Method for Estimating the Efficiency of Pulverizers
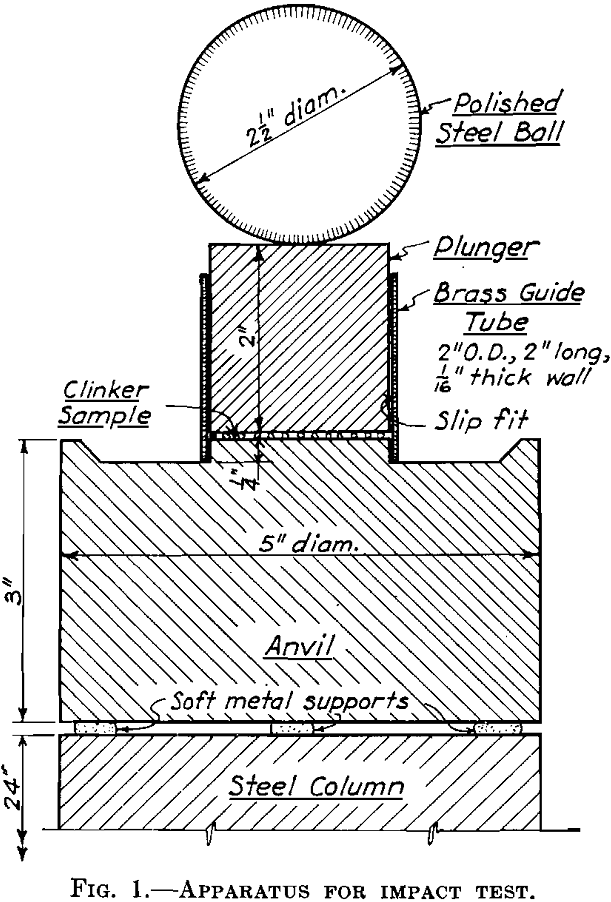
Grinding costs are an important item in cement manufacture, and the cost of power is one of the large items in grinding costs. Even where power is of secondary importance, cost items dependent on mill capacity are influenced by the efficiency with which the mill uses power. Tube mills typify the grinding mills most generally […]
Ball Mill Grinding
Three “ores” were used in the Ball Mill Grinding experiments. It is doubtful whether material more resistant to grinding can be found among the world’s ores. When flotation was newer and regarded as the panacea in ore treatment, the Tri-State operators were critized for not grinding the entire mill feed to flotation size and thereby […]
Ball Mill Pulverizing
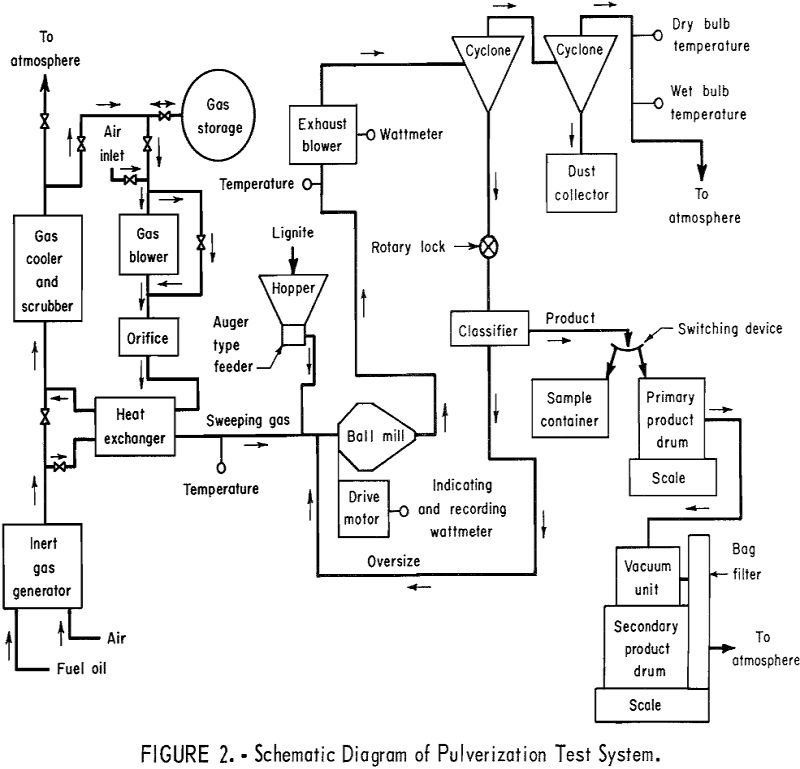
As in a pilot-plant-scale hammermill, the effect of moisture content in the pulverization of lignite in a similar size ball mill was observed to be a highly significant factor with respect to power required and in pulverization capacity. Both predrying before pulverization and drying in the mill were found to be highly beneficial in pulverization […]
How to Remove Pyrite from Coal
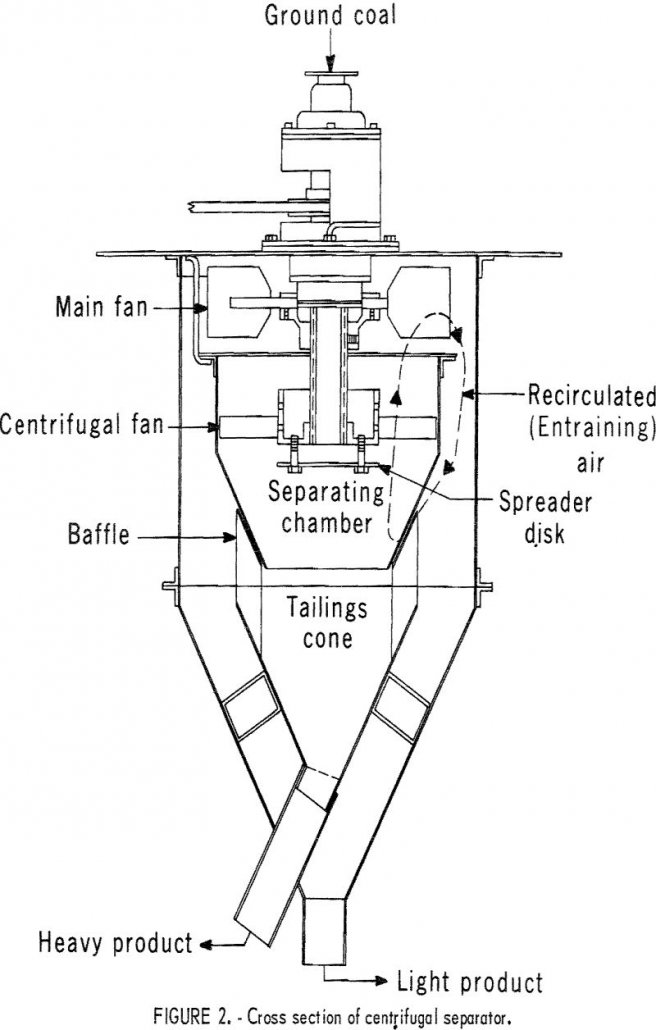
In recent years, coal research has been directed toward environmental problems of the electric power generation industry. A major problem of coal-burning power-plants is reducing the air pollutants in stack gases. In most of these plants, the chief pollutant is SO2, which results from the combustion of sulfur compounds present in the coal. Stack-gas cleaning […]
Kaolin Attrition Grinding
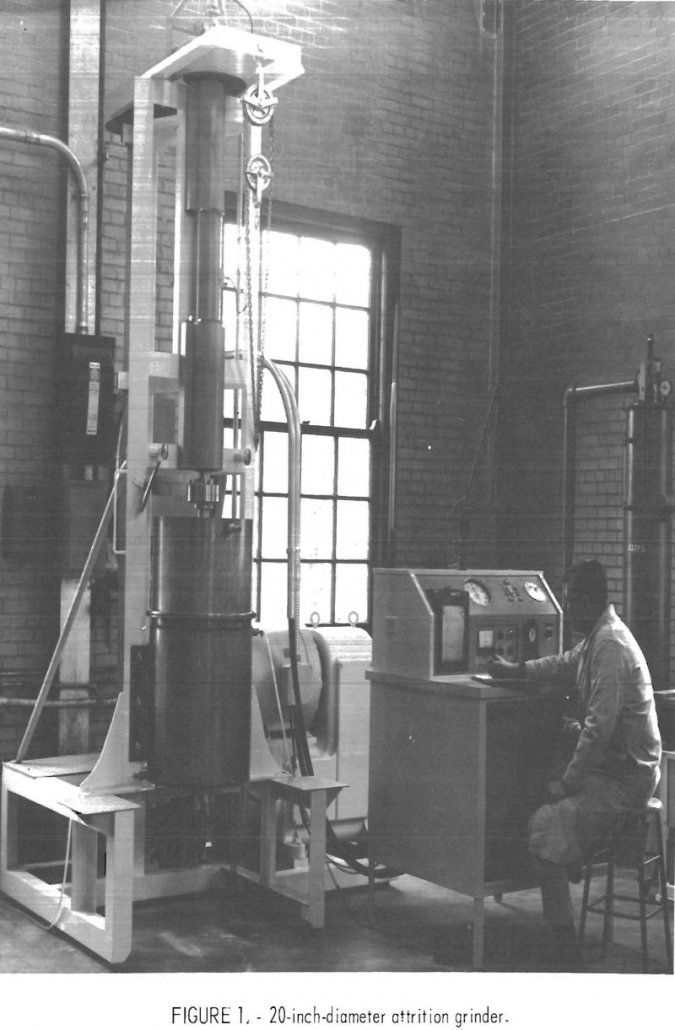

Fine grinding research has resulted in the development of an attrition grinding process: that has been successfully used for ultrafine grinding of various solid materials. The process was initially developed and patented by the Bureau at the Tuscaloosa Metallurgy Research Laboratory to grind coarse paper-filler kaolins to finer, paper coating-grade clay. The fundamental objective of […]
Ball Mill Capacity and Power Consumption Relationship to Mill Speed
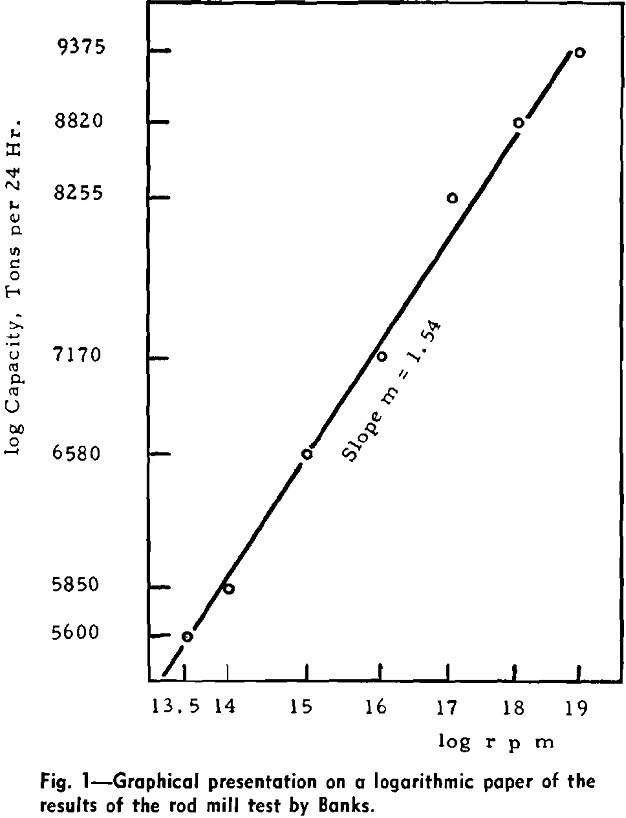
The accepted basis of comparisons between mills of different diameter is the percentage critical speed. If n = actual mill speed, rpm, nc = calculated critical speed, rpm, np = calculated percentage critical speed, and D = inside diameter of the mill in feet, In the following analysis capacity, T, is expressed in short tons […]
A Physical Explanation of the Empirical Laws of Comminution
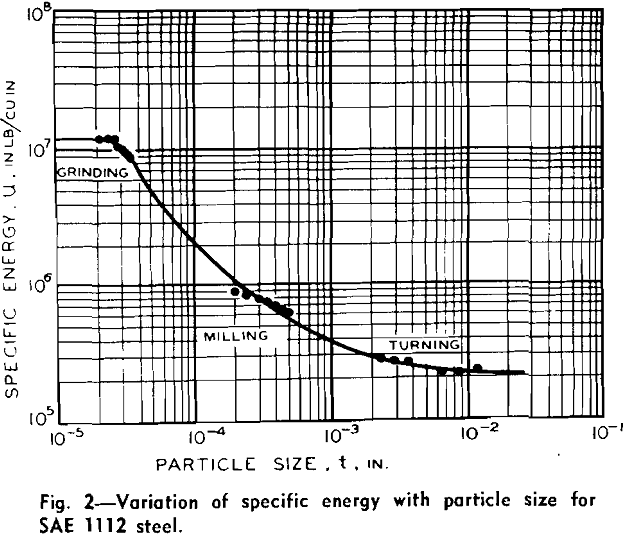
The laws of comminution of Kick and Rittinger have been debated for many years. Certain data obtained from ball mill and drop tests are found to be in approximate agreement with Rittinger’s law while other data would seem to support Kick’s law. In all these tests the energy required to produce a wide variety of […]
Theory of Comminution
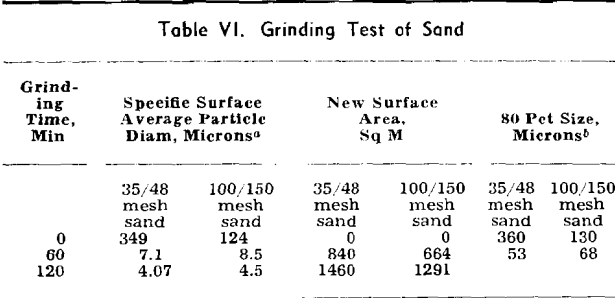
H. J. Kamack (E. I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc., Wilmington, Del.)—Rittinger’s law usually is stated to the following effect: “The work (or energy) consumed in particle size reduction is proportional to the new surface area produced.” The law has been stated substantially in this way by Taggart, Berry, Dalla Valle, Coghill and […]
Comparison of Overflow and End Peripheral Discharge Mills
In a previous article the authors outlined a study of the variables in rod milling and also reported data from a series of open circuit grinding tests on a massive limestone in a 30-in. x 4-ft end peripheral discharge rod mill. As a second part of the experimental program, an analysis is now presented for […]
Effect of Mill Speeds on Grinding Costs
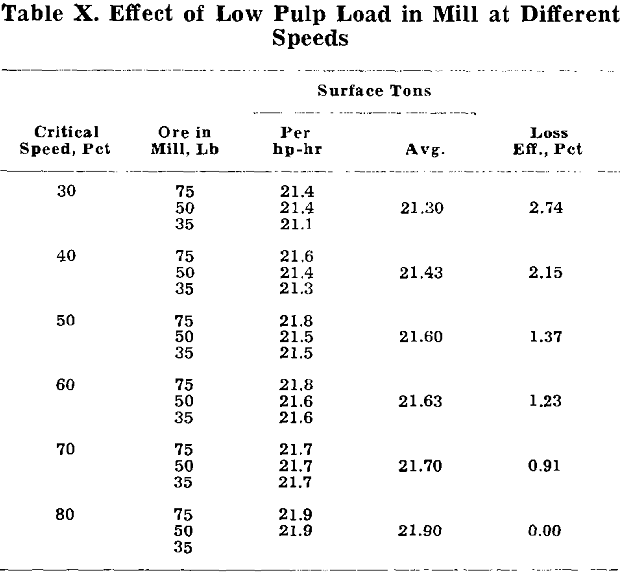
In my opinion, the effect of mill speeds on grinding costs must be studied along with capital investment and dollars gathered together as profits. Comparing the entire groups of operators with those who have had the opportunity to make slow-speed mill studies, I think you will find the latter small in numbers. Most managers want […]
