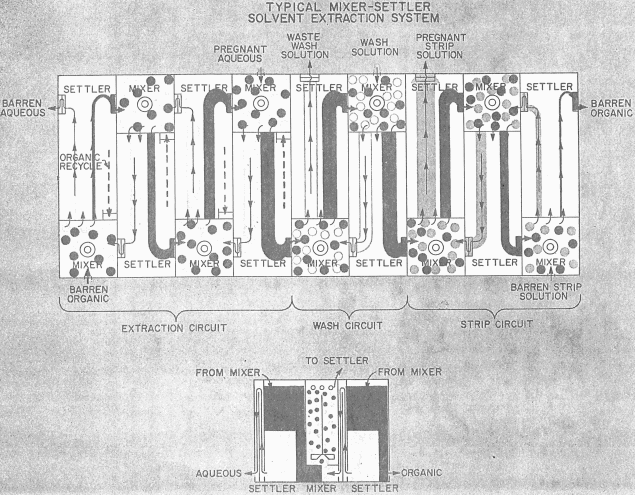
In recent years, the principle and theory behind solvent extraction has gained wide acceptance as one of the new tools of modern hydro-metallurgy. With the growing demand for metals of ever higher purity, the increasing use of unusual metals, and the necessity for treating ores of lower grade and greater complexity, solvent extraction has joined the […]
Hydrogen Peroxide & Gold Cyanidation
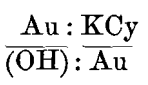
The peroxide of hydrogen used was Marchand’s medicinal, containing 3.3 per cent, of available peroxide, as determined by titration with permanganate of potassium. According to the new theory, the H2O2, (±) takes up from the gold strip o, which becomes positive, two units of negative electricity and dissociates into 2 (OH) (—). In the first […]
How Air’s Oxygen Makes Gold to Dissolve in Cyanide
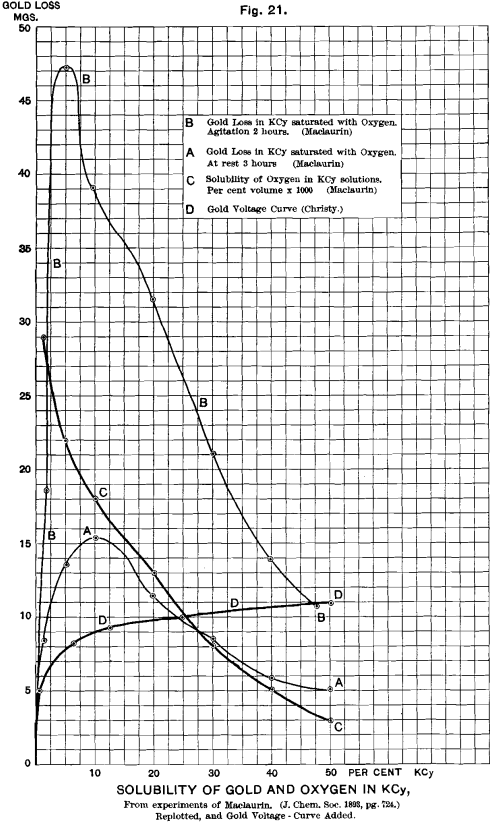
We have another substance at hand with a great tendency to form negative ions. This is the oxygen of the air. In the presence of water, the molecule of oxygen, O2, tends to assume the ionic state, combining with water to form four negatively electrified ions, thus: O2 (±) + 2H2O (±) = 4 (OH) […]
Metal’s Electrochemistry of Cyanide Solutions
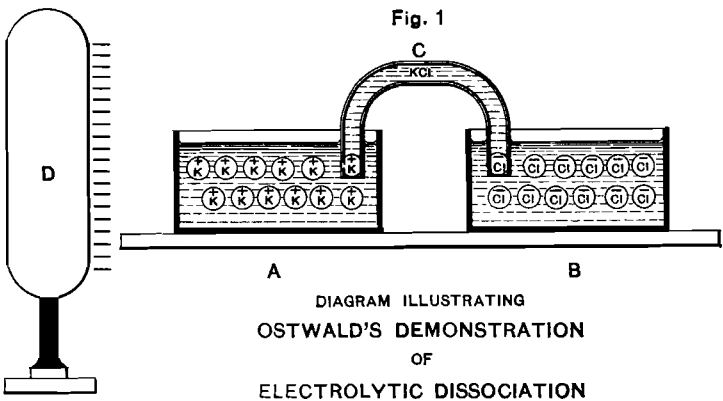
The practice of the cyanide-process of gold-extraction has brought to light many important contradictions of familiar chemical analogies, which still obscure both the theory and the practice of the art with distinctions subtler and more difficult to make or follow than those which delighted the heart of the old-time metaphysician. Yet Nature herself has drawn […]
Relative Affinity of Metals for Cyanide
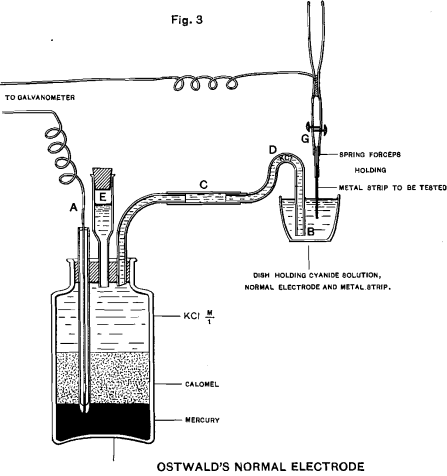
In looking about for some means of determining the relative affinities of the metals for cyanide solutions, I long ago came to the conclusion that the determination of the relative electromotive forces of the metals in solutions of different strengths was the simplest, readiest, and most certain that could be selected. For, properly considered, it […]
