Table of Contents
Size reduction of ore in the refining process is necessary to liberate or expose the desired component of the raw ore. The geology of the ore deposit and the nature of the ore determine the extent to which the ore must be reduced to maximize the recovery economically. Size reduction of the raw ore is costly. Reduction of the ore to a size finer than is economically necessary is wasteful. Utilizing a size separation device in the grinding circuit can mar.y times reduce costly overgrinding.
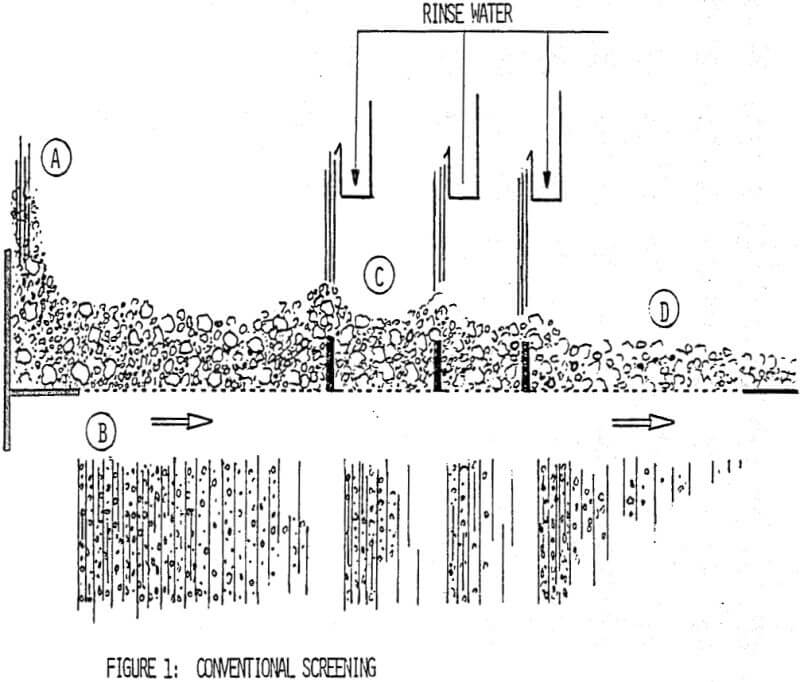
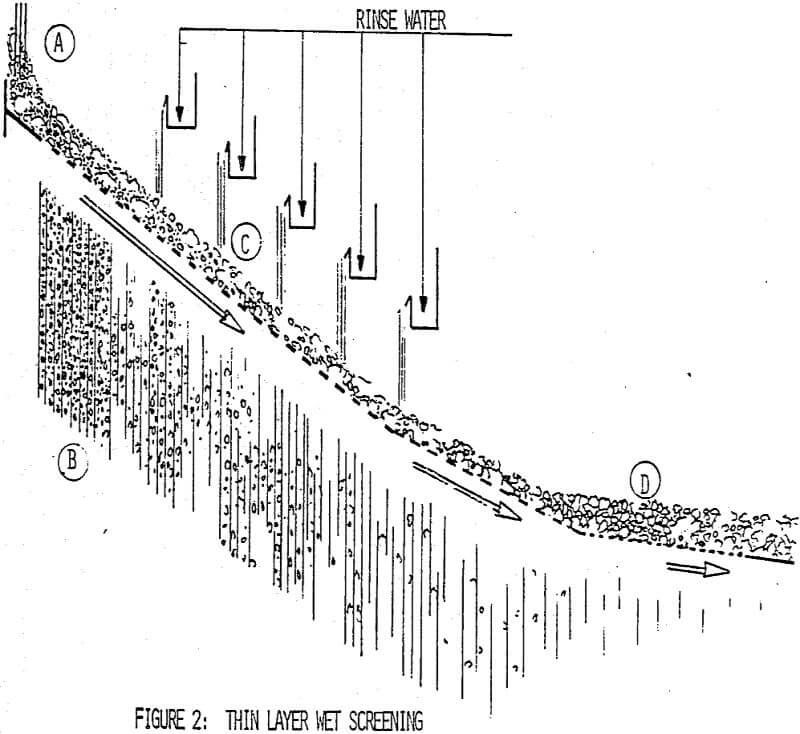
Thin Layer Wet Screening
The concept of thin layer screening on dry solids was extended to wet fine screening. Thin layer wet screening involves the creation of a thin layer of slurried material on the screen feed plate. The layer is created by the acceleration of the slurried material to a velocity of two to four meters per second along the screen surface: the material layer has a normal bed thickness of four to six times the separation size. The liquid in this slurry drains through the screening media carrying with it the particles finer than the separation size. The liquid with the fine material in this slurry drains much the same way as in conventional screening.
The Mechanics of Thin Layer Wet Screening
With the basic concept of thin layer wet screening in mind, the mechanics of creating and maintaining the thin layer are of interest. The material layer thickness is determined from the feed rate, the effective screening width and the material flow velocity. Specific acceptable values for feed and discharge bed thickness are determined based on the application. With the feed rate fixed by the process, the effective screening width and the material flow velocity are the variables in the screen selection.
Once a screen width is selected, variations in the material flow velocity are used to obtain the desired bed thickness. The thin layer is created by accelerating, maintaining, and varying the material flow velocity. In the feed region, a high velocity is necessary to create a thin material bed depth.
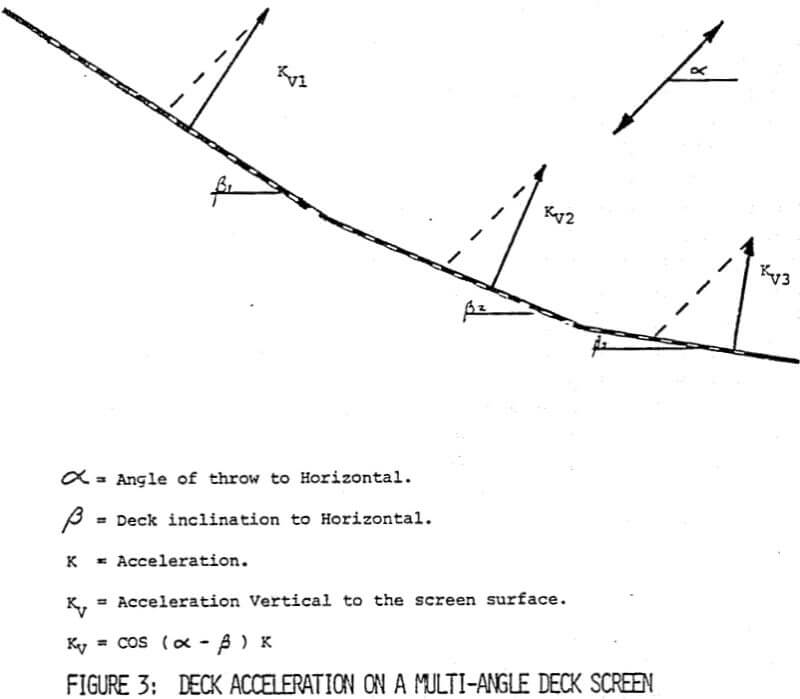
The multi-angle deck screen provides a means to control bed thickness by the generation of distinct flow velocities along the screening length. Each angled section in combination with the screen stroke, frequency, angle of throw and material characteristics results in specific flow velocities. The desired bed thickness is achieved through careful selection of each variable.
The advantages of using the thin layer wet screening process are two fold. Blinding of the screening surface can be substantially reduced and greater drainage capacity can be achieved. These combine to benefit the user with higher screen capacity and efficiency per unit screen area. This benefit has been demonstrated on various applications throughout the world.