Carbonates are a very rare and volumetrically insignificant family of igneous rocks composed mainly of carbonate minerals, and normally are described in terms of their habits (intrusive) and composition (mineralogy). No other association of igneous rocks exhibit as great a diversity of rock types and intrusive habit. They vary in shape and size with depth as well as the completeness of differentiation, so that differences in the internal structure, habit and compositions of associated (co-genetic) rocks, as well as the type of metasomatic alteration (fenitization) with the country rock should be exposed with the depth of erosion level since emplacement.
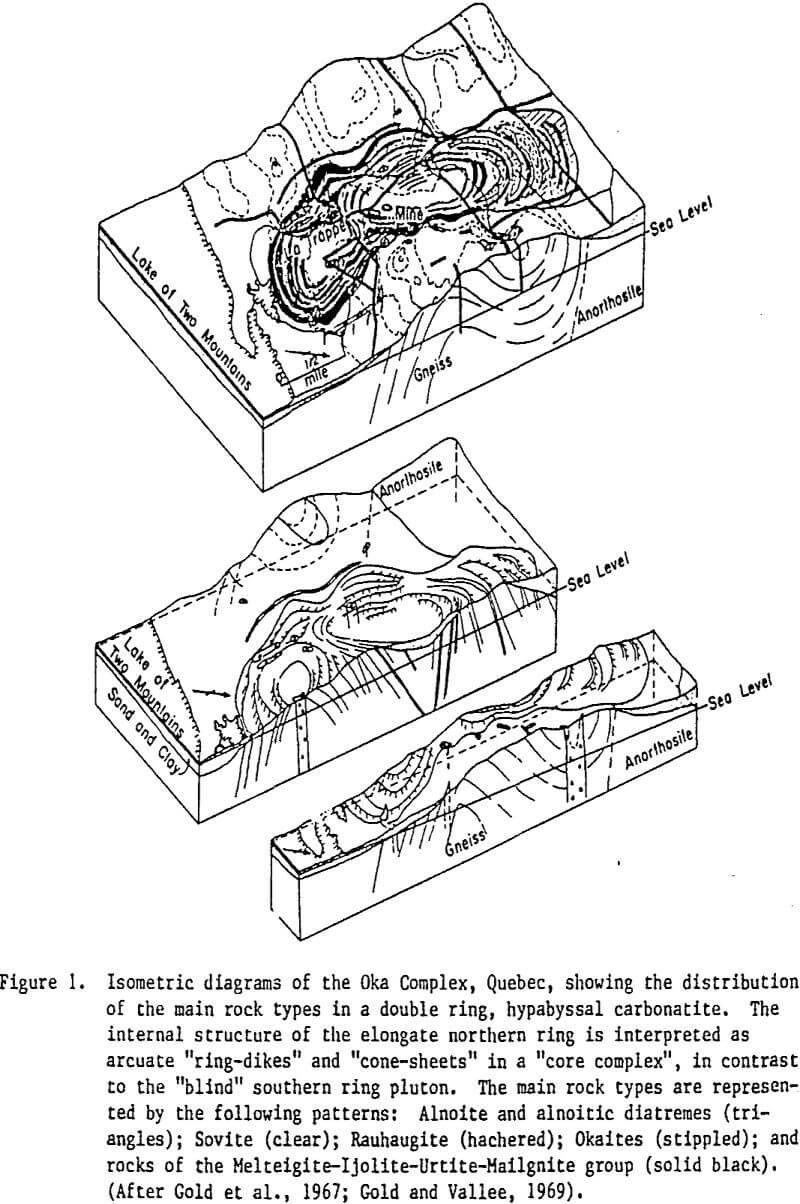
Morphology of Carbonatite Complexes
- Core carbonatite, in which (a) a carbonate-rich core is surrounded, in part or completely by, (b) cone-sheets and/or ring- dikes in the intermediate, outer, and fenite rings (aureole) of the complex, and (c) radial, tangential and irregularly distributed dikes within the complex, in the fenite aureole or at some distance into the country rocks. A variant of the above is the carbonatite that occurs only as arcuate dikes (ring-dikes and/or cone-sheets), and breccia zones in alkali ring complexes. These probably represent an unroofed core carbonatite.
- Some carbonatites occur as a thick sheet and tabular to irregular mass(es) associated with alkalic complexes. Others occur as dikes, dike-swarms, stockworks and hydrothermal veins, or sills within or as satellites to alkalic complexes of irregular structure.
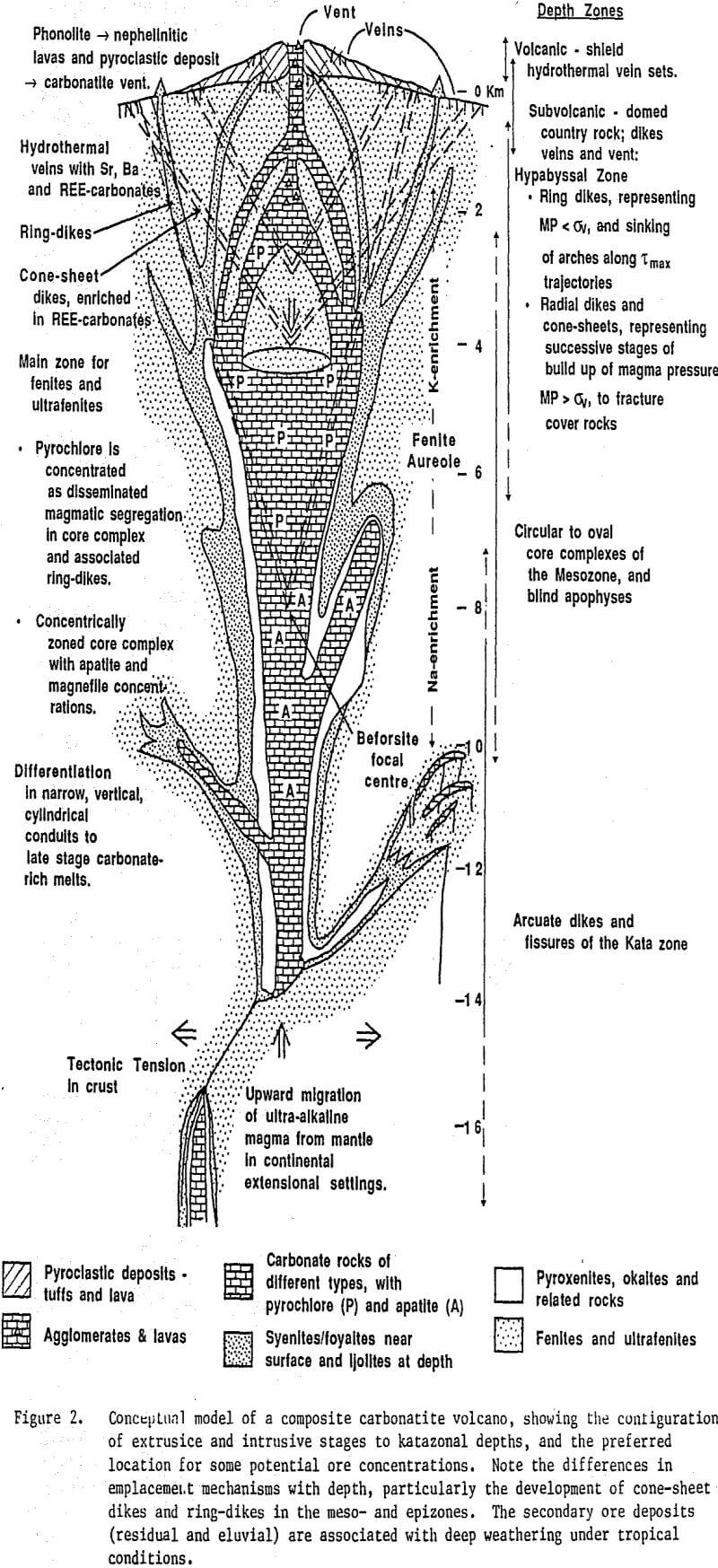
Although the plumbing system of carbonatitic volcanoes could be of either type, the presence of axi-symmetric intrusions in many volcanic piles suggests a core-ring type feeder system. While every carbonatite volcano has to have a magmatic source, it is not a necessary requirement that every carbonatite pluton had to be linked to a volcano.
Summary of Main Characteristics
Carbonatites are a very rare and volumetrically insignificant family of igneous rocks whose petrologic associations are restricted to:
(a) Miaskitic alkalic rocks (undersaturated and saturated).
(b) Alkaline ultrabasic rocks.
(c) A fenitized aureole of variable thickness and intensity is the characteristic wall-rock alteration, and its nature varies with emplacement level.
Sequence And Stages
(a) The evolution of lavas in carbonatitic volcanoes is from andesitic to phonolitic, to melilitites, mela-nephelinites to nephelinites to calcitic or natro-carbonatite lavas.
(b) In hypabyssal plutons the sequence is fenites, followed by emplacement of ijolite-urtite series, then okaite-uncompahgrite-turjaite series prior to a carbonatite series in cone-sheets followed by the core carbonatite plug or stock, with waning phase rare-earth carbonatite dikes and veins, and a late regional intrusive stage of lamprophyres and minor carbonatites in thin veins and dikes, and small plugs and diatreme pipes.
Commodities
Most of the world production of Nb (as pyrochlore), REE (as bastnaesite and monazite), and vermiculite is mined from carbonatites. In addition, there is a substantial production (mainly as byproducts) of apatite (Siilinjarvi, Finland; Khibina Massif, USSR; Palabora, S. Africa), magnetite, copper (Palabora), V (Potash Sulfur Springs, Arkansas), and Ti (Magnet Cove, Arkansas; Lovozero Massif, USSR; Salitre I & II, Serra Negra, Tapira, Catalao I. Brazil). In other carbonatites, the potential for Sc (Fen peralkaline complex.
Norway), barito. fluorito, Sr, Th. U. nnd Zr (Magnet Covo) attest to the diversity and local concentration of unusual minerals in these bodies.
Apatite is the largest bulk commodity mined from carbonatites, followed by calcite, and foscorito (apatite-magnetite-carbonate- serpentine-vermiculite rock, suitable for fertilizer). Current producers (with estimated output in either million pounds per annum (mpa), or in ton per annum (tpa)) are listed by commodity in Table 2. along with other potential producers for that commodity.



