Segregation Process of Mixed Sulphide Copper Ore
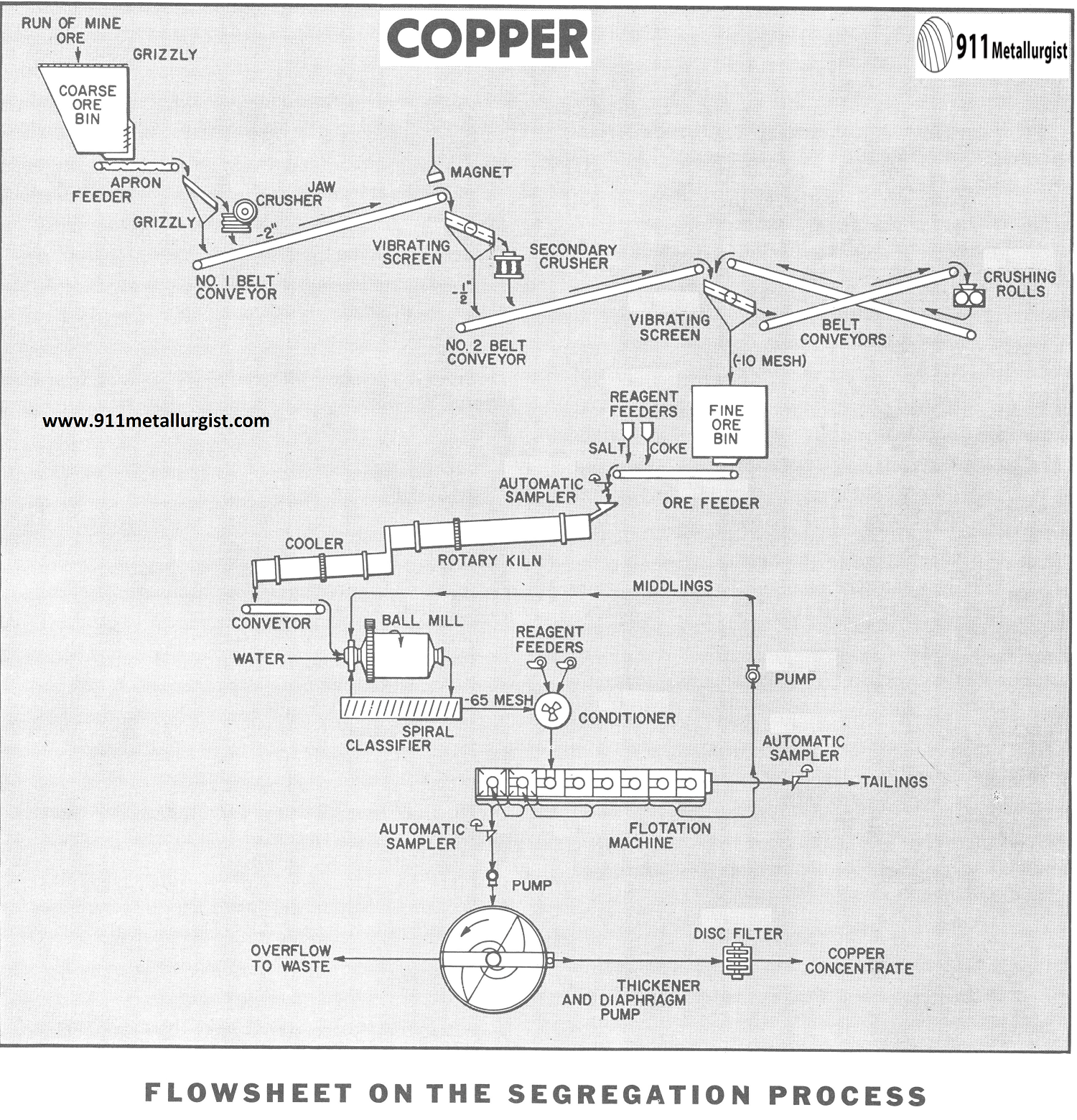
Sulphide copper ores are normally concentrated by flotation while the oxide ores undergo hydrometallurgical treatments. The mixed sulphide-oxide copper ores may be processed by combined methods such as flotation followed by leaching and precipitation of the oxidized portion, or vice-versa. Also a Leach-Precipitation-Float Process (LPF Process) has been successfully applied. However, when oxide or mixed […]
Copper Flotation
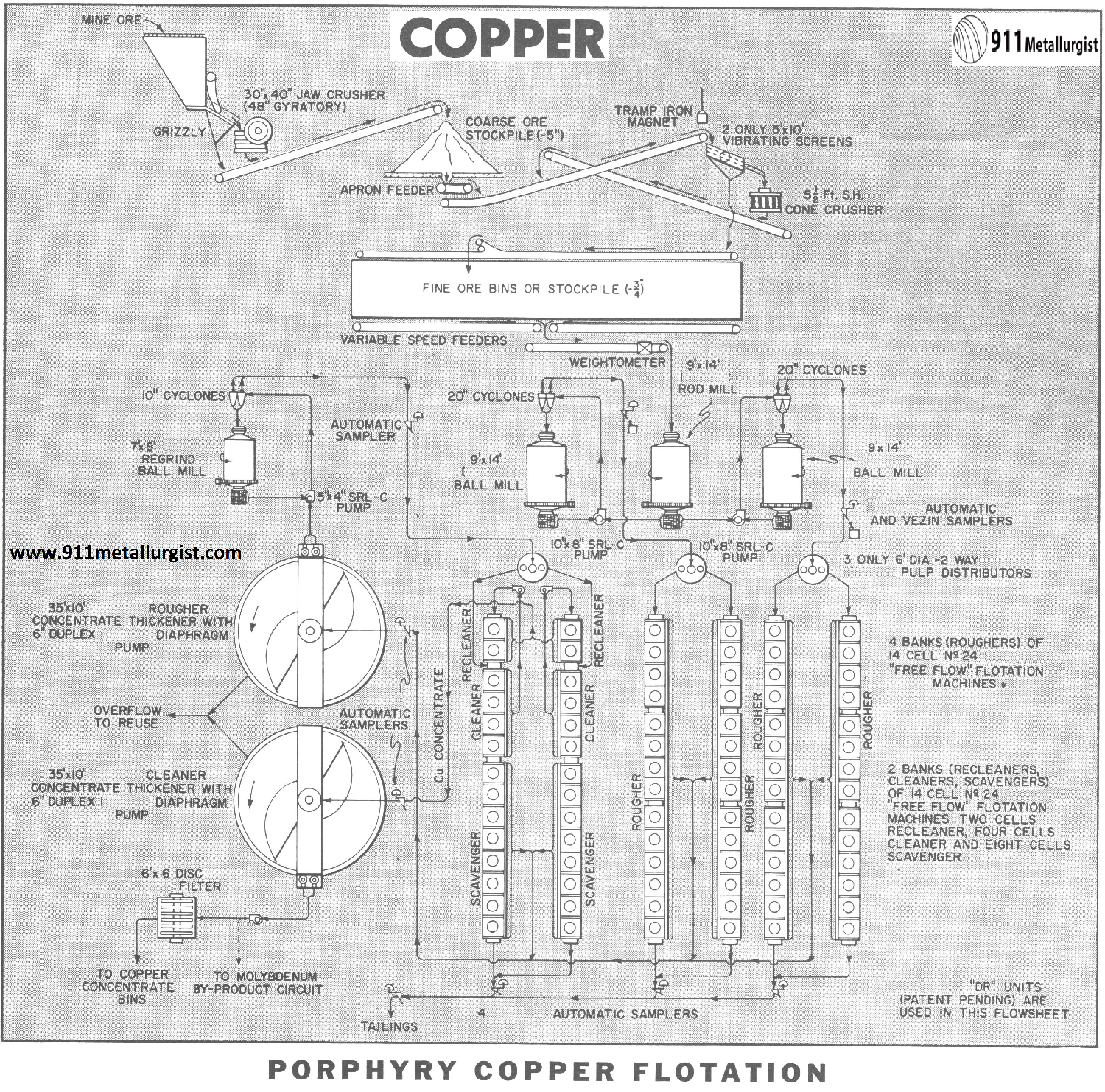
Although basic porphyry copper flotation and metallurgy has remained virtually the same for many years, the processing equipment as well as design of the mills has continually been improved to increase production while reducing operating and maintenance costs. Also, considerable attention is paid to automatic sensing devices and automatic controls in order to assure maximum […]
How Antimony is Processed by Flotation

The problem discussed in this antimony process study is limited to a concentrator capable of beneficiating 150 tons per day of antimony ore. The antimony in this study occurs as the mineral stibnite (Sb2S3) in association with small amounts of pyrite, arsenopyrite, galena and lead sulfantimonides. The gangue is composed largely of quartz but contains, in […]
Small Mineral Processing Plant Design
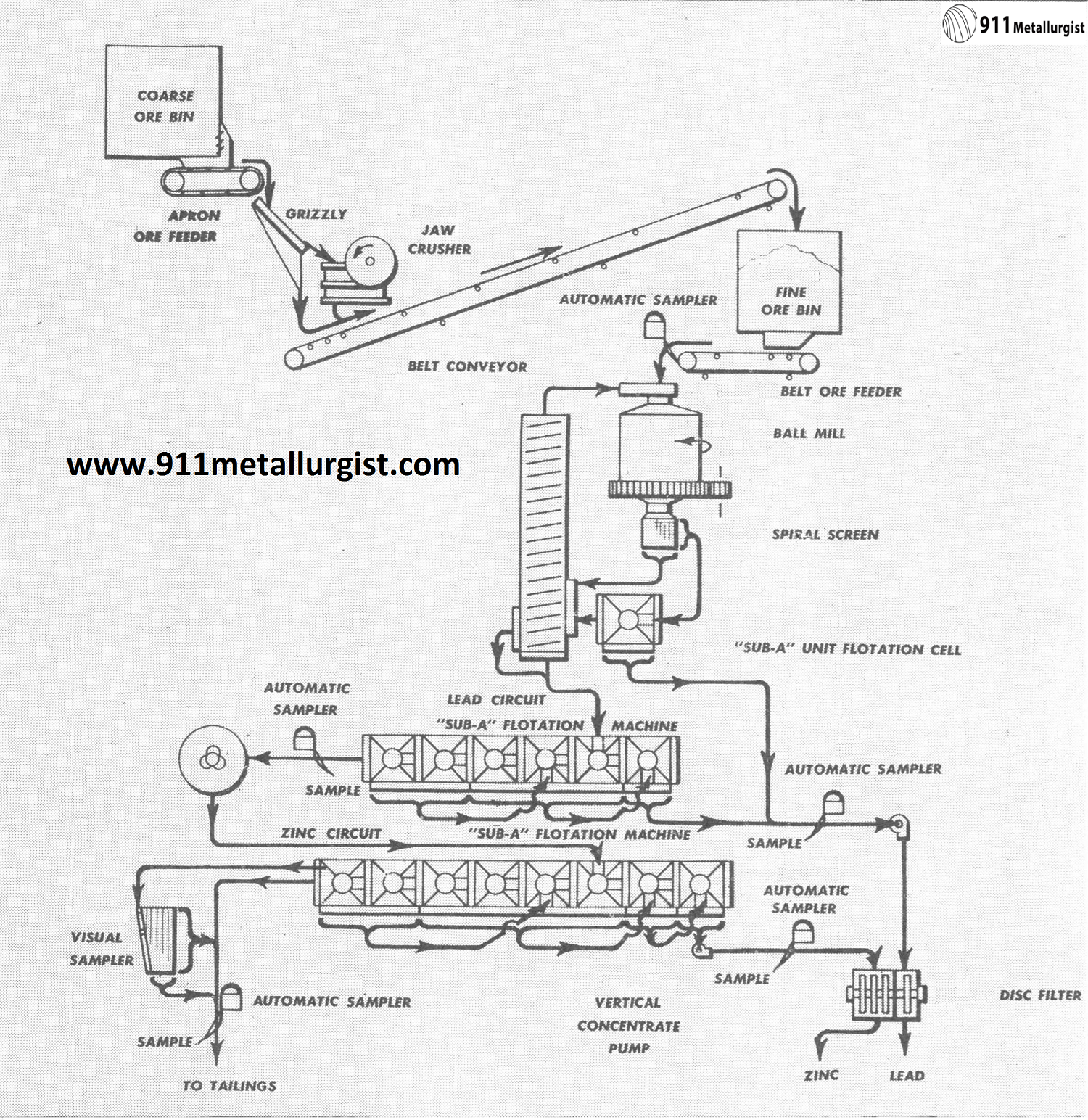
Every ore is distinctive and presents its own individual problems in profitable mineral recovery. 911Metallurgy’s experience in treating the many different ores submitted to our laboratories assures the development of the best treatment with most economical and profitable recovery. This will prevent any “weak links” and makes your mill make money. 911Metallurgy strives to develop the […]
Uranium Ore Processing Methods
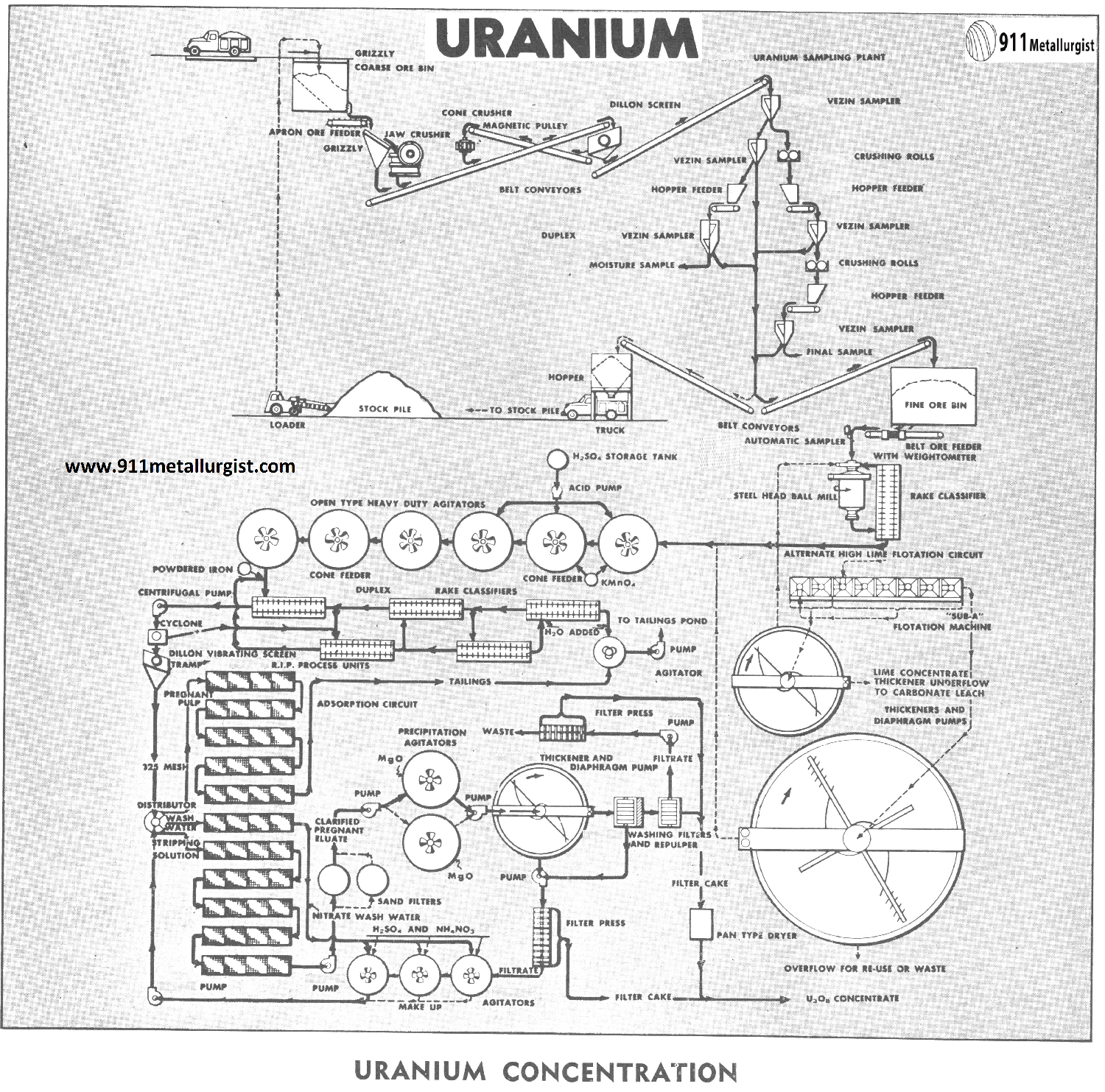
The process flowsheet of Uranium generally outlines the latest proven processes for uranium concentration known as “Resin In Pulp” more commonly referred to as RIP To date it is not applicable to ores containing vanadium, where the vanadium must be recovered. Crushing Uranium Ore Depending upon ore shipment schedules, it is desirable to operate the […]
Tungsten Metallurgy
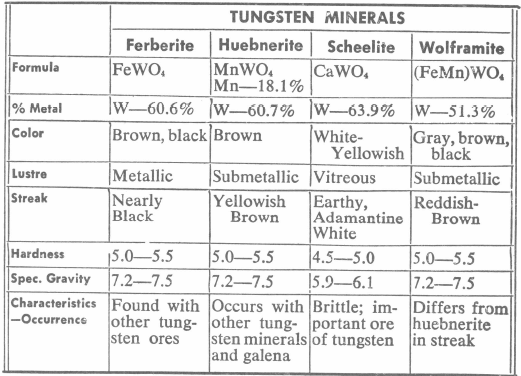
Nearly all alloy steels containing tungsten are made in the electric furnace where tungsten is introduced to the steel’s metallurgy in the form of ferro-tungsten. Ferro-tungsten, melts between 3500 and 3700 degrees F., while tungsten powder melts between 6000 and 6200 degrees F. Neither will actually melt in a steel-making furnace, but the ferro-alloy because […]
Extracting Tungsten from Wolframite Gold Ore
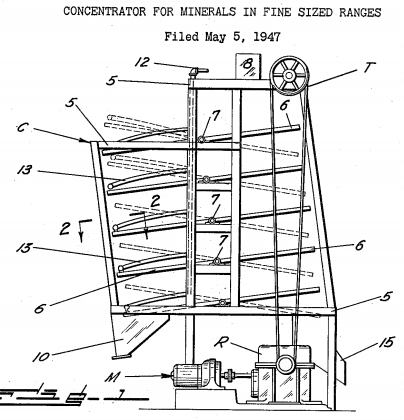
The present great demand for tungsten due to world conditions has resulted in an increase of tungsten ore dressing problems for our metallurgists. The flowsheet study shown here was recently developed for treatment of a very complex tungsten-gold ore. The flowsheet study previously shown for tungsten was devised for a simple tungsten ore free of […]
Extraction of Tungsten from Scheelite Ore

High price and ready market for acceptable tungsten concentrates present a very attractive incentive for the mining and processing of tungsten ores. Since all tungsten ores are very friable and slime easily, concentration must take place as soon as the mineral has been liberated by either crushing or grinding methods. Regardless of the care taken […]
Crushing and Grinding Wet & Sticky Ore
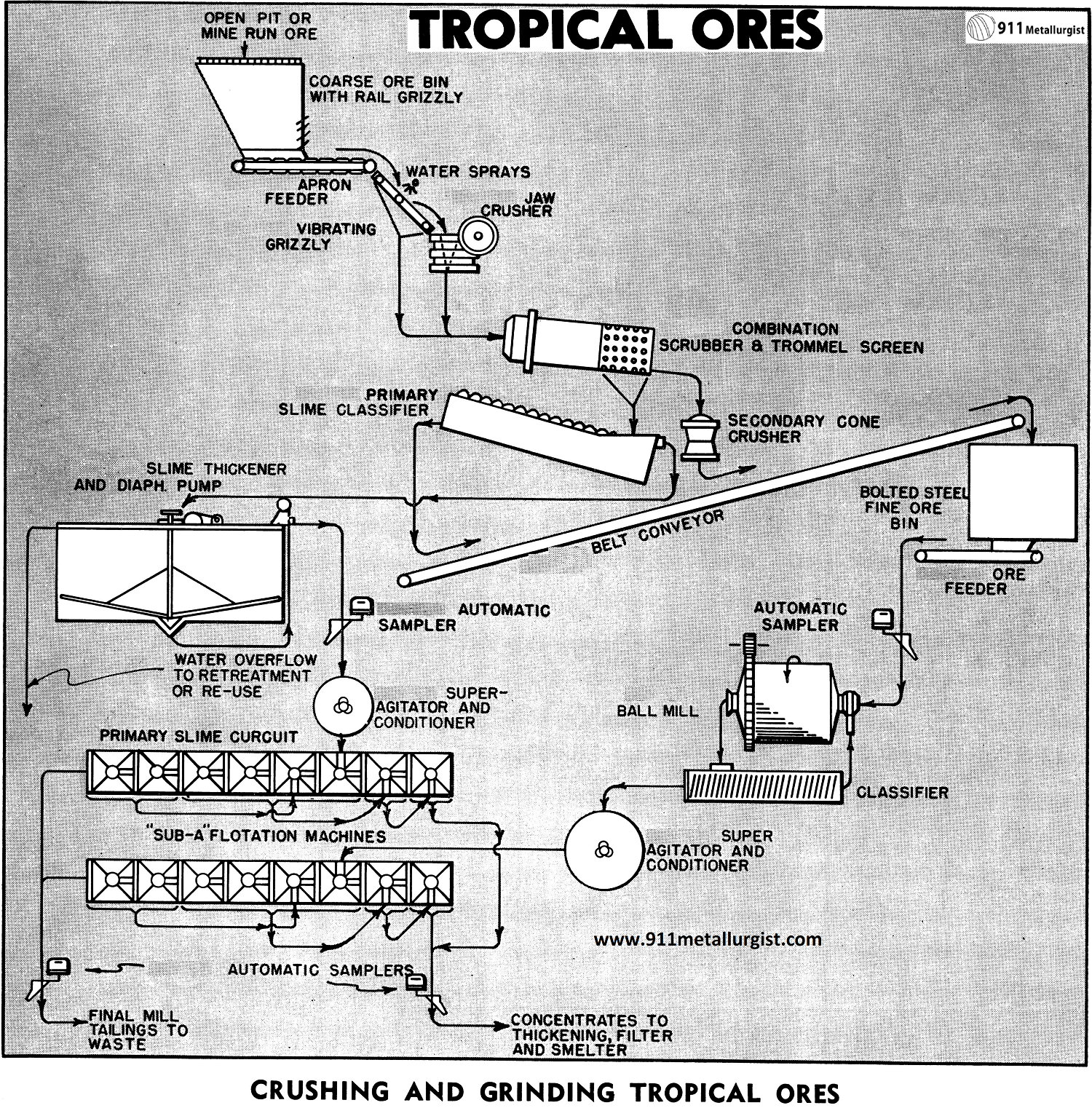
In the handling of wet, sticky ores such as encountered in tropical areas having distinct dry and rainy seasons, the crushing plant is a section of the mill which must be planned very carefully. Unless this is done, crushing becomes a constant source of trouble resulting in lost production and high milling cost. In some […]
Titanium Ore Processing and Beneficiation

To develop a flowsheet for separation of high grade titanium-rutile from ilmenite, that will meet market requirements. Rutile has a SG of 4.2, hardness 6.0 to 6.5 and is non-magnetic; while ilmenite has a SG of 4.5 to 5.0, hardness of 5.0 to 6.0, and is weakly magnetic. Both minerals are amenable to gravity concentration. Titanium, “the […]
