Gold Rocker Box
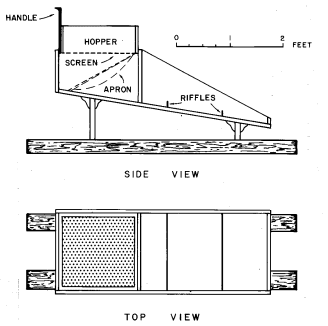
One of the first devices used after the gold pan was the gold rocker box. The rocker allowed small operators to increase the amount of gravel handled in a shift, with a minimum investment in equipment. Rockers vary in size, shape, and general construction, depending upon available construction materials, size of gold recovered, and the […]
Mafic Layered Intrusions -Chromite and Platinum
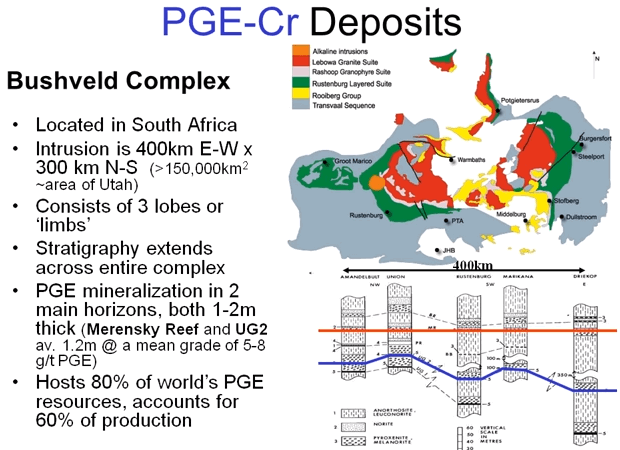
Another major groups of deposits in the mafic layered complexes are platinum group elements and chrome deposits but unlike copper nickel massive sulfides they don’t form as puddles on the floor of the intrusions they form in discrete layers well up in the magma chamber. The PGE’s that’s platinum palladium, rhodium with less amounts of […]
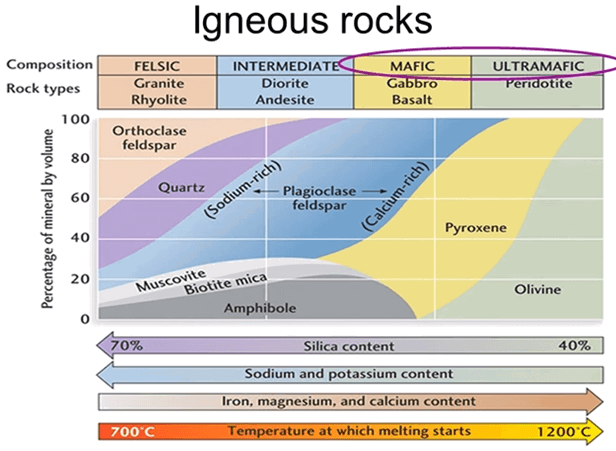
Igneous Rocks Formations

Igneous rocks; those that are formed from molten magma are broadly classified according to their chemical composition using silica, potassium, sodium, calcium, iron and magnesium as the key indicators. Magma is rich in silica, sodium and potassium generally form pale colored feldspar when they crystallize and are termed felsic. They are clustered on the left-hand […]
Mafic Layered Intrusions -Copper/Nickel Massive Sulfide
Mafic Layered Intrusions and complexes including copper nickel massive sulfide, chrome and platinum group elements or PGE deposits. This course on massive sulphide deposits includes copper and nickel exploration methods, nickel sulphide inclusions exploring for copper and nickel sulphide minerals. In the introductory Exploration Geology Course I mentioned felsic, mafic and ultramafic rocks but before […]
Rate of Gold Recovery by Size of Particle

Here is a review of various gold recovery machines/methods and the gold particle size they are best suited to recover. Compare Jig, shaker tables, dry washer, sluice box, spirals, bowl concentrators, falcon, Knelson and leaching. The size distribution of the raw material will also determine if classification of the ore is necessary for better recovery. […]
Kimberlite Deposits and Geology Formation of Diamonds

The geology of Diamonds consist of crystalline carbon although a significant proportion of diamonds are derived from placid deposits i.e. hosted in sediments, placid’s are secondary deposits and all diamonds were at one time or another hosted by kimberlite igneous rocks. The name Kimberlite comes from the town of Kimberley which grew up around the […]
Mineralogy of MVT Mississippi Valley Type Deposits

Where are the VMT A Mississippi Valley Type Deposit or commonly called VMT offers some of the simplest, cleanest and “easiest” mineralogy and therefore metallurgy in the world. As shown in the image below, a near perfect liberation of all minerals at 100 microns grind. As seen below, Mississippi Valley Type Deposits liberate very well as coarse […]
Sample Preparation Flowchart
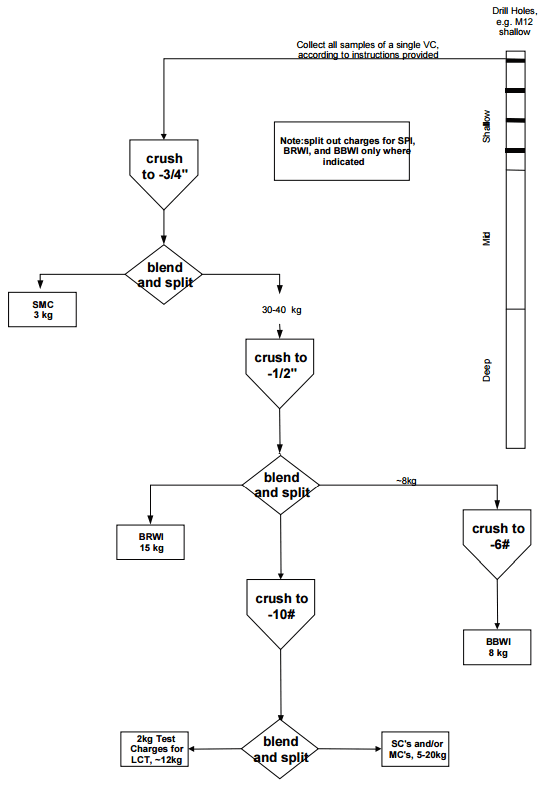
The samples set aside for the Super Composites (SC) were blended to form the four composites used for the initial flowsheet development program. Each SC was crushed to 100% passing 10 mesh and rotary split into 2 kg charges and a reject fraction. A flowchart summarizing the sample preparation procedure is presented here below. Eighteen […]
Carlin Type Gold Deposit
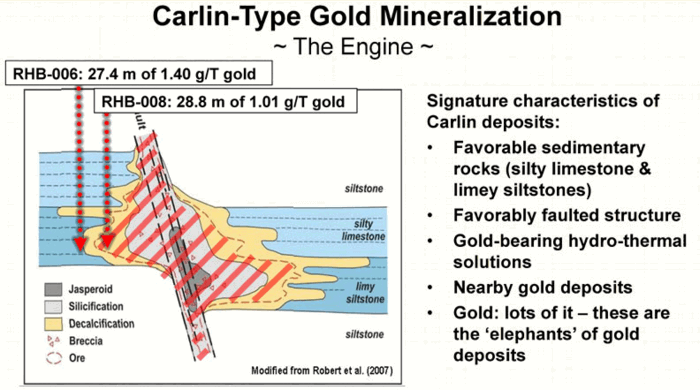
Prospectors frequently talk about being in elephant country, meaning in good hunting grounds for big deposits. Historically Carlin Type Gold Deposit are big elephants but until recently they were largely known to occur only in the limited hunting ground of Northern Nevada that limitation is now beginning to change. How Carlin gold deposits fit into […]
World’s Main Gold/Auriferous Mineral Deposits
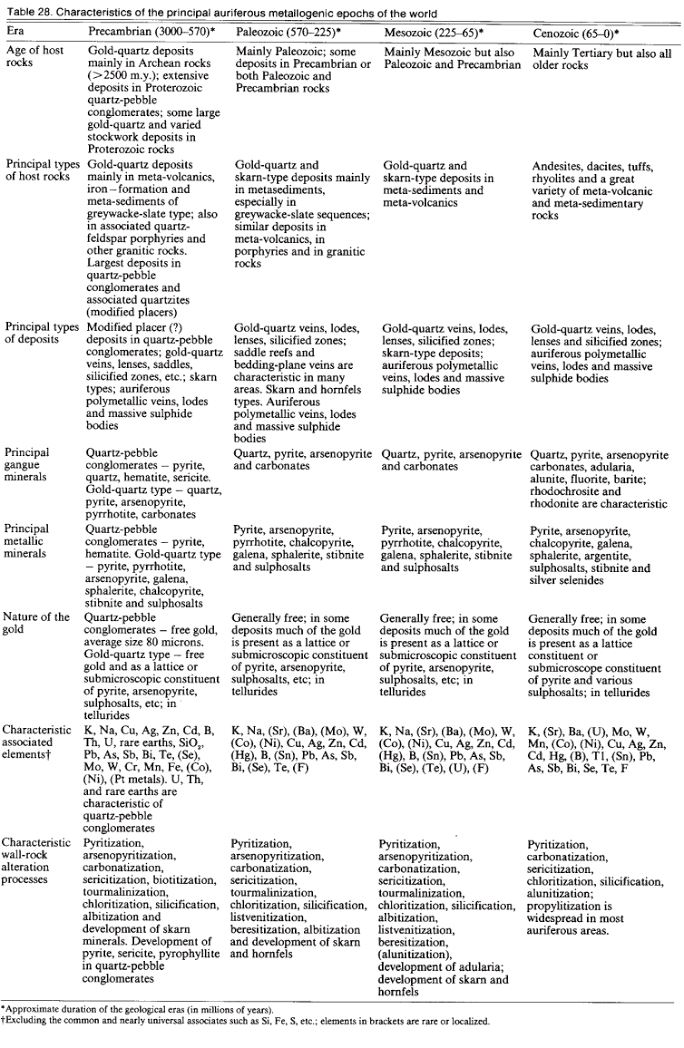
Era Precambrian (3000-570)* Paleozoic (570-225)* Mesozoic (225-65)* Cenozoic (65-0)* Age of host rocks Gold-quartz deposits mainly in Archean rocks (>2500 m.y.); extensive deposits in Proterozoic quartz-pebble conglomerates; some large gold-quartz and varied stockwork deposits in Proterozoic rocks Mainly Paleozoic; some deposits in Precambrian or both Paleozoic and Precambrian rocks Mainly Mesozoic but also Paleozoic and […]
