
In a vertical shaft impact crusher, the aggregate feed is introduced into a shoe or pump spinning on a vertical axis. The aggregate feed is thrown centrifugalLY against a series of anvils, pockets of aggregate particles (i.e., autogenous), or a combination thereof. Vertical shaft impact crushers produce a small reduction ratio and arc often used for crushing tines.
In hammer mills the impact of a fast-moving hammer on a slow-moving rock causes shattering. It can also be caused by the collision of a rock traveling at high velocity with another rock or a breaker plate. This is the concept of a vertical-shaft impact crusher.
|
 |
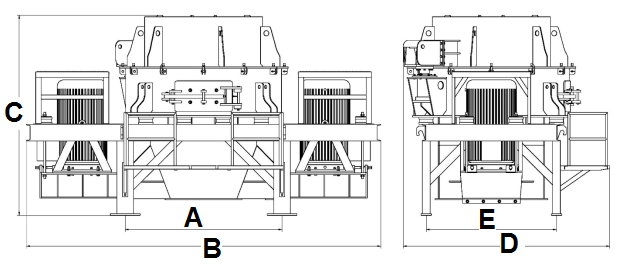
Vertical Shaft Impact VSI Crusher


The Vertical Shaft Impactors or VSI Crusher are one type of impact crushers, which offer higher reduction ratios at a lower energy consumption. These impactors
can be considered as a ‘stone pump’ operating like a centrifugal pump. The material is fed through the centre of the rotor, where it is accelerated to high speed before being discharged through openings in the rotor periphery. The material is crushed as it hits the liners of the outer body at high speed and also due to the rock-on-rock action. These crushers are mainly used in the production of fine materials, including sand, with a good cubical shape.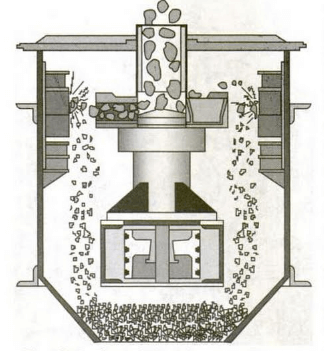
A number of VSIs are available in the market. The most popular VSIs are the Sandvik’s CV Series by Sandvik Mining and Construction, Sweden, and the Barmac B and VI Series by Metso Minerals, Finland. These crushers use the impact and rock-on-rock crushing principle for size reduction, which minimise wear costs.
Sandvik’s CV range of VSI crushers are autogenous VSI crushers covering a capacity range extending to 600 tph nominally. The whole range has been designed to ensure maximum production and yield of product for the lowest possible power consumption.
Sandvik’s VSI crusher is primarily a third or fourth stage crusher. The rock-on-rock crushing principle offers two main advantages:
- product gradation remains constant, even as rotor-wear parts wear, and
- contamination rates are extremely low, as no wear parts are used to directly crush the rock.
Feed material enters the crusher via a rock-lined hexagonal feed hopper. Rotor-material feed rate is controlled by the hydraulically operated rotor throttle gate. This material falls by gravity into the feed tube, which subsequently feeds the hurricane rotor. The crusher uses a rock-lined hurricane rotor to accelerate material. This material is accelerated by centrifugal force to typically 45 to 62 m/s. The crushing chamber is lined with a solid bed of material against which the energised rotor material impacts. It is this high-velocity autogenous impaction that causes impact, cleavage and attrition of the feed material.
The computer-designed crushing chamber geometry of these crushers give improved crushing action within the chamber when combined with the Bi-Flow system. The path of the material from entry (feed hopper) to exit (discharge chute) is controlled via autogenous rock-lined pockets within the crusher. This improved design further reduces points of contact within the crusher, resulting in extremely low crusher component wear.
Sandvik VSIs have the ability to handle hard, abrasive, fine, moist, or sticky feed materials, which makes them suitable for all of applications, such as quarries and gravel plants (production of premium-shaped aggregates for concrete and asphalt); recycling (processing glass bottles, etc., to sand specification and recycling of ceramics); mines (liberation of ores for heap leaching and differential liberation of hard particles, e.g., gemstones from softer matrix); cement works (crushing cement clinker to maximise fines prior to milling); and industrial minerals (crushing of highly abrasive minerals, e.g., fused alumina, silicon carbide, zirconia, mulochite, calcined bauxite, etc.).
