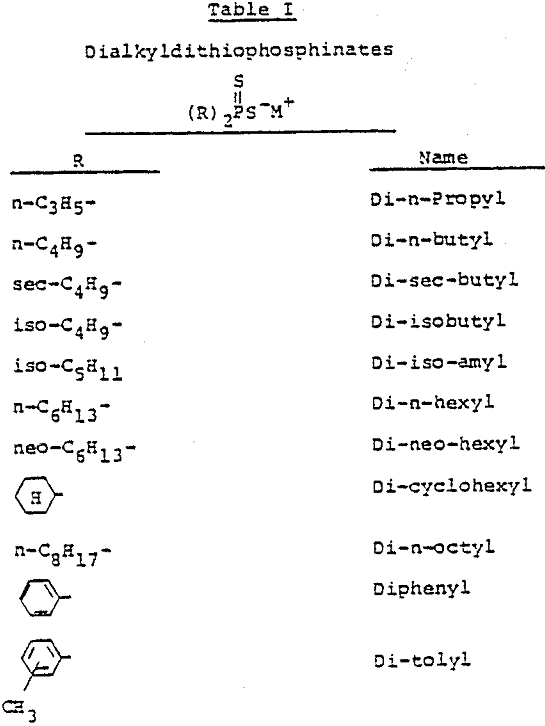
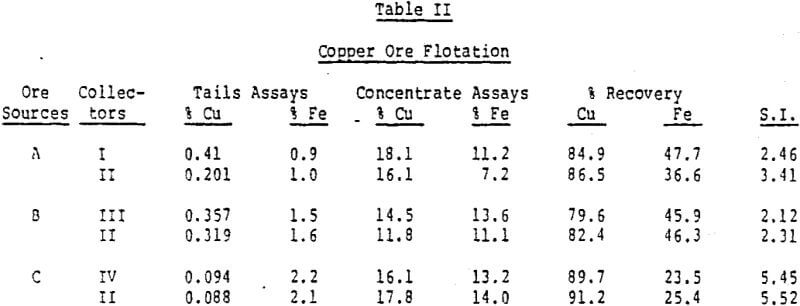
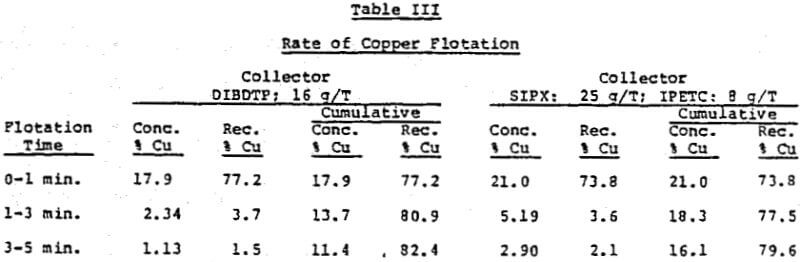
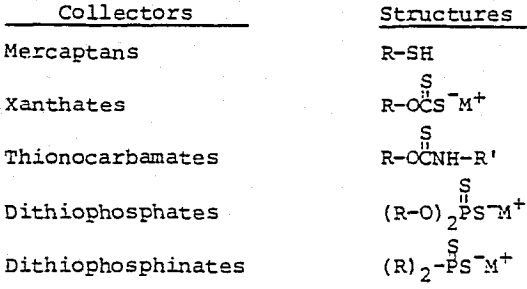
Dialkyldithiophosphinates are a new class of flotation collectors for base metal sulfide ores. Structurally, they are quite different from the conventional collectors such as mercaptans, xanthates, thionocarbamates and dithiophosphates.
Organophosphines and their derivatives form strong metal complexes. Thus, they offer potential applications in mineral beneficiation, metal recovery, corrosion inhibition, lubrication, sequestering agents and catalysts.
One of the dithiophosphinates has reached an advanced state of commercial development. AEROPHINE 3418A has been tested extensively in numerous milling operations, often with excellent results.
Phosphine is then reacted with olefins under the influence of a free radical catalyst to yield a secondary phosphine.
![]()
Secondary phosphine can then be treated with two equivalents of sulfur in dilute ammonia or alkali solution to obtain the dialkyldithiophosphinate in high yields (Rauhut, M.M. et. al. 1961).
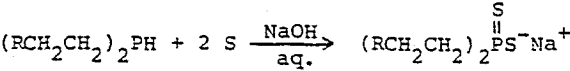
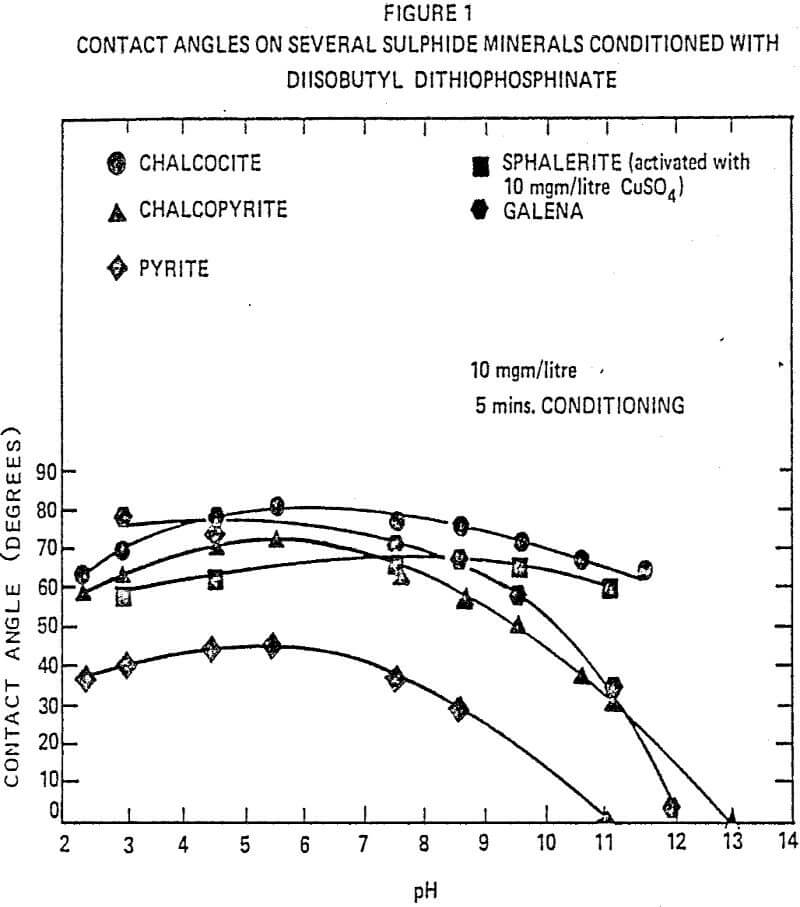
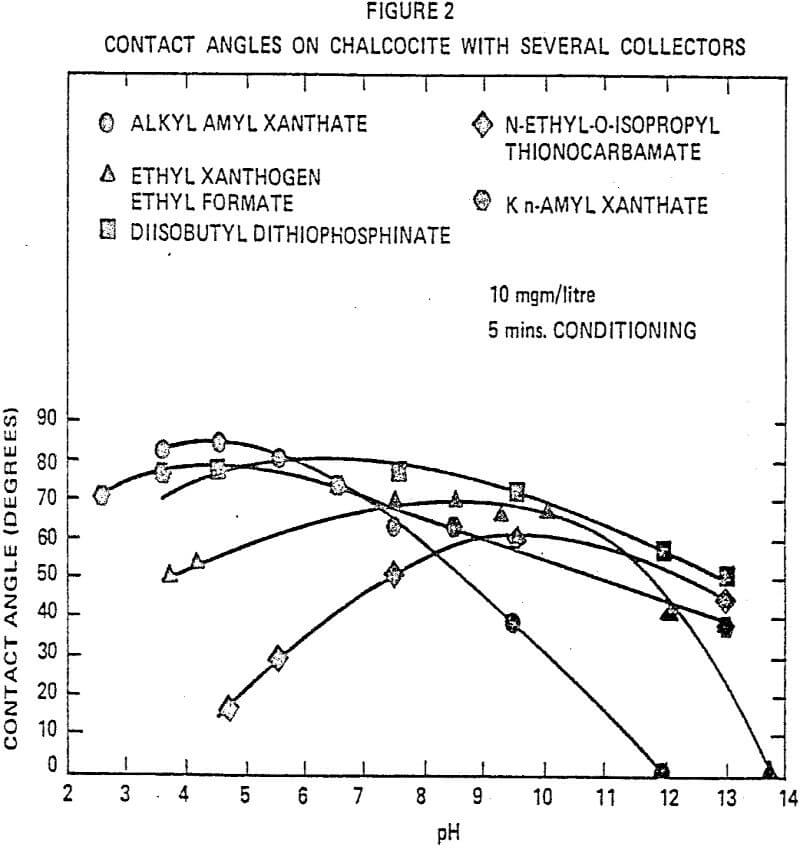
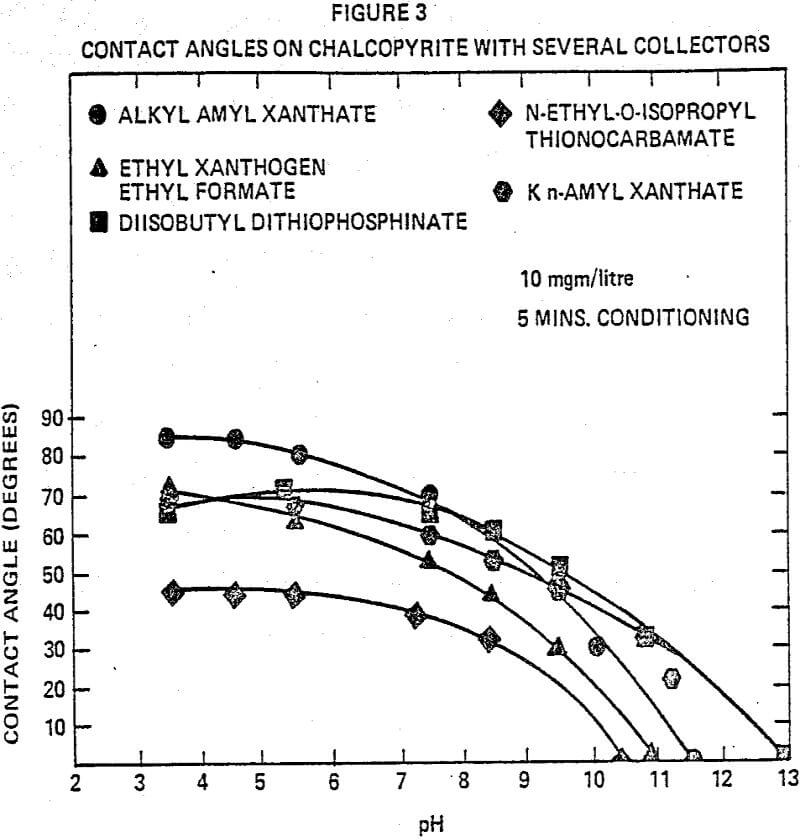
The effects of diisobutyl dithiophosphinate collector on the interfacial tension were studied by contact angle measurements. Pure mineral surfaces such as chalcocite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, sphalerite (activated with CuSO4) and galena were studied over a wide pH range. The contact angles of diisobutyl dithiophosphinate with chalcocite over the wide pH range remained more constant than those of other collectors. The contact angles of diisobutyl dithiophosphinate on the chalcopyrite surface are slightly below those of allyl amyl xanthate ester from pH 3 to 7. Above pH 7, the dithiophosphinate collector gave the highest contact angles.
The rate of flotation and recovery of copper as a function of particle size was also investigated with a South American ore. Most of the increased recovery obtained with this collector occurred during the first minute of flotation.
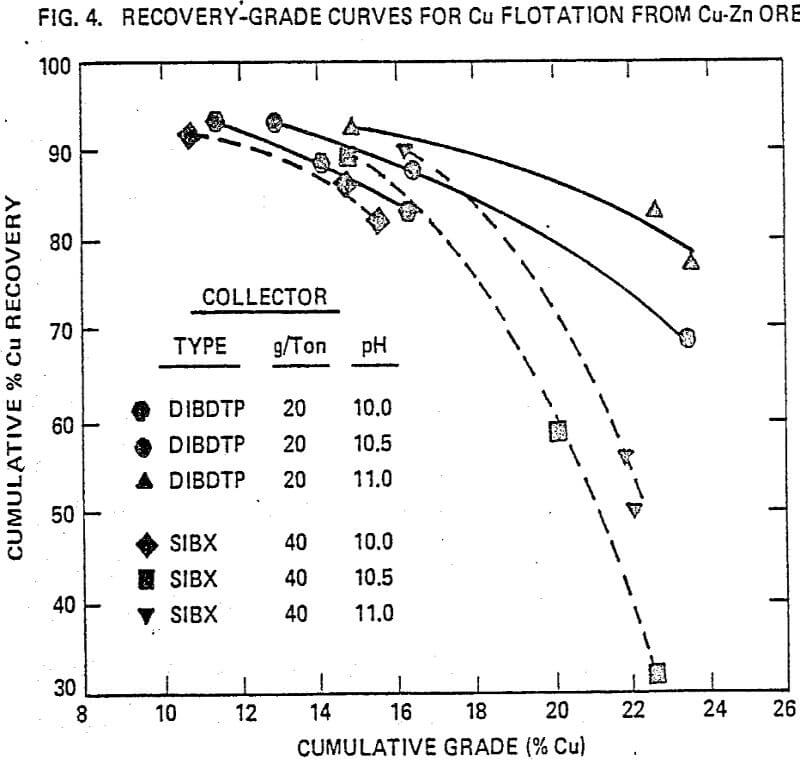
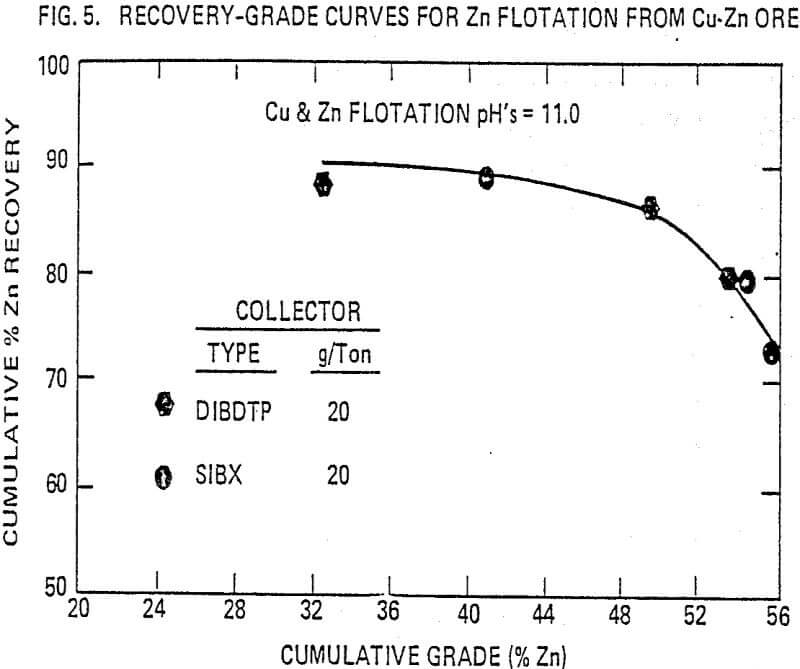
In a copper-zinc flotation, the metallurgical performance is compared to that of sodium isobutyl xanthate. In this ore, copper occurs as chalcopyrite and zinc as-sphalerite (marmatite) in a pyrite gangue. The flotation procedure is based on a standard flow sheet of copper flotation followed by copper sulfate activation and zinc flotation (rougher-scavenger-cleaner flotation).
The metallurgy of diisobutyl dithiophosphinate was evaluated with a copper-lead ore composed of chalcopyrite and bornite as the copper minerals, and galena as the lead minerals.
A copper bearing Pb-Zn ore composed of chalcopyrite, galena and sphalerite was used to test the effects of using diisobutyl dithiophosphinate as an additional reagent rather than as a replacement of the standard collectors.