Chemoremediation of Acid Mine Drainage
The chemical alteration of water by acid mine drainage begins with the exposure to the atmosphere of pyrite associated with coal during the mining process. The exposed sulfide minerals, which are relatively insoluble in their original state, are converted by oxidation to soluble sulfuric acid, which in turn dissolves other minerals containing manganese, aluminium and […]
Dual-Alkali Scrubbing
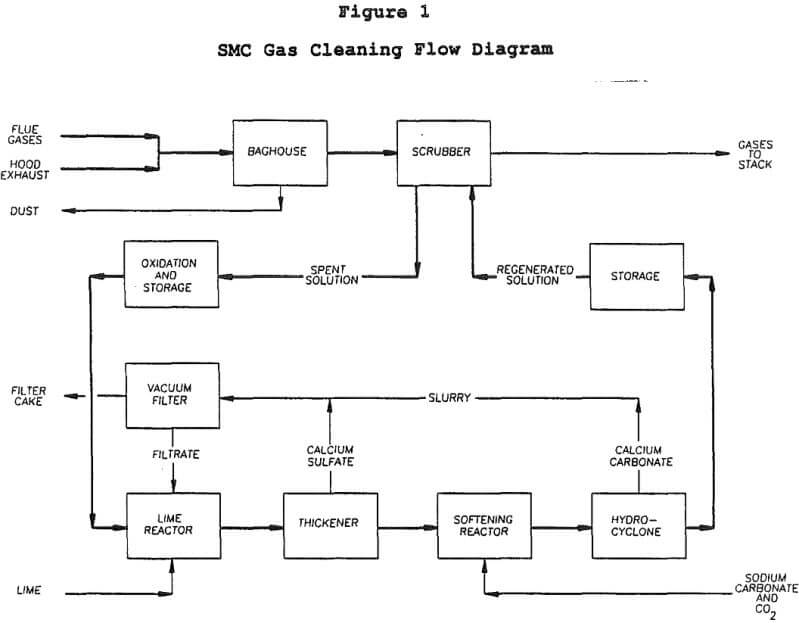
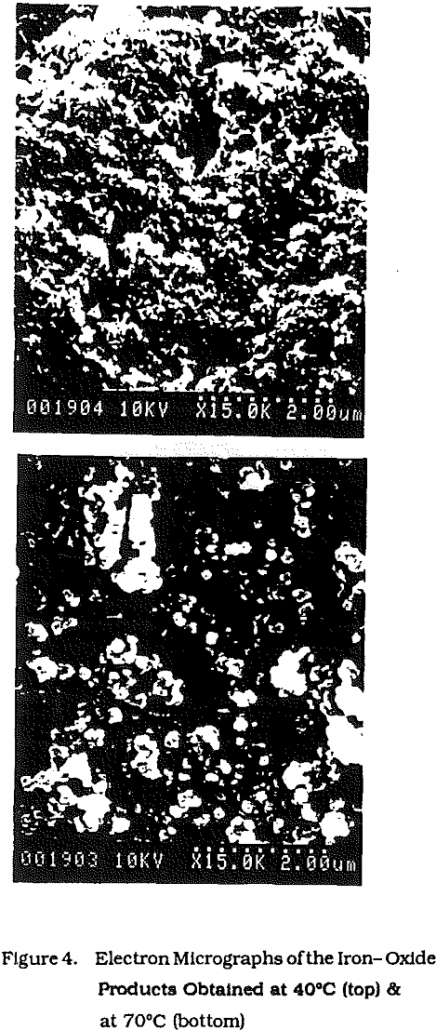
SMC’s smelting process is composed of a submerged-arc electric furnace and a top blown rotary converter (TBRC). The 1.5 MW rated furnace operates continuously while the 0.15 M³ TBRC is operated on a batch basis. Process flue gases are combined with tapping hood exhaust air and ducted to a gas cleaning system prior to release […]
Kaolin Tailings Ponds
Kaolin tailings ponds play an important role in reclamation of land and water. Discharges impounded from kaolin plants include oversize fractions consisting of coarse kaolin, mica, quartz as well as magnetically extracted contaminents, acid filtrates, and plant washdown streams. Tailing ponds perform an essential function in sedimentation of particulates, blending and reoxygenation of liquid waste, […]
Magnesium Oxide to Remove Metals in Water
Conventional practice for treating mine drainage and other water sources contaminated with heavy metals is lime precipitation and settling of the hydrous oxides. This produces a voluminous toxic sludge that results in another type of disposal problem. In addition, settling of the precipitated hydrous oxides often does not produce sufficiently pure water to meet statutory […]
Using Wetlands for Treatment of Mine Water
Acid mine drainage is one of the most persistent industrial pollution problems in the United States. Over 5,000 miles of our country’s streams and rivers still fail to meet water quality standards due to acid mine water that originates primarily in abandoned mined lands (Kim et al., 1982). Less than 10 percent of this total […]
Passive Acid Mine Drainage Water Treatment
Summary and Conclusions The treatment of contaminated coal mine drainage requires the precipitation of metal contaminants and the neutralization of acidity. In conventional treatment systems, distinctions between these two treatment objectives are blurred by additions of highly basic chemicals that simultaneously cause the rapid precipitation of metal contaminants and the neutralization of acidity. Passive treatment […]
Acid Mine Drainage Water Treatment
Removal of Contaminants by Passive Treatment Systems Chapter 2 described chemical and biological processes that decrease concentrations of mine water contaminants in aquatic environments. The successful utilization of these processes in a mine water treatment system depends, however, on their kinetics. Chemical treatment systems function by creating chemical environments where metal removal processes are very […]
Pyrite Oxidation Inhibition
The results of studies to ameliorate acid mine drainage by retarding the rate of oxidation of pyrite at source are discussed. In the transpassive region, pyrite oxidizes by reactive dissolution, mass transfer through the product layer and diffusion in the bulk solution. One can decrease the rate of pyrite oxidation by inhibiting either oxidation reactions […]
Inorganic Contamination of Groundwater from Copper Dump-Leaching
What is the potential of copper leaching operations in the western states to increase human health risk from drinking water? Should new leach pads be designed for worst case scenarios or for the most likely scenario? With limited funding, is money being spent on highest priority areas to reduce the greatest risk to human health […]
Nitrate Concentrations Prediction in Tailings Effluent
The disposal of spent ore from cyanide heap-leach processing facilities is of concern to the mining industry, regulatory agencies, and the public. Disposal of several hundred million tons of additional spent ore is planned in the western United States during the next decade, with increased amounts likely if gold prices rise. In the past decade, […]
