The oxidation kinetics of pyrite and refractory gold concentrates in acidified ferrous sulfate solutions in the presence of oxygen-sulfur dioxide gas mixtures has been studied. The effect of temperature, pulp density and gas composition were determined. The optimum oxidation rate was obtained at 80°C and 2 percent sulfur dioxide in the gas mixture. The oxidation of the sulfide minerals is attributed to the presence of ferric ions, which are continuously regenerated by the gas mixture.
Pyrite oxidation has been studied by several investigators, and it has been found that the oxidation reaction leads to the formation of elemental sulfur and/or sulfate, depending on the pH and potential of the system. At low potentials, a layer of elemental sulfur is formed on the pyrite surface, which is protective and leads to low oxidation rates:
FeS2 + ½O2 + 2 H+ = 2 S° + Fe²+ + H2O
The oxidation of ferrous sulfate by S02-O2 gas mixtures have been found to proceed according to the following chemical reaction:
2 FeSO4 + SO2 + O2 = Fe2(SO4)3
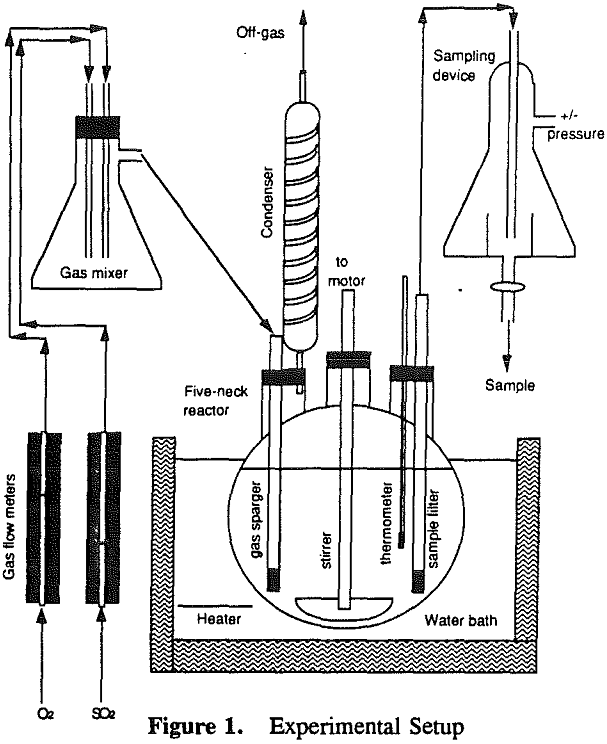
The gas composition was adjusted by controlling the O2 and SO2 flowrates. The gases were mixed in a closed flask and then introduced into the solution through a fine dispersion tube at a rate of 2.5 liters/minute. Condensers were used to recover water vapor from the off-gases.
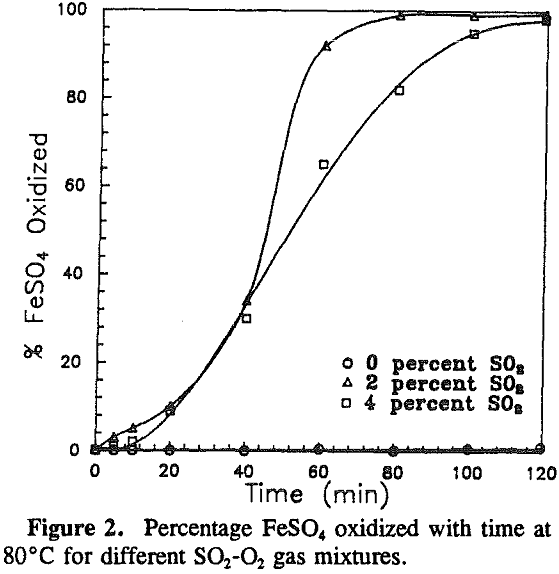
The effect of the gas composition on pyrite oxidation was investigated over a range of 0 to 4% sulfur dioxide at 80 °C. Pyrite oxidized at constant rates throughout the experiments. The maximum rate was observed at a gas composition of 2% sulfur dioxide.
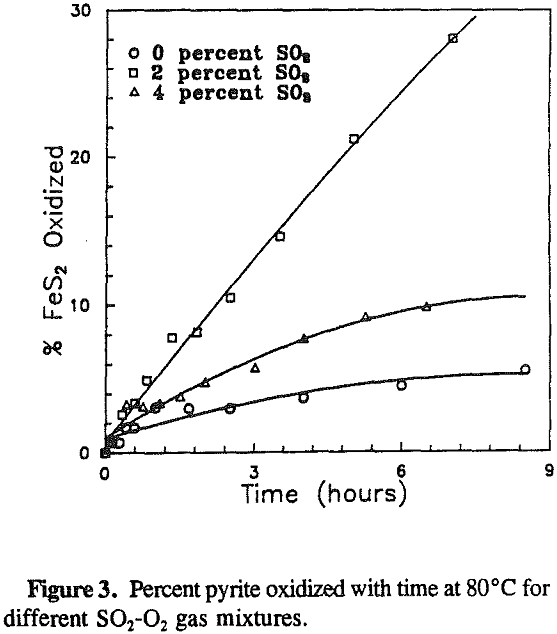
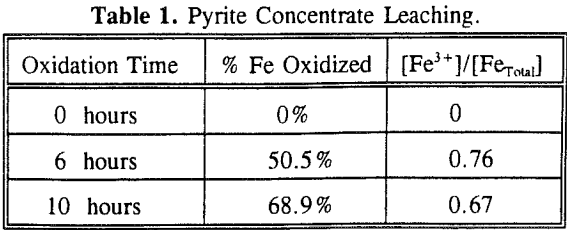
The experimental results show that the pyrite oxidation rate is proportional to the Fe3+/Fetotal ratio. The maximum oxidation rate was observed at 80°C and 2 % SO2 in the gas mixture, which are also the optimum conditions for reactions.
