Mechanical Weathering of Rocks
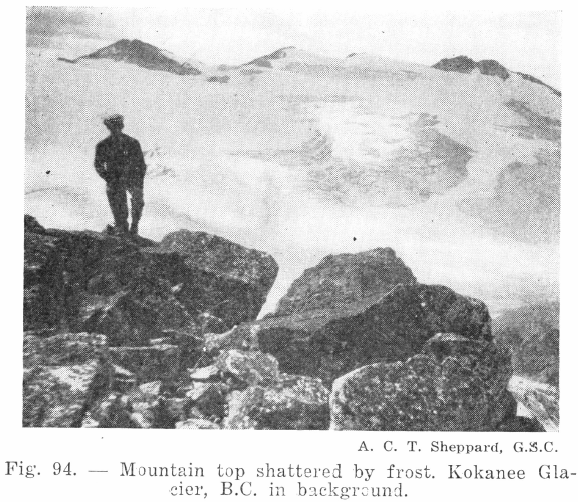

Weathering Forces Under this head are grouped a number of agencies that have their origin in the atmosphere, and which work not only on the surface but as far down as air and water, heat and cold, can penetrate. Because these forces work invisibly, they are apt to be more or less overlooked, although the […]
Landforms Created by Glaciers
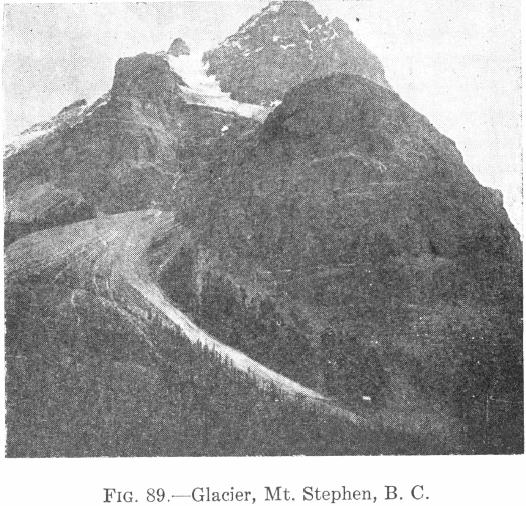

Origin of Glaciers In temperate and cold climates, and even in tropical countries, where there are very high mountains, the wastage of the snow by melting and evaporation may be less than the snowfall on the tops of the mountains; the snow, therefore, accumulates continually. In cold climates, like that of Greenland, snow accumulates even at […]
Types of Formations Caused by Erosion
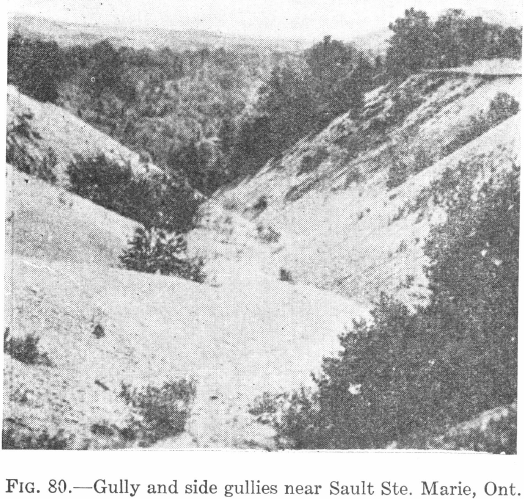

Forces Causing Erosion It is plain that ever since the crust of the earth became stable enough to allow water to stand, waves to form, rain to fall, and weather to act, these forces have been working on the surface much as they are doing now. It is quite possible that in earlier ages they […]
Origin of the Earth
The Earth As a preparation for the systematic study of rocks, it will be useful to look at the earth as a whole, inquiring into its origin, the changes that it has undergone and is still undergoing, and the nature and causes of the great variety of surface features. Origin of the Earth From comparison […]
Rocks and Mineral Identification Table
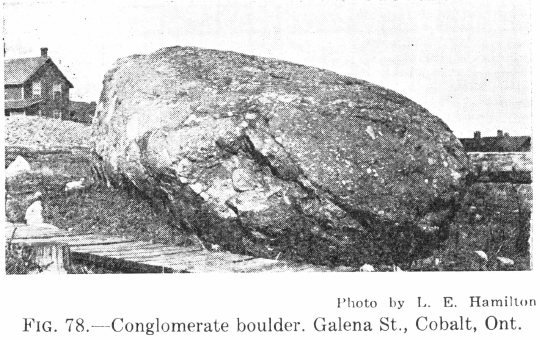
It is strongly recommended to the student of this book that he obtain specimens of rock, not labelled, and study their features with a view to naming them. The Table for Identification of Rocks will help in naming them. It may here be mentioned that the identification of rocks presents peculiar difficulties. Rocks are not […]
Mineral Identification Tables

The various minerals have been described individually, so that any mineral specimen may be compared with a careful description of that mineral. The prospector’s task is to discover valuable minerals; and to be proficient in this, he must be practised in their identification. The best method of obtaining the requisite experience is to work in […]
Sulphate Mineral Group
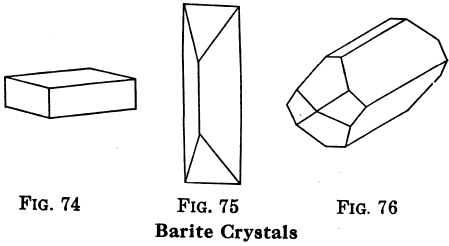
The group of sulphates correspond to sulphuric acid, H2SO4. In the list of sulphate minerals, there are metals in place of the hydrogen of the acid; they are to be distinguished from sulphides, which contain no oxygen, but are made up of sulphur and metals. Barite or Barytes Barite or Barytes; BaSO4. — Also called […]
Phosphate Mineral Group
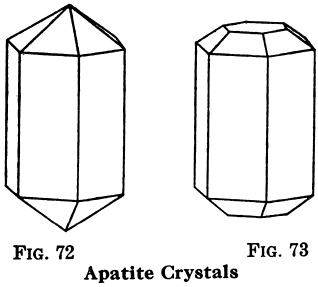
The Phosphate Mineral Group includes a number of the rarer minerals and apatite. Pitchblende or Uraninite is of Color, pitchy black, greenish, or brownish black; powder, brownish black, grayish, greenish; luster, dull and pitchy, sometimes slightly metallic. H = 5.5; G = 9 to 9.7; no cleavage; contains uranium, radium, etc. Found in pegmatite granite dikes, […]
Mine Geology Sampling

The sampling and estimating of the orebodies in a mines have been made a part of the work of the geological department. The wisdom of this assignment is apparent, considering the organization of that department, the nature of its records, and the scope of its regular work. In the first place, the district is divided […]
Mica Mineral Types
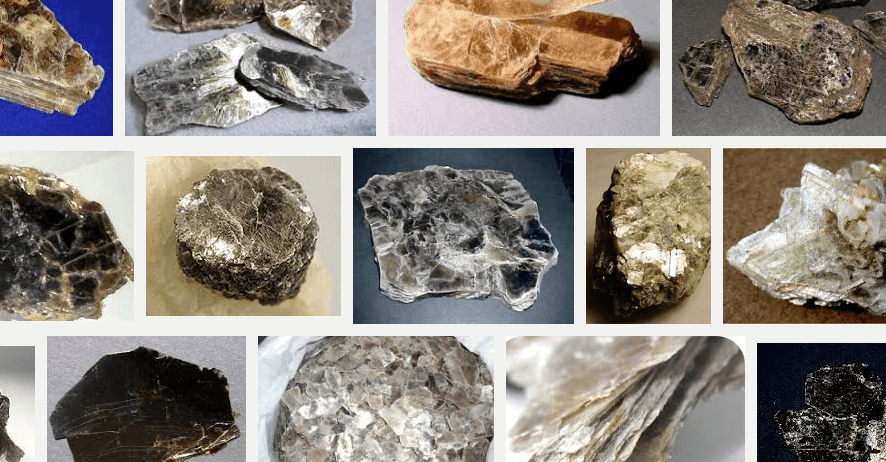

Mica type minerals make a group of silicates of alumina, with potash, iron, magnesia; characterized by easy cleavage into thin, flexible, elastic sheets. Mica gives off water when strongly heated. Muscovite Muscovite, or white mica, (K,H) AlSiO4, is colorless, sometimes gray, brown, ruby, etc.; powder, white; luster, glassy or pearly; H = 2 to 2.5; G […]
