This video best details and explains the fundamentals of an XRF’s Principle of Operation.
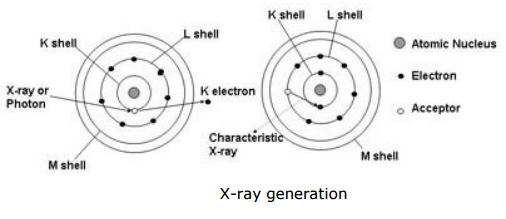
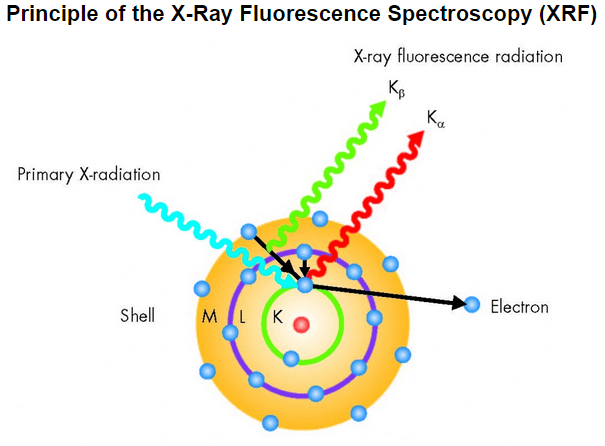
A prepared sample specimen is excited by the radiation of an X-Ray. This causes a electrons from the inner electron shells to get knocked-off. Electrons from outer electron shells drop-in to fill the resultant voids emitting a fluorescence radiation characteristic in its energy distribution for a particular element/material. This fluorescence radiation is counted/measured by the detector.
Generation of the XRF‘s X-ray fluorescence radiation is shown below (simplified):
- One electron from the K shell is knocked.
- Resultant voids are filled by either an electron from the L shell or an electron from the M shell.
- Meanwhile the Kα and Kβ radiation are generated, which is characteristic for the particular element capable of XRF measurements.