Table of Contents
Laboratory Batch Classifier
The Laboratory Batch Classifier is used to classify or settle the pulp from Laboratory Batch Ball Mills, and the results approximate the work done by standard commercial classifiers and ball or rod mills in closed circuits.
This unit consists of a funnel with a variable spigot discharge through which the material passes into the hopper-shaped tank. The size of the overflow material is controlled by the slope of the tank and the size of the spigot opening in the bottom of the funnel. As the pulp passes into the tank the sands settle to the bottom and the slimes overflow at the discharge lip. This unit is of simple, sturdy construction and foolproof operation. It is recommended for classifying —100, —150, or —200 mesh, and is usually supplied with Laboratory Batch Ball Mills. Shipping weight is 10 pounds.

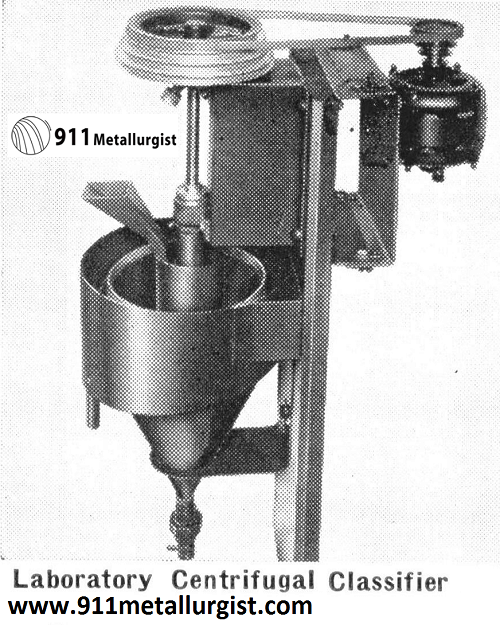
Laboratory Centrifugal Classifier
The Laboratory Centrifugal Classifier embodies a new principle in classification. The feed is introduced into a center well where it falls on a rotating impeller which forces the material outward and upward. The sands settle through the upward current and are discharged at the bottom spigot. The slimes rise and overflow around the rim of the classifier, while a portion of the slimes is recirculated with the primary feed to help in washing the sand particles. The velocity imparted to the pulp by the rotating impeller supplies the necessary rising current without an excess of water. There are several adjustments for regulating the size of the particles in the overflow and sand discharge. Recommended where sand grains are coated with colloids and a very fine and uniform overflow product is desired without excessive dilution, this unit also made in commercial sizes.
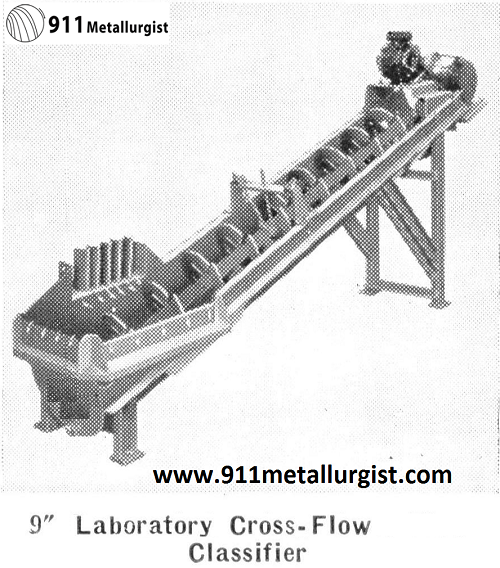
Laboratory Cross-Flow Classifier
Laboratory Cross-Flow Classifier is designed to operate continuously for washing, classification or desliming of industrial materials as well as metallic minerals. This unit is built in three different sizes to fit the variety of problems encountered in continuous test work.
The wide adjustable overflow weir with straight line surface flow provides efficient classification of coarse and fine material. An outstanding mechanical advantage, especially for intermittent operation, is provided by having the lower bearing entirely above the pool. No contamination of pulp is caused by surplus of forced lubrication required in other classifiers. Adjustable cast iron flights are easily replaced. Steel tank includes supporting legs to form a complete unit.
More complete information can be obtained by writing any Equipment Company office.
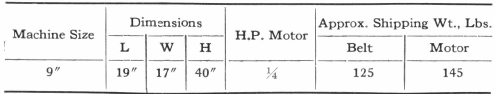
Capacity
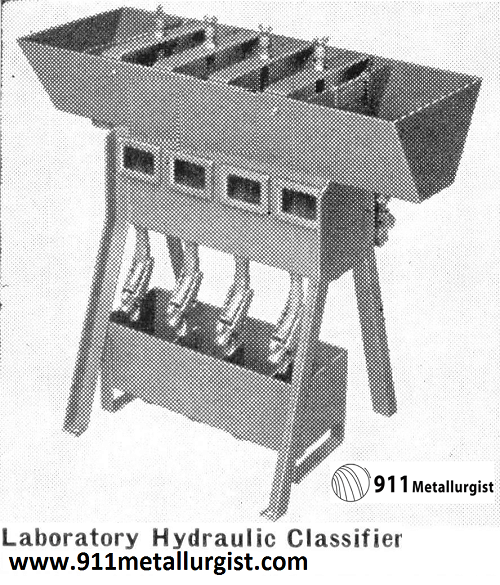
Laboratory Hydraulic Classifier
The Laboratory Hydraulic Classifier is designed for use in laboratories where tests on sizing or the concentration of feeds are conducted.
This unit is made in 2, 4, or 6 compartments. Each compartment is 4″x 4″ and is provided with glass sides so that the conditions existing in each chamber can readily be observed. Only enough water is necessary to keep the solids in full teter. As the sands accumulate in the classifier pockets, the effective density of sand- water mixture increases and thumb-screws on valve rod assemblies may be adjusted to discharge sand from each compartment as required. The finer the sand the less water required. When pressure regulating valves and product valves are set, no further adjustment is necessary.
The compartments are so arranged that the perforated constriction plates for the coarser feed are nearer the feed end with each succeeding compartment arranged for a smaller mesh product.
Each compartment has an average capacity of 500 to 600 pounds of aggregate per hour.

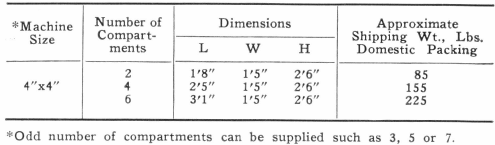
Laboratory HydroClassifier
Laboratory Hydro-classifier is suitable for a variety of classification, desliming, and washing problems in continuous testing laboratories. By splitting a portion of the pulp circuit in large tonnage plants, useful operating and control information can be easily and accurately obtained.
Specifications of the Laboratory Hydroclassifier are similar to those of the commercial unit. Totally enclosed running-in-oil gear mechanism drives the steel shaft and rugged spiral rakes. The bottom washing cone ensures the complete removal of any mechanically entrapped fine material. Welded steel tank and sturdy frame make this a self-contained portable unit. Discharge is controlled by a spigot, or positively by a Laboratory Suction-Pressure Diaphragm Pump.
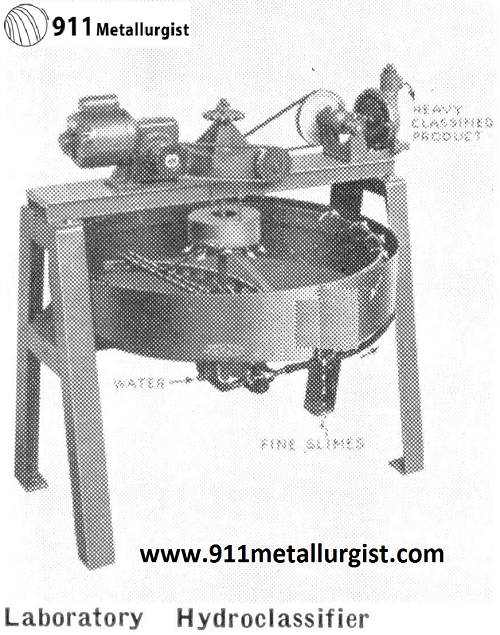
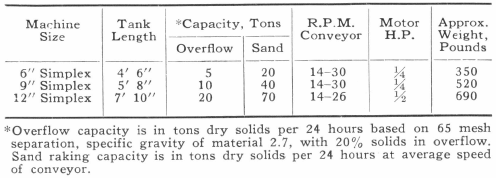
Capacity
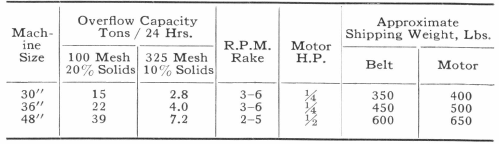
Laboratory Dry Classifier
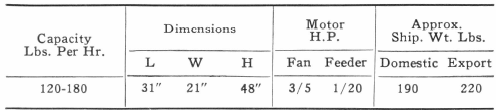
Laboratory separation of dry material finer than 200 mesh is efficiently made in the Federal Air Classifying Unit B. Powder metallurgists, as well as those working in plastics, ceramics and other non-metallics, report that results are constant. Variations of 1/10 of one per cent in duplicate tests are obtained. Fractionation of uniformly dense material at 2.5 and 5 microns, with unit B, is not unusual.
Sample to be tested is fed by a screw conveyer into centrifugal classifier, shown centrally. Air is admitted and controlled by pressure valve, directly above motor. Collector, on left side of unit, is built similar to the classifier. It may be equipped with a graduated mesh valve to govern both maximum and minimum size of particles delivered to bottom flask. Impalpable dust is caught in 5″ cloth tubes, not shown, fastened to the panel back. Final air discharge is from these cloth tubes.
The classifier has a diameter of 8″, and the collector 12″, both being fabricated from 24 oz. copper sheets. Head section of classifier is lined with sheet of hard brass to resist abrasion. Elbows are seamless and connected by sleeves to facilitate cleaning. Fan and feeder motor will operate on any 110 or 220 volt lighting circuit. Unit is mounted on a 31″x 42″ steel shelf. Size of packing case 21″x 33″x 48″.
Capacity
Source: This article is a reproduction of an excerpt of “In the Public Domain” documents held in 911Metallurgy Corp’s private library.
