Gold Washing and Gravity Circuit for Placer Gold
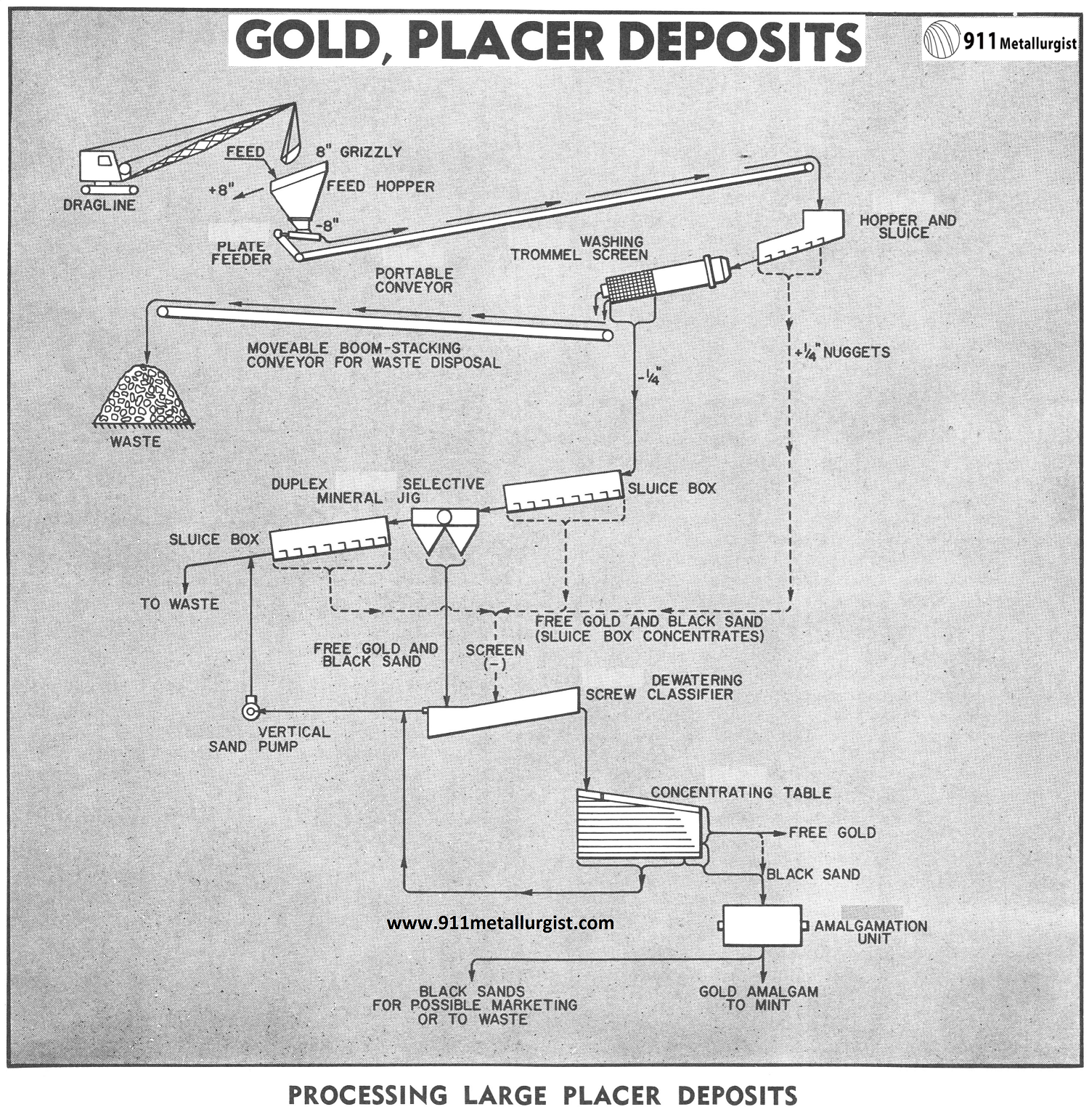
The handling of large quantities of gold-bearing gravels is of utmost importance for most successful placer operations. In addition to providing efficient washing and recovery methods, the placer plant should be constructed as a compact unit that can be readily moved. This is an important consideration because the washing and recovery plant should be close […]
Easy Mill Expansion – Float Coarse at Higher Tonnage
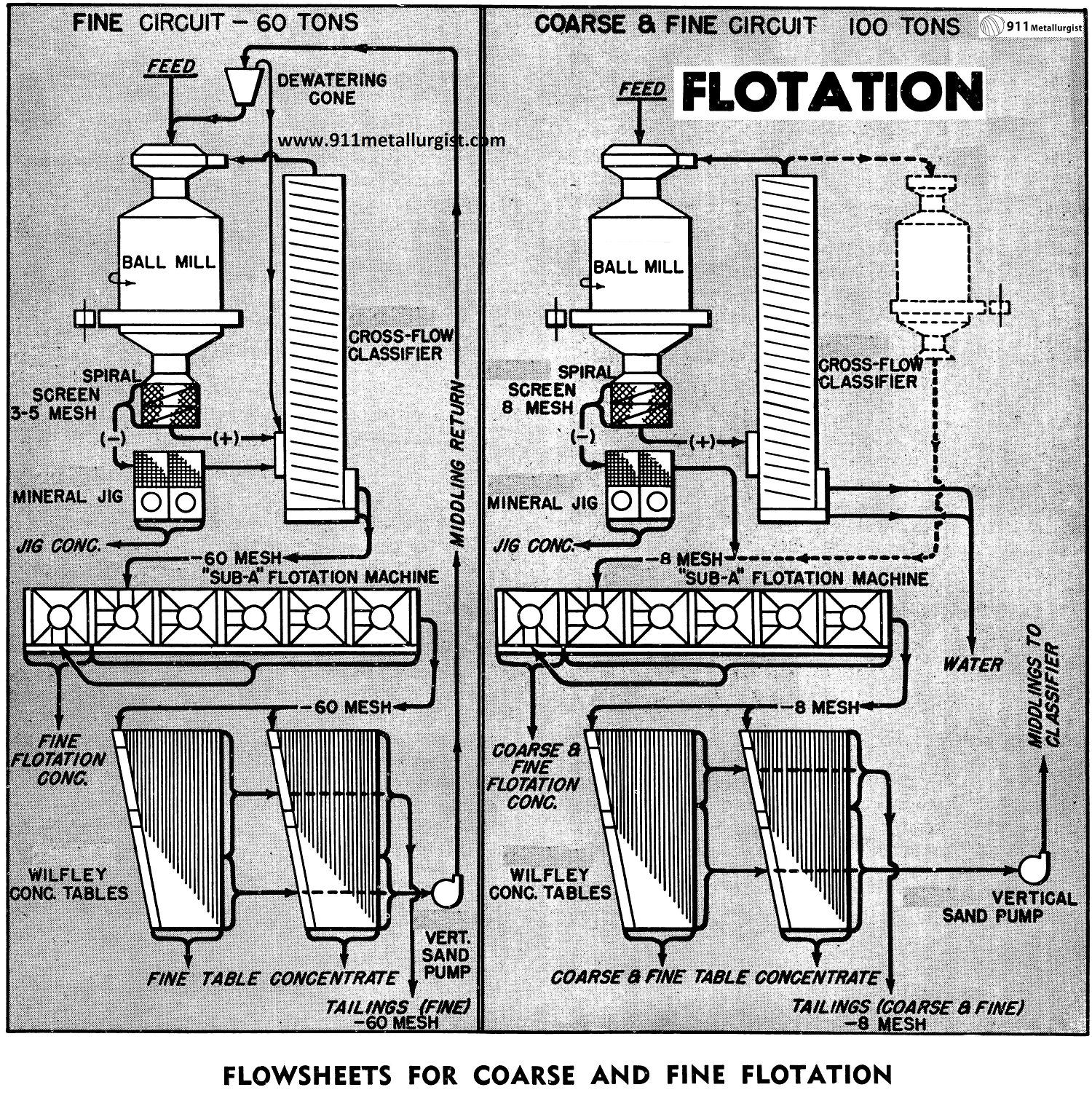
The Problem with Coarse Flotation and Recovery Many flotation plants today are grinding to fine sizes. This means that money is being spent grinding worthless gangue which might be discarded at a coarser mesh. Many plants are treating ores in which the gangue is free at a coarse mesh and where a coarse bulk concentrate […]
How to Operate a Wilfley Shaker Table
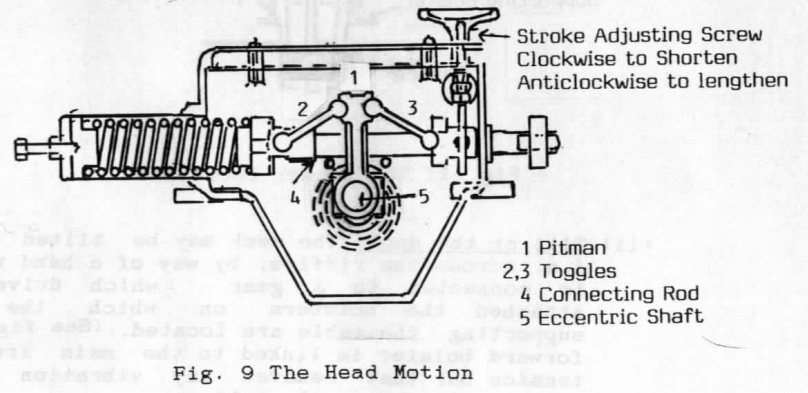
The Wilfley shaker table shown is a standard No.12 right-hand version. It is a mechanically operated reciprocating action table, consisting of a self-oiling enclosed type of head motion, a partly riffled rectangular deck, and an understructure with a tilting device for the table. Head Motion The head motion is a self-oiling Pitman and toggle type. […]
Gravity Spiral Concentrator Working Principle
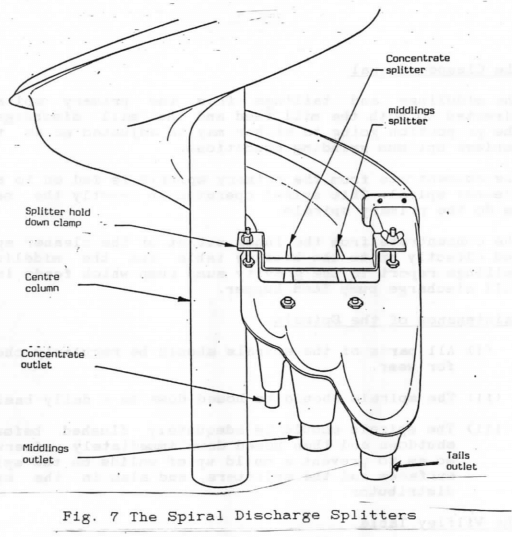
The gravity spiral circuit is designed to extract and concentrate “coarse gold’ from the recirculating load in the mill grinding circuit and hence prevent a build-up within that circuit and the eventual escape of some of that gold into the C.I.L. tanks and thereon into the final tails. (See fig. 4) Optimum Operating Conditions of […]
Small Gold Ore Processing Plant
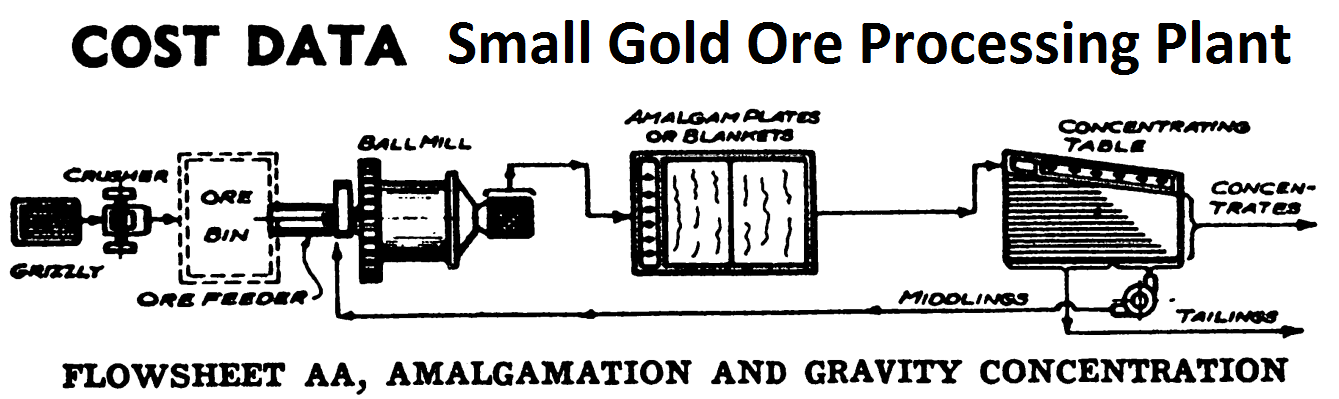
These five illustrated flowsheets fully described in the article “Small Gold Ore Processing Plants” follow a natural sequence. These start with a very simple. Flowsheet AA, and then by the addition of the more extensive equipment, it is possible to take care of slight changes in the ore as well as improve recovery. The following […]
Mineral Jigs for Concentration of Lead Ores
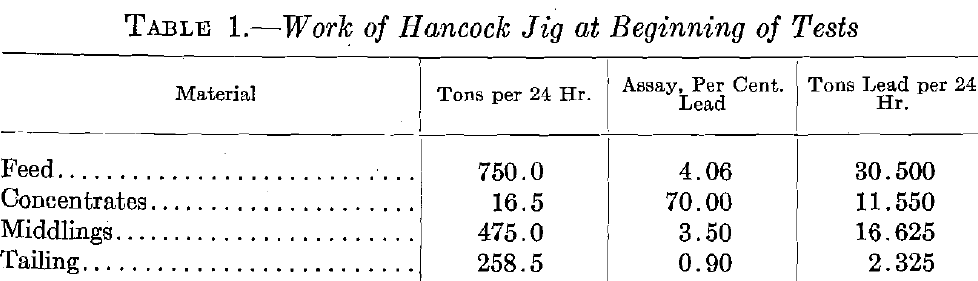
The following notes are taken from results obtained on a standard 25-ft. Hancock jig tested during regular operation. The object of the tests was to determine the conditions for most effective work, and the nature of products that could be made. The material treated was sized between 9-mm. and 2-mm. round- hole screens, and was […]
Cyanide Processing Equipment and Plant Options

The Jig, placed between the ball mill and classifier, is one of the most valuable and affordable improvements in cyanidation in recent years and was developed by the metallurgical engineering and Mining Equipment Companies. This Mineral Jig has the marked advantage of removing a large portion of the metallic values without excessive dilution, and water […]
Gravity Recovery or Flotation ahead of Gold Cyanidation

Process Flowsheet NO. CY-3 is shown one of the outstanding improvements made in cyanidation whereby the coarse metallic minerals are removed from the grinding circuit by means of the Mineral Jig. The hutch product from this jig is amalgamated with a Amalgamator or Clean-Up Pan and thus the coarse mineral values, such as metallic gold, are […]
Gold Cyanidation Circuits

The principle of dissolving gold and silver values in solutions of potassium or sodium cyanide is old and has been thoroughly carried out in practice for many years. There have been only a few changes in the chemical procedure and also few changes in the type of equipment used. The gold and silver are dissolved […]
Round Concentrating Tables
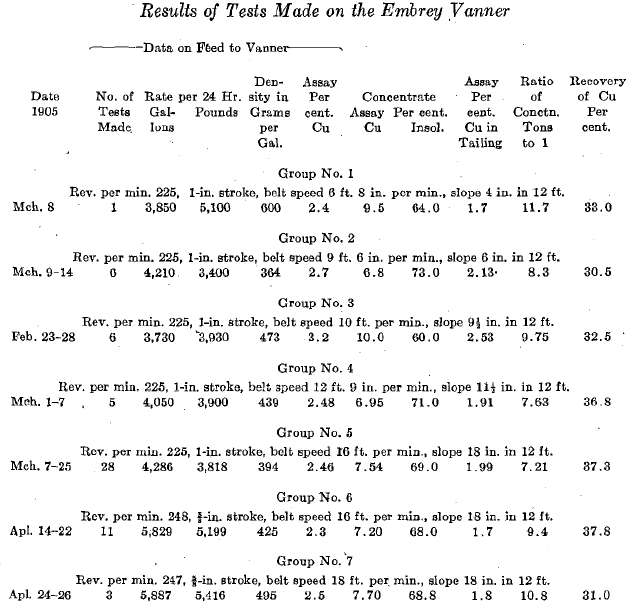
The principal object of this paper is to present data on the development of the revolving convex round table as a concentrator for the through 0.07-mm slimes from the ores of the Butte district, although some brief notes on the earliest recorded use of this type of concentrating table in the ore-dressing plants of the […]
