Stamp Battery

The stamp battery must be regarded from two different points of view, (a) as a crushing machine, (b) as an amalgamating machine, and it should be remembered that the modifications designed to make it a more efficient crusher often reduce its power as an amalgamator, and vice versa. Stamps were originally designed as crushing machines, and […]
Optimize Gold Amalgamation Recovery

Minimizing losses of gold in amalgamation will result in optimum Gold Amalgamation Recovery which may be ranged under the following heads: Loss of free gold contained in amalgam, due to flouring of mercury, scouring of plates. This has been dealt with above under the heads “Treatment of the Plates” and “Loss of Mercury.” Loss of gold which […]
How Mercury & Gold Amalgamation Works

In order to keep the plates in proper condition so that successful amalgamation may be maintained, they must be prepared carefully, and the closest watch kept over them. The setting of the plates has already been described on p. 121. The silver-plated copper table is preferred in California from the ease with which it is […]
Mercury Retorting
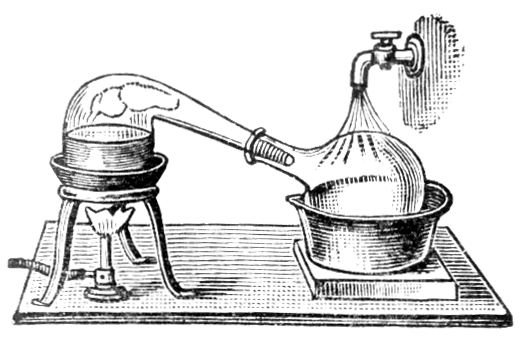
The solid amalgam, which is retained in the canvas or wash-leather filters, usually contains from 30 to 45 per cent, of gold and silver, according to the state of division of the gold present in the ore, and also to the degree of care exercised in squeezing out the excess of mercury. For separating the gold […]
Using Mercury in Gold Ore Crushing

The earliest machines used for the purpose seem to have been stone mortars, in which the gold quartz was crushed by stone-hammers, or by large rocks raised by levers and let fall, whilst the fine material was subsequently washed out with water. The heavy particles of gold then settled to the bottom of the mortar, […]
High Production Sluice Box

The gold sluices in which the gold is caught are constructed on exactly the same principles as those already described, but are larger and, though usually made of wood, are of more massive construction, in accordance with the great quantities of gravel to be handled and the continuous nature of the work. The sluices are commonly […]
Hydraulic Mining

The method of working by Hydraulic Mining consists, as has been already stated, in breaking down banks of gravel by the impact of powerful jets of water, and passing the disintegrated material through a line of sluices, without the agency of hand labour. The chief requisites for the successful application of hydraulic mining are: Large quantities […]
How Gold is Deposited into Placers

The origin of the gold in deep placers has long been a vexed question. It was formerly accepted without question that the erosion of auriferous quartz lodes existing at higher altitudes furnished both gravel and gold. In support of this it was urged that the same districts which furnished auriferous gravels abounded in quartz veins […]
Gold in Deep Gravel Deposit

Both in Australia and California, besides the superficial placer deposits situated in or near the existing rivers, which in the deep canons of the Klamath and other rivers in the extreme north of California attain a thickness of 250 feet, there exist auriferous gravels which bear no apparent relation to the present drainage of the […]
Placer Mining Cost
In work on shallow placer deposits by individuals the results differ greatly, both according to the strength and skill of the worker and to the contents of the gravel. Under the best conditions of climate a strong, well-nourished, American digger may be able to raise by the shovel from 10 to 12 cubic yards of […]
