Outcrops
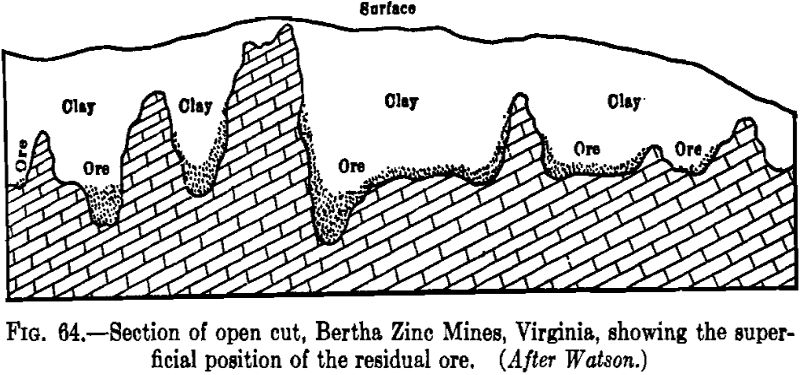
In the examination of an undeveloped prospect a decision must be arrived at from an inspection of the outcrops and the exposures in a few shallow pits. Prospects that are offered for sale rarely expose any important quantity of good ore, work having usually been stopped when the immediate exploration no longer yielded favorable results. […]
Black Sand Minerals in Gold Placer Deposit
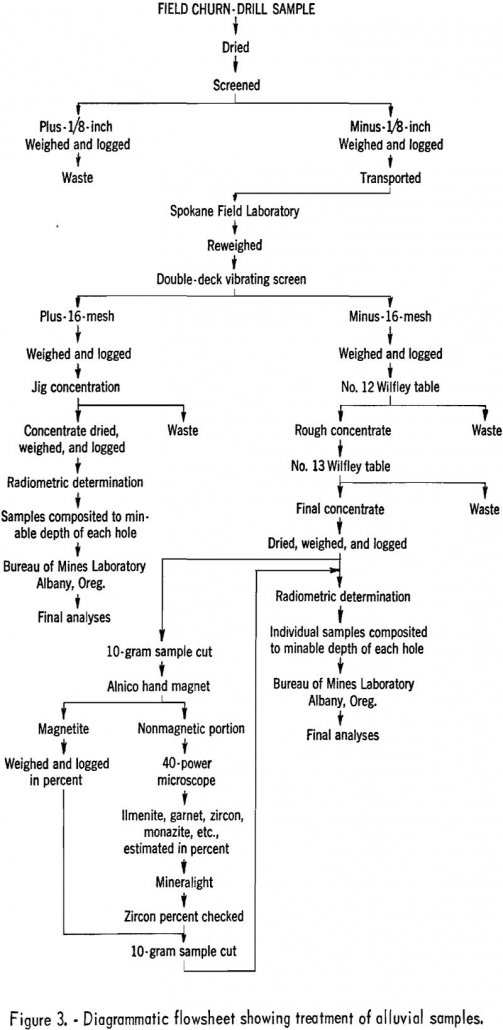
This report describes work done as part of a Bureau of Mines program to appraise the titanium-mineral resources of Idaho. The work included both field reconnaissance and a spot churn-drilling program. Much general information was available, as a result of earlier work done under the Western Radioactive Minerals Exploration Program conducted between 1950 and 1954 […]
How to Sample Gold Lode Deposits
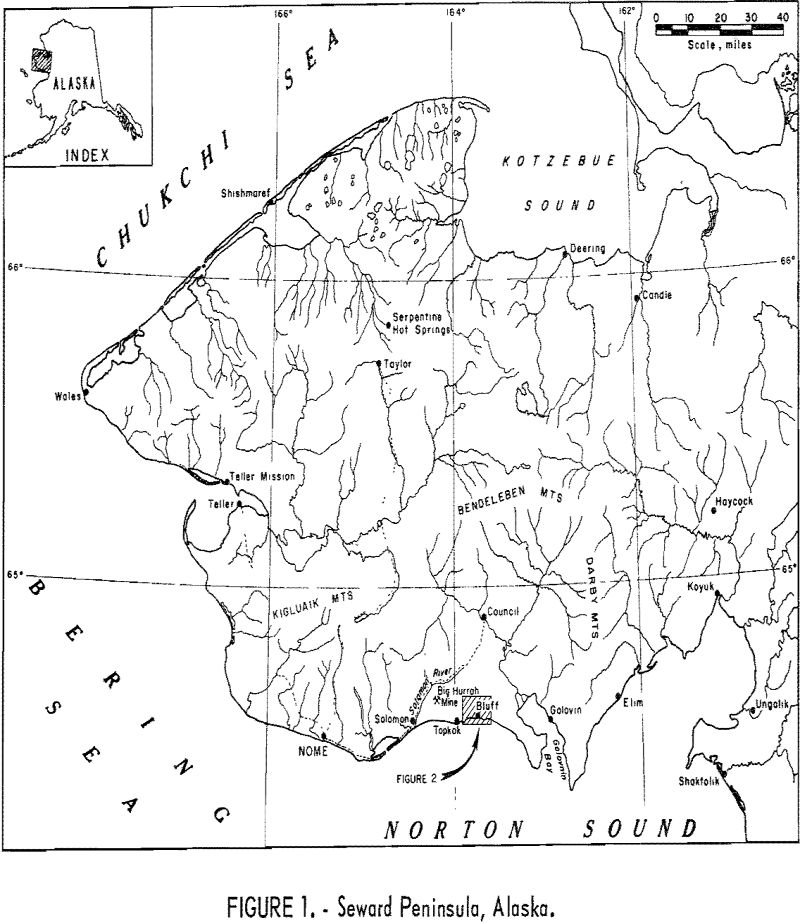
Placer and lode gold deposits near Bluff, Seward Peninsula, Alaska (fig. 1), were investigated during July and August 1966. The primary objective of this Bureau of Mines investigation was to sample a typical gold lode deposit as a basis for estimating the potential economic value of the lode sources of the productive Seward Peninsula gold […]
Applied Mining Geology
The geologic notes are taken as soon as possible after the ground is broken so that any mistake in the mining may be corrected at once, or any particularly advantageous procedure may be suggested before any useless work is done. Taking the notes underground is a comparatively simple matter, but a few necessary precautions may […]
Fractured Limestone Cores
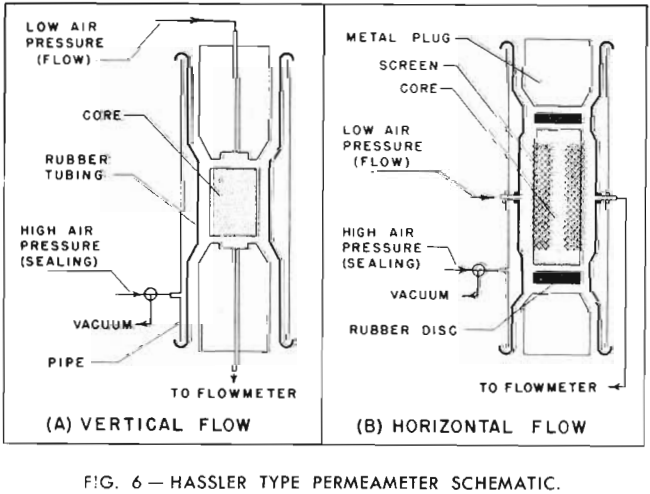
A method is outlined for the analysis of large cores, developed primarily for the purpose of obtaining reliable data on fractured or vugular limestones. Porosity and fluid saturations are determined by a modified Dean-Stark extraction after initially bringing the samples to 100 per cent liquid saturation by a vacuum-pressure method. Horizontal permeabilities on the whole […]
Weighting Core and Cuttings in Diamond Drilling
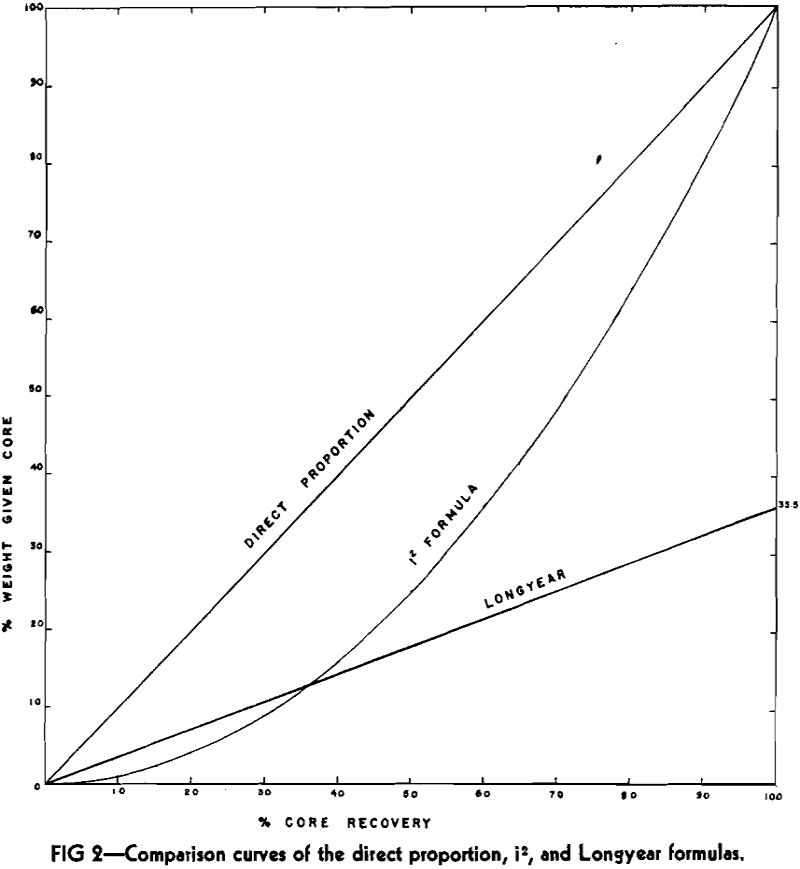
A drill hole is bored in iron ore exploration principally to test variations in rock composition with depth and is usually directed as nearly normal to the bedding of a horizon to be tested as possible. This practice has a tendency to minimize variation in composition laterally which in any event is not likely to […]
Laboratory Measurement of Relative Permeability
This paper presents the results of laboratory measurements of relative permeabilities to oil and gas on small core samples of reservoir rock by five methods, and describes the influences of such factors as boundary effect, hysteresis, and rate upon these measurements. The five methods used were the “Penn State,” the “single core dynamic,” the “gas […]
Geology Silver Lead Zinc Deposits
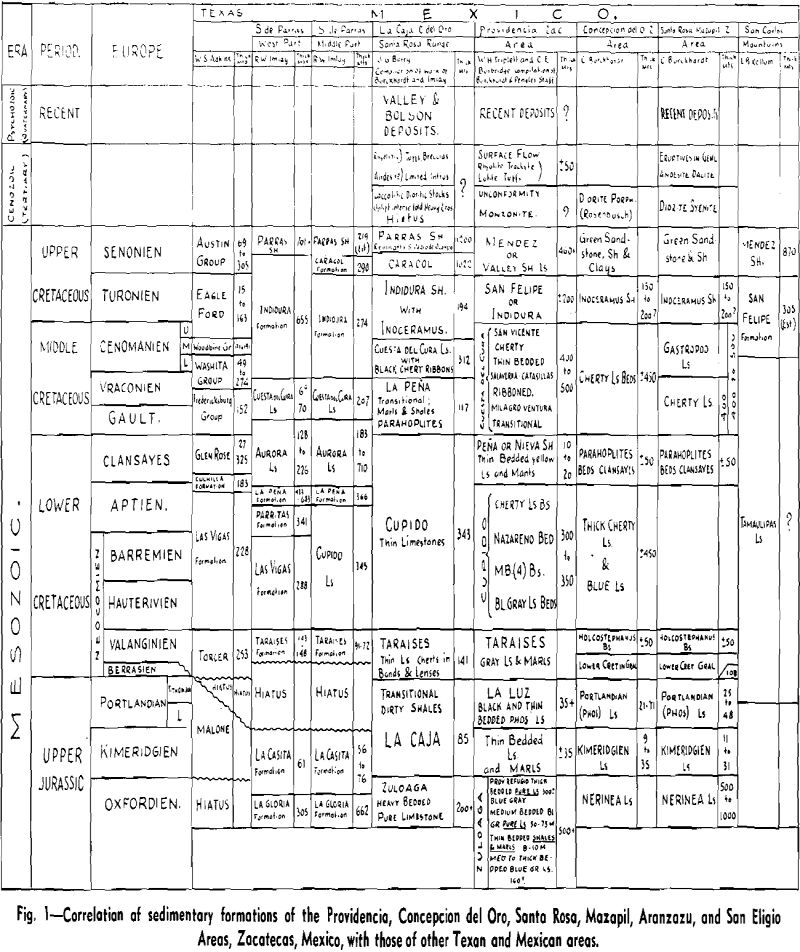
The Avalos unit of the Compania Minera de Penoles, S. A., operates the Alicante, Bonanza, Providencia, Albarradon, San Eligio, Nazareno, Leona, Salaverna, and Santiago mines situated between Avalos rail-road station and Concepcion del Oro on the Coahuila and Zacatecas railroad in the State of Zacatecas, Mexico. Some of these mines are within Penoles property while […]
Pegmatites Geology
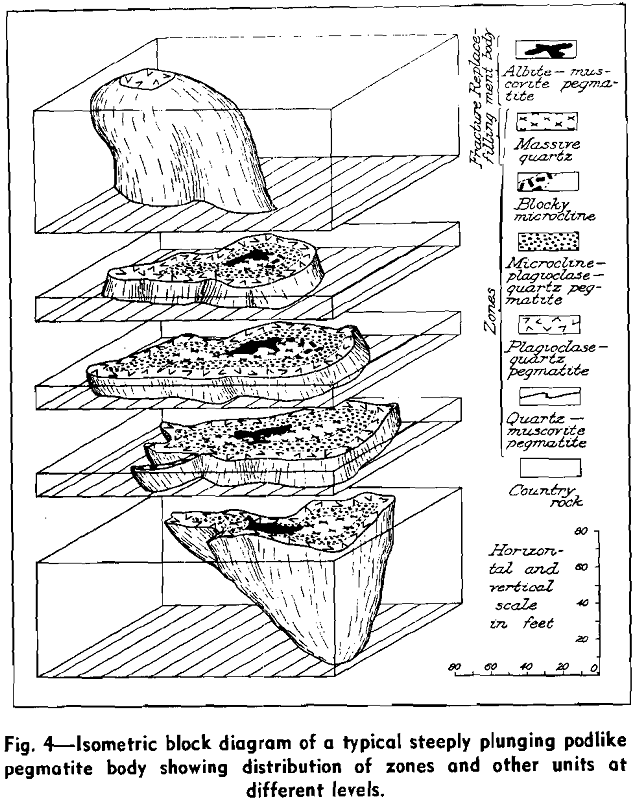
Granitic pegmatite deposits are the chief source of commercial feldspar, sheet mica, beryllium, tantalum-columbium, and lithium minerals, and certain types of kaolin. They also have yielded significant quantities of cassiterite, gems, scrap mica, molybdenite, tungsten minerals, uranium-thorium and rare-earth minerals, and zircon, either directly or as the sources of placer deposits. The output from […]
Gravity Drainage Theory
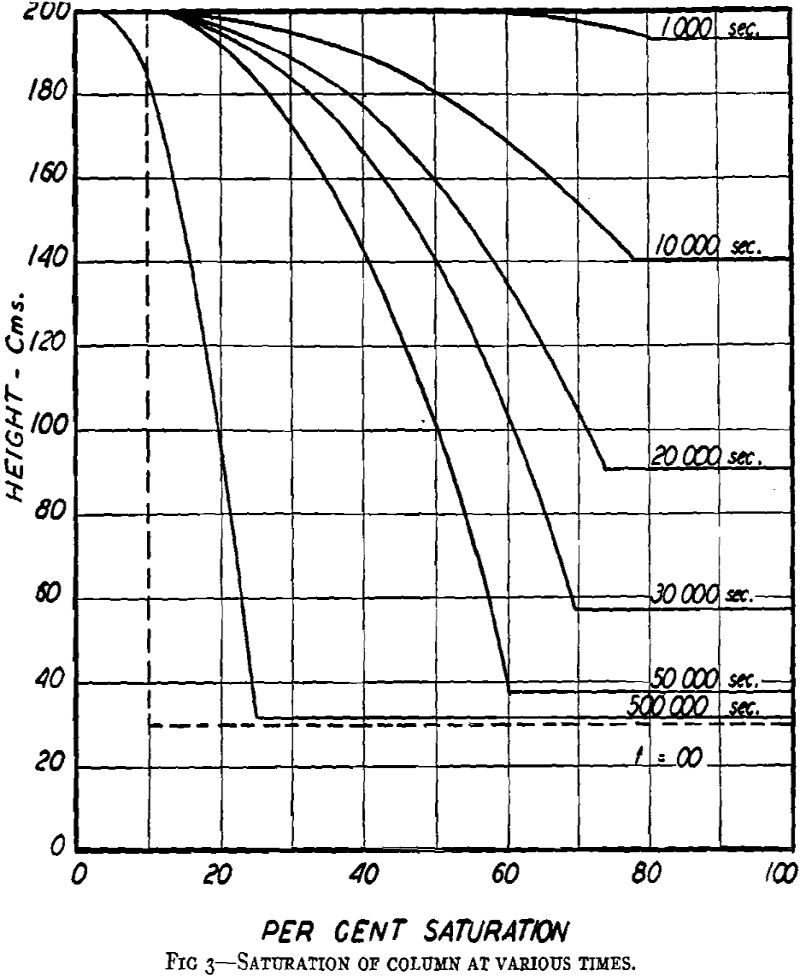
This paper presents a theory for estimating the rate of gravity drainage of a liquid out of a sand column. Account is taken of the variation in permeability to the liquid as the saturation in the upper part of the sand becomes less than 100 pct. Differential Equations of Capillary Flow The flow of liquids […]
