Where to Find Gold
So tonight’s topic of interest is kind of near and dear to me, I’m going to start with the first slide; Rocks and Gold Clues. What rocks tell you about where to find gold, there are clues that they give and those are very important if you’re going to find gold and that’s what we’re […]
Effect of Cupric Ammine on Gold Dissolution Rate

The dissolution of gold in ammoniacal solutions cannot take place in the absence of oxidants. Cupric ammine can act as an oxidant in this system according to Equation 3. The effect of cupric ammine concentration on the dissolution rate of gold was investigated in a solution of 0.6 M total ammonia concentration (0.1 M (NH4)2SO4 […]
Gold Pyrite, Pyrrhotite and Arsenopyrite Recovery

One of the more common classes of ores containing gold is when gold is associated with pyrite, pyrrhotite, and arsenopyrite. This is the area of gold recovery that has probably received the most research and plant optimization support especially in light of the long history of South African industrial practice. From a reagent viewpoint, charged […]
Carbonaceous Gold Ore Treatment Method

Flotation The simplest method of treating a carbonaceous ore is the method described by R. W. Nice (1971) at the McIntyre Porcupine Mine where the carbon, which contains very little gold, is floated off and discarded. The remaining ore is then responsive to cyanidation. This does not work at Carlin because the carbonaceous compounds have […]
Thiourea Silver Leaching

Unlike base metals which are readily soluble in mineral acids, noble metals like gold and silver require the presence of oxidizing and complexing agents for dissolution. Silver approaches base metal behavior in acidic thiourea solutions (Ag + 3Thio ↔ Ag(Thio)3+ + e, E° = 0.025 V) requiring only mild oxidizing conditions for dissolution. Accordingly, the following […]
How to Pan Gold
I told you I wanted to do a panning video. So what you’re going to do is, I’m going to break this down a little bit differently. I’m not going to get real scientific on this; I’m just going to put it in plain terminology. Now unfortunately we are probably going to listen to gunshots […]
Zinc Box Gold Precipitation

The simplest precipitation equipment for a small mine is what is known as a zinc-box (Fig. 150). This consists of a long, narrow, sloping, wood or painted sheet-iron box divided into wide compartments or cells which are separated by baffle-boards and narrow compartments. The bottom of the box slopes to one side to facilitate the […]
Mercury Amalgamation
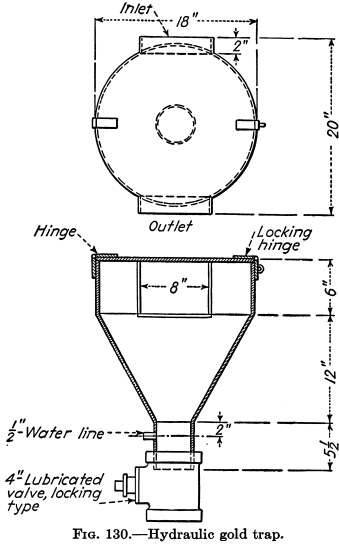
Mercury or quicksilver fed into stamp mortar-boxes and riffles or applied to copper plates has been for ages the method of catching free gold. Many millions of ounces of gold have been saved thereby, and the mercury has been returned to circulation with small loss. Amalgamation is still practiced, but the recovery of gold by […]
Magnetic Black Sand Separator
During the past 50 years or more there has been a great waste of money, energy, and time in devising, building, and trying many machines to recover gold and platinum, also gemstones, from black sand. Volumes have been written on the subject, and many inquiries have been made by prospectors and others who thought that […]
Cyanidation
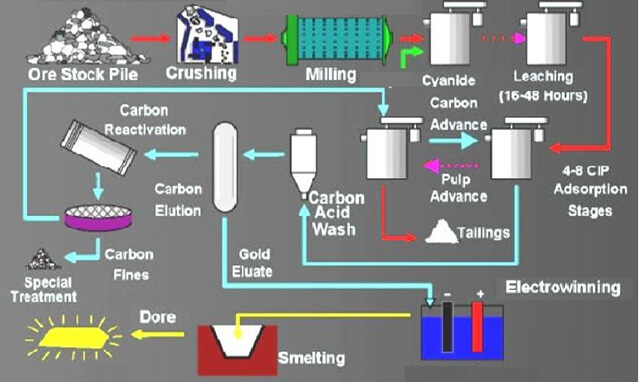
As coarse gold is not dissolved by cyanide, it must be removed from an ore by one of the methods already described. Weak solutions of sodium cyanide (or potassium cyanide, seldom used) will dissolve the fine, untarnished gold and silver in ores and tailings, provided the latter have been ground fine enough and do not […]
