Table of Contents
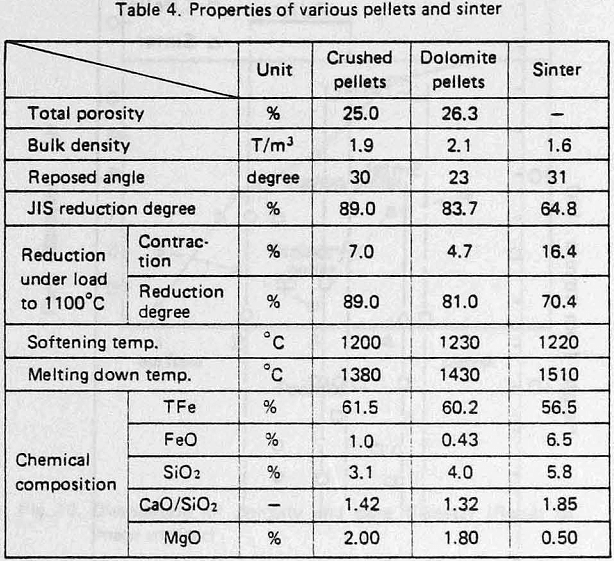
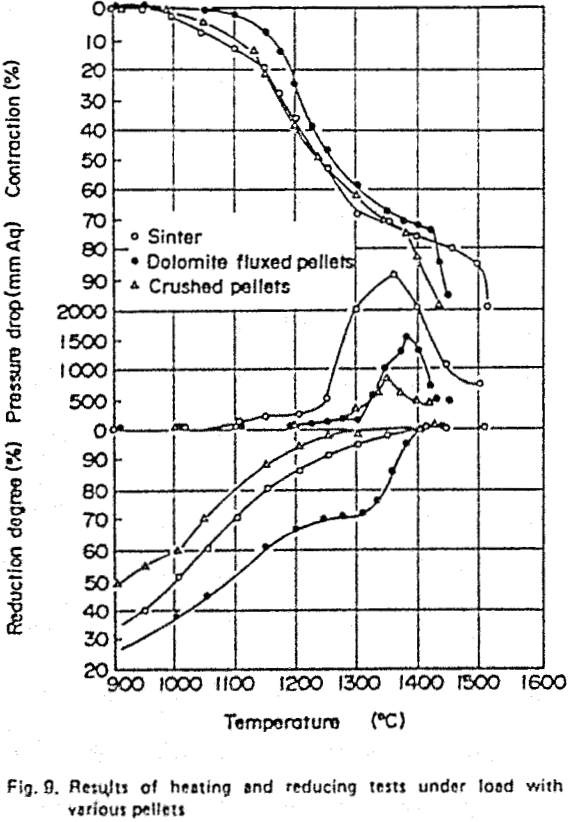
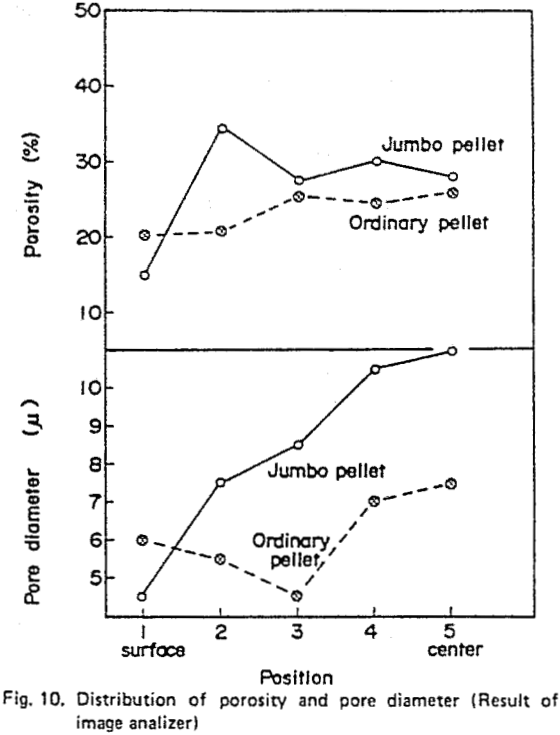
At the Kakogawa works of Kobe Steel. Ltd., the agglomeration facilities are composed of a pelletizing plant and sintering plant. This aim is to utilize raw materials efficiently and stabilize the raw material resources. Therefore at Kakogawa works, the blast furnaces (BF) have been operated with high pellet ratio and various developments for pellet properties have been achieved to improve the blast furnace performance. These developments include dolomite-fluxed pellets, new-porous pellets and crushed pellets. As a results of these improvements, pellets have achieved almost the same performance as sinter at high temperature regarding properties such as the softening, melting and reduction behaviour.

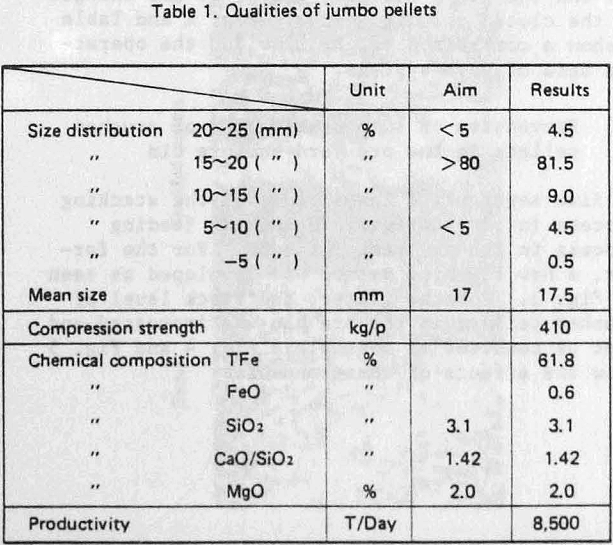
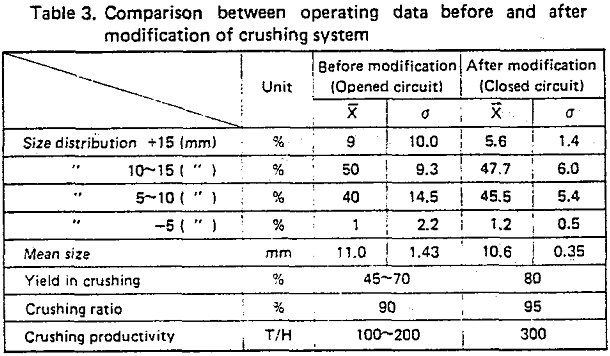
To decrease production cost of crushed pellets, it is important to get high yield in crushing. The target for this yield was above 80%.
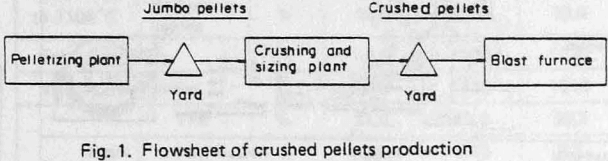
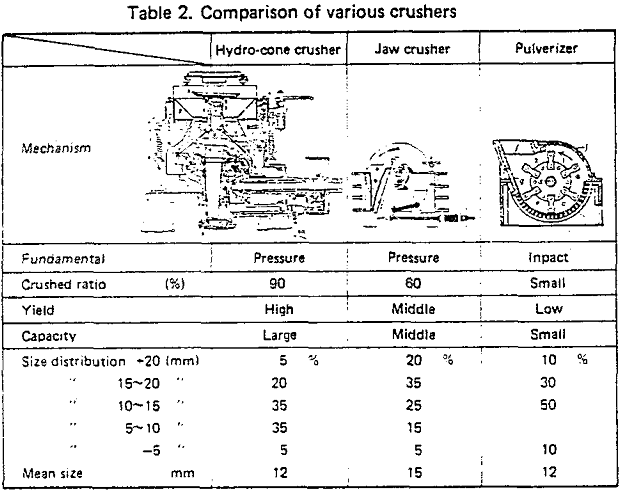
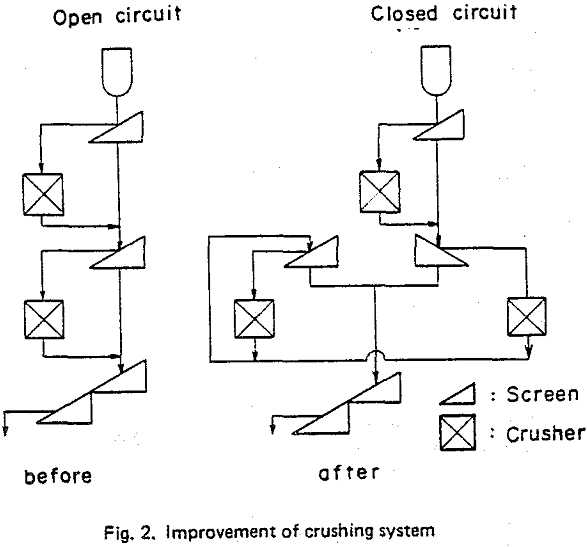
In crushing and sizing of jumbo pellets, the following characteristics should be controlled.
- Crushing ratio (the rate of non-spherical pellets to total pellets) This should be high to improve the shape of pellets.
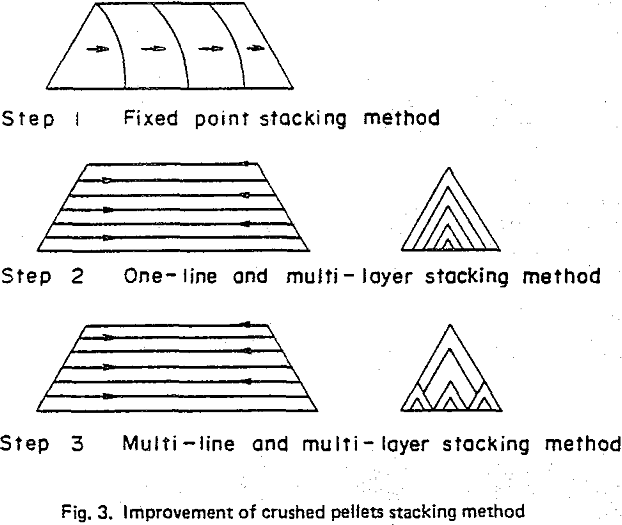
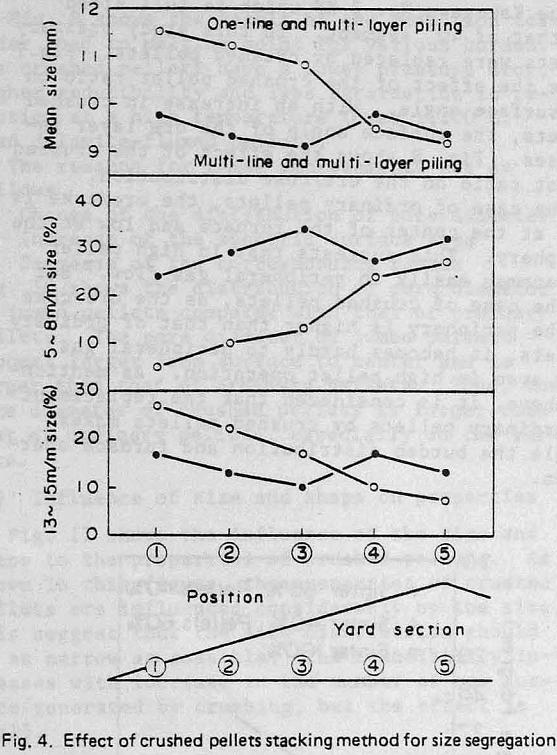
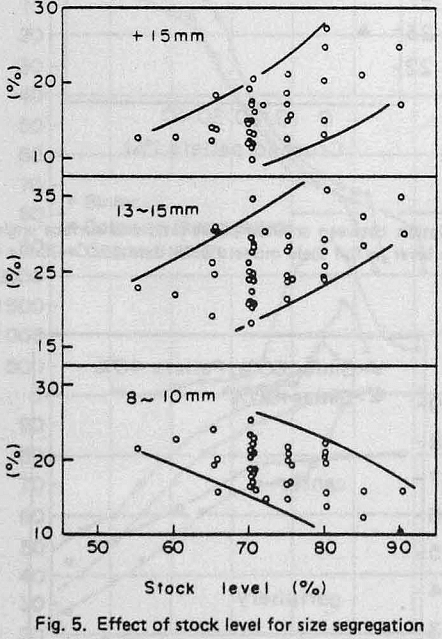
- Size distribution This should be narrow and stable to keep constant the reducibility pellets and the permeability of the BF. To this end, the portion of large and small size should be controlled,
- Crushing yield This should be high for economy.
Blast furnace operation test using crushed pellets

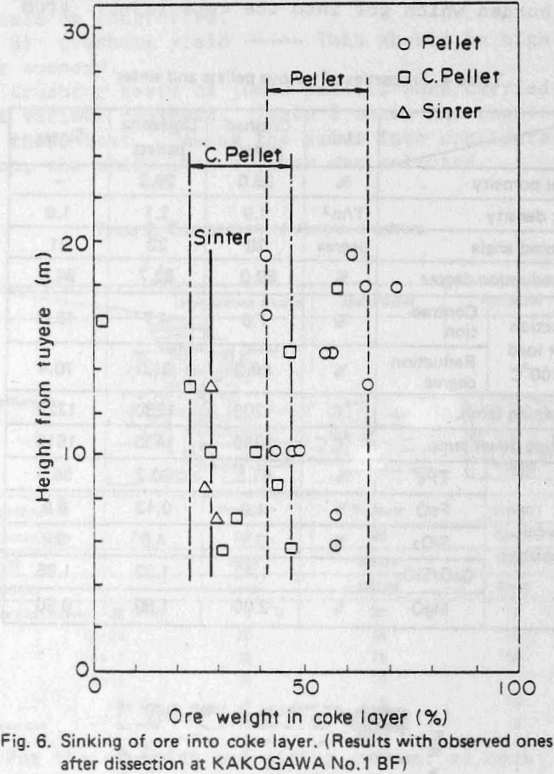
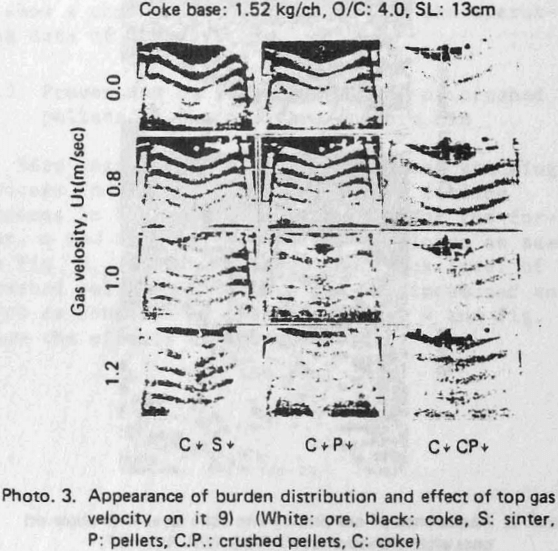
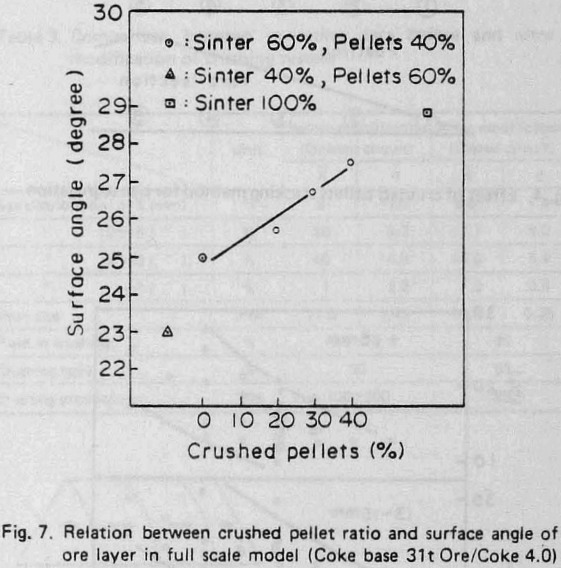
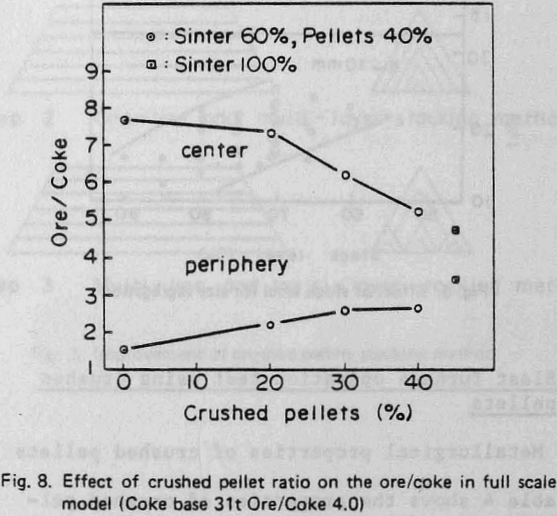
Further, the influence of crushed pellets on burden distribution was studied by test model of the Kakogawa No. 3 BF which is full sized and that of 40° segment. In this study ordinary pellets were replaced by crushed pellets.
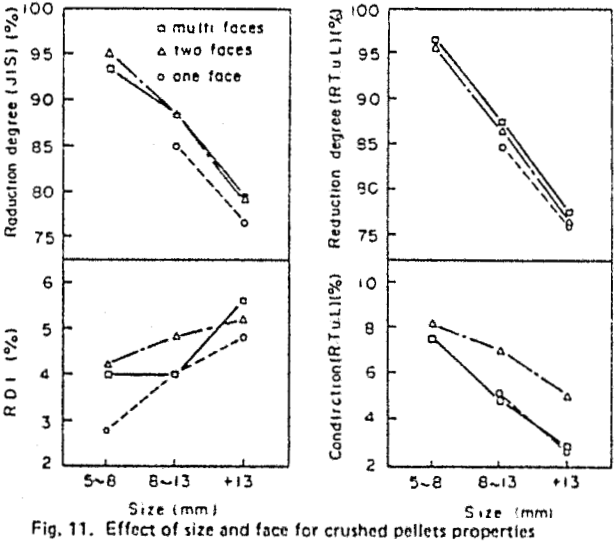
Influence of size and shape on properties
the properties of crushed pellets are influenced considerably by the size. This suggest that the size distribution should be as narrow as possible. The reducibility increases with increase in the number of new surface generated by crushing, but the effect is small.
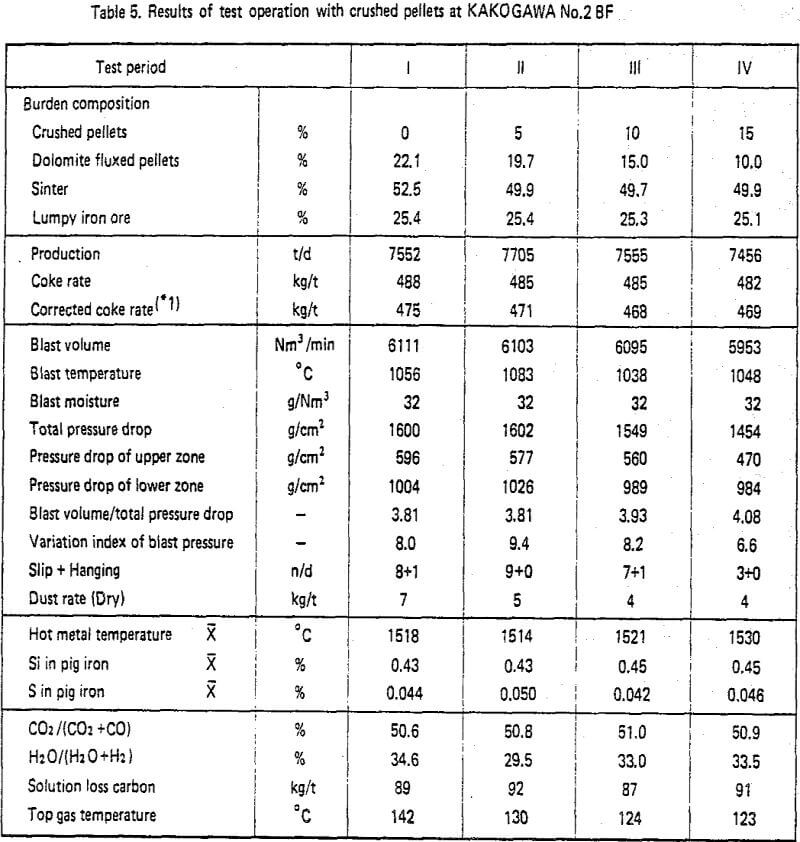
Results of blast furnace operation test with crushed pellets
A BF operation test with crushed pellets was carried out from September, 1981 to December 1981 at Kakogawa No. 2 BF (inner volume: 3,850m³, hearth diameter : 13.1m). Ordinary pellets were replaced by crushed pellets, and other burdens were kept almost constant.
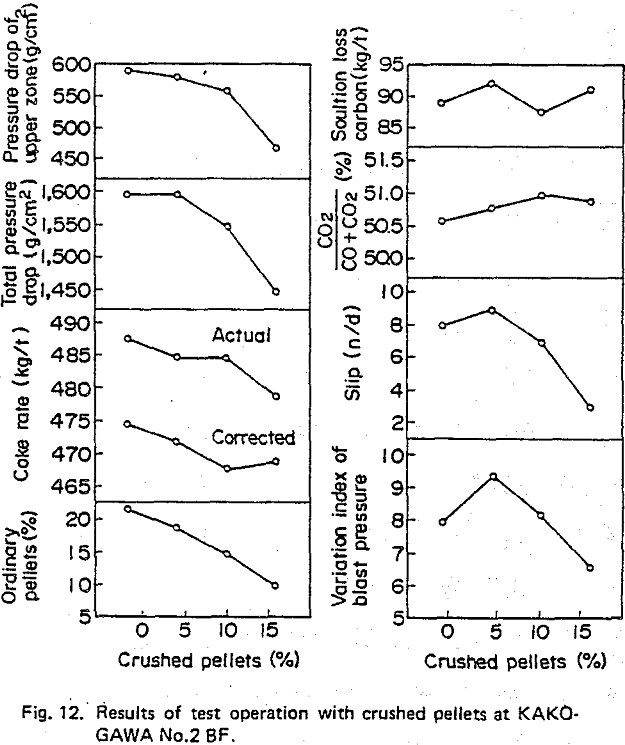
So it is considered that the replacement of ordinary pellets by crushed pellets caused the improvement in pellet behavior at the upper zone of the BF and this in turn is affected by the shape-based characteristics of crushed pellets.
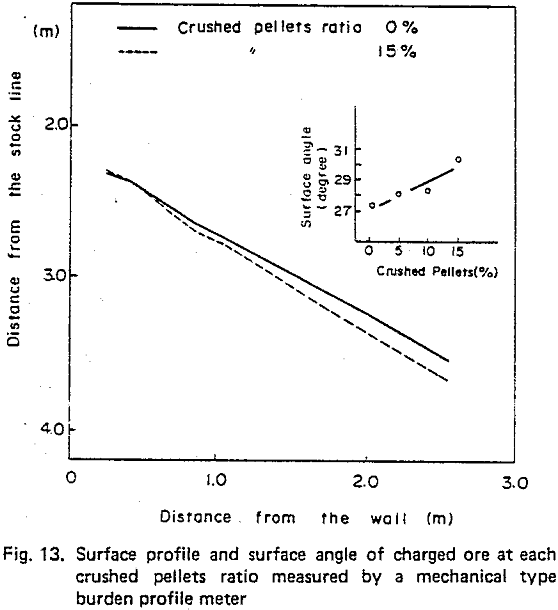
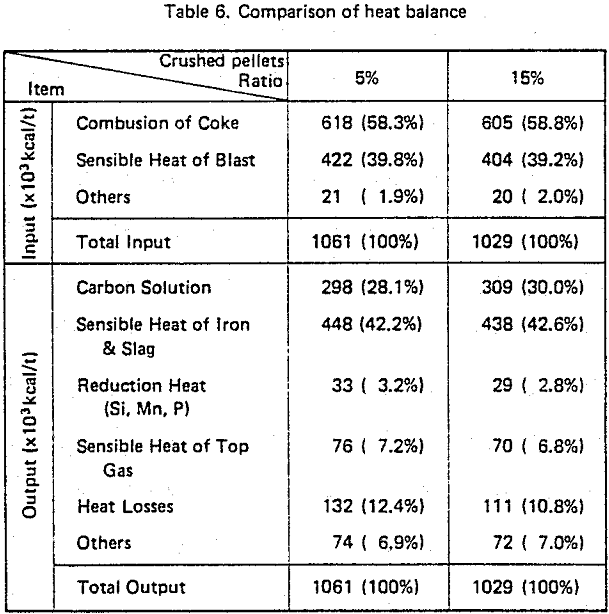
Test operation using crushed pellets were carried out at Kobe Steel’s Kakogawa No. 2 BF and successful results obtained. The furnace permeability was improved by replacing ordinary pellets with crushed pellets, the fuel rate also being lowered.

