Where are Gold Deposits in Canada
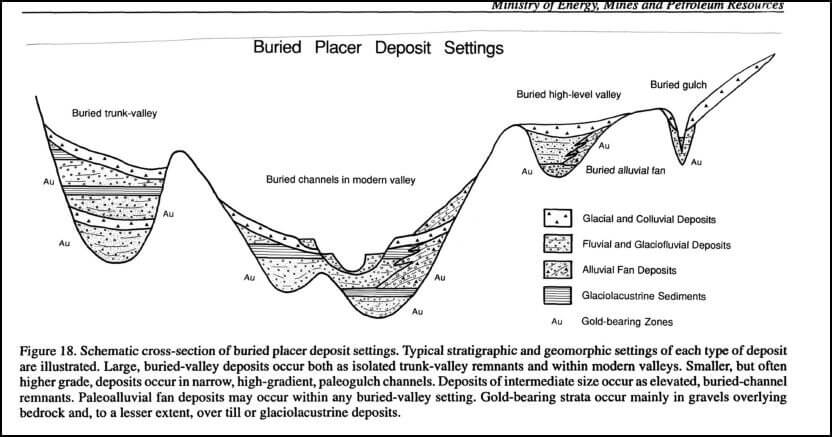
Placer Gold Placer deposits of gold are formed by the concentration of the gold from the debris of gold veins and other deposits of gold in rock. As the loose material is washed down hillsides into gullies and valleys, the gold, being six or seven times as heavy as quartz and other rock- minerals, quickly […]
Strike VS Dip Faults
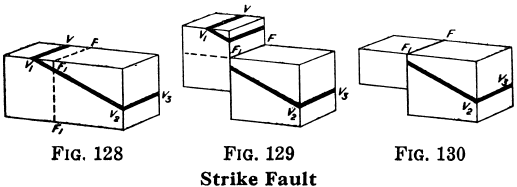
The complete study of faulting belongs to mining rather than to prospecting. But there are surface results of importance to the prospector. As explained, faulting is due to the breaking of the rock under strain; there has been displacement at the same time, so that the two sides of the break do not fit. If the […]
Sedimentary Mineral Deposits
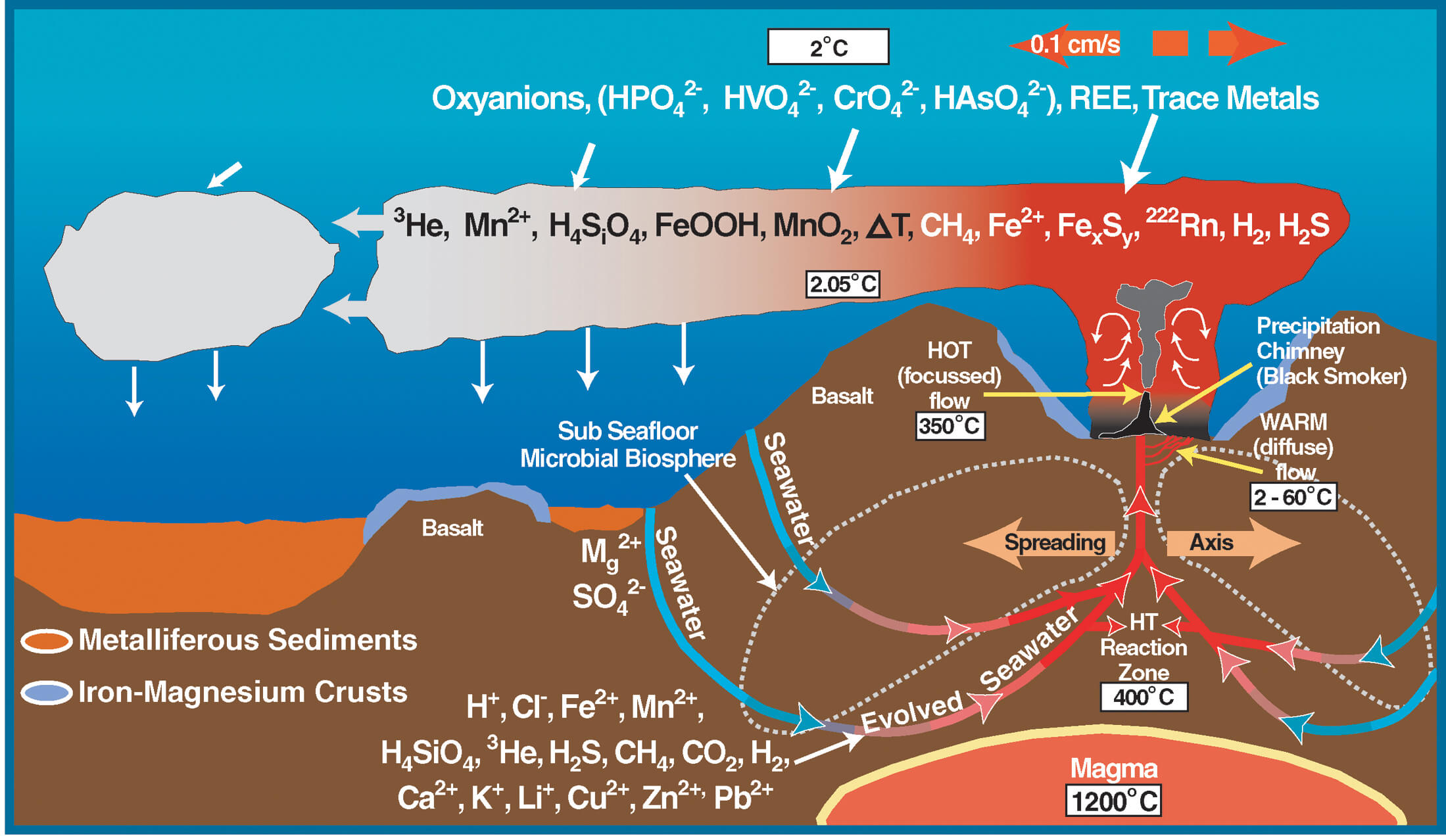
Mechanical Deposition of Sedimentary Mineral Deposits In some cases, the ore mineral, on account of its resistance to weathering and its hardness, survived the destruction of many of the rock minerals; and, during sedimentation, on account of its weight, it was sorted out from the fragments of quartz and other resistant minerals. Thus, the ore-mineral was deposited, […]
What is a Mineral Deposit by Definition
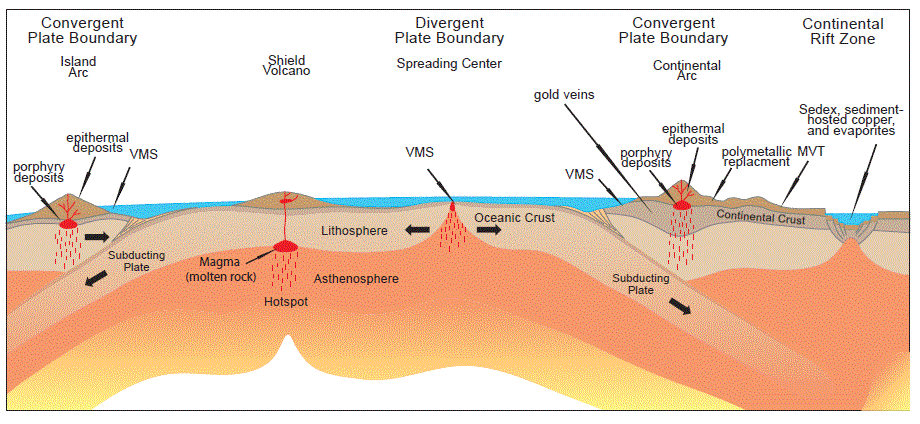
An ore is defined as a mineral or rock from which some valuable constituent, usually a metal, can be profitably extracted. Thus hematite and magnetite are ores of iron; galena is an ore of lead; zinc blende is an ore of zinc. With the ore-mineral is more or less material of no value, called gangue; […]
List of Metamorphic Rocks
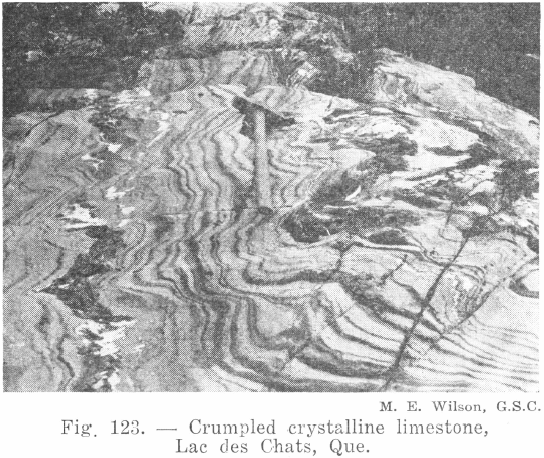
Rocks that have been formed from other rocks, sedimentary and igneous, by internal changes caused by pressure, heat, and the chemical action of the solutions and hot gases, are called metamorphic rocks and here is a list: Crystalline Limestone Crystalline Limestone is a rock that results from the crystallization of the calcite in sedimentary limestone. […]
Types of Porphyritic Rocks
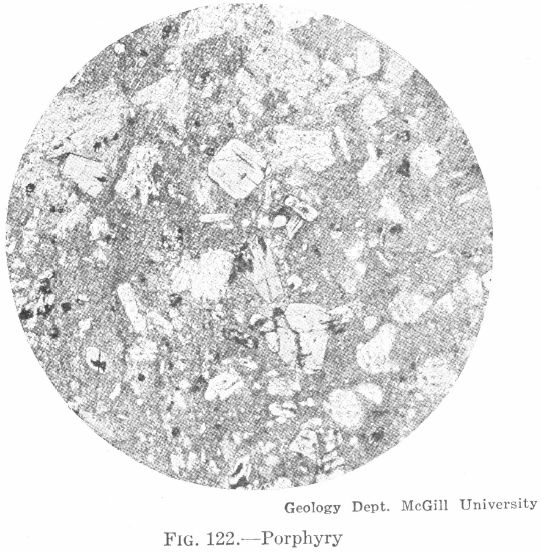

Porphyry. — This name refers to the structure, which is formed of larger crystals set in a fine-grained or glassy ground-mass. The porphyritic structure may be plainly visible, the larger crystals being easily seen (phenocrysts), or it may require the microscope to bring it out. Porphyritic structure may appear in any igneous rock, but the […]
List Volcanic Rocks
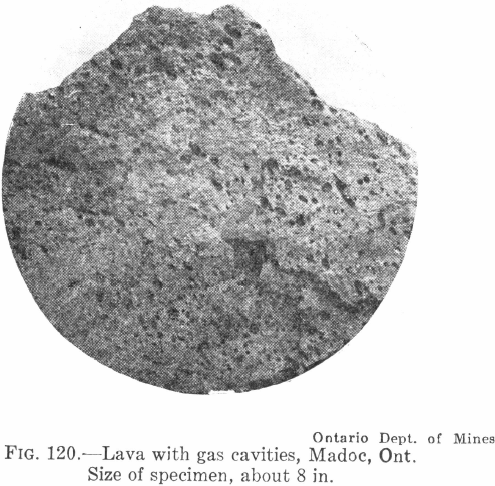

We can list volcanic rocks that are formed at or near the surface by comparatively quick cooling of lava, cannot be classified without the aid of the microscope and chemical analysis, except roughly as light-colored and dark lavas, conveniently called rhyolite, and basalt or trap. Rhyolite Rhyolite is made of light-colored acid lava flows, often called […]
Examples of Plutonic Rocks

It is strongly recommended that these descriptions and examples of plutonic rocks be read with the specimens in hand, obtainable, as noted before, from the Geological Survey. Granite Granite is a coarse or medium- grained rock, composed of quartz, an acid feldspar or two of them (orthoclase, microcline, albite), and generally mica (biotite, or muscovite, or […]
How are Different Rock Types Formed

There are three great rock-making processes, namely: sedimentation movements of the melted rock or rock magma from within outwards metamorphism, or transformation of rocks by heat, pressure, and the influence of hot liquids and gases. These will now be discussed in order; and after the description of each process, there follows an account of the […]
Classes of Rocks

Three Classes of Rocks.—The rocks are divided into three great classes: Sedimentary rocks, made of fragments of older rocks more or less water worn or ground to powder, and then spread out and deposited in layers of gravel, sand, mud, etc., to be later consolidated by pressure and natural cementing. The material may also consist […]
