Soluble Metal Xanthates and their Effect on Differential Flotation
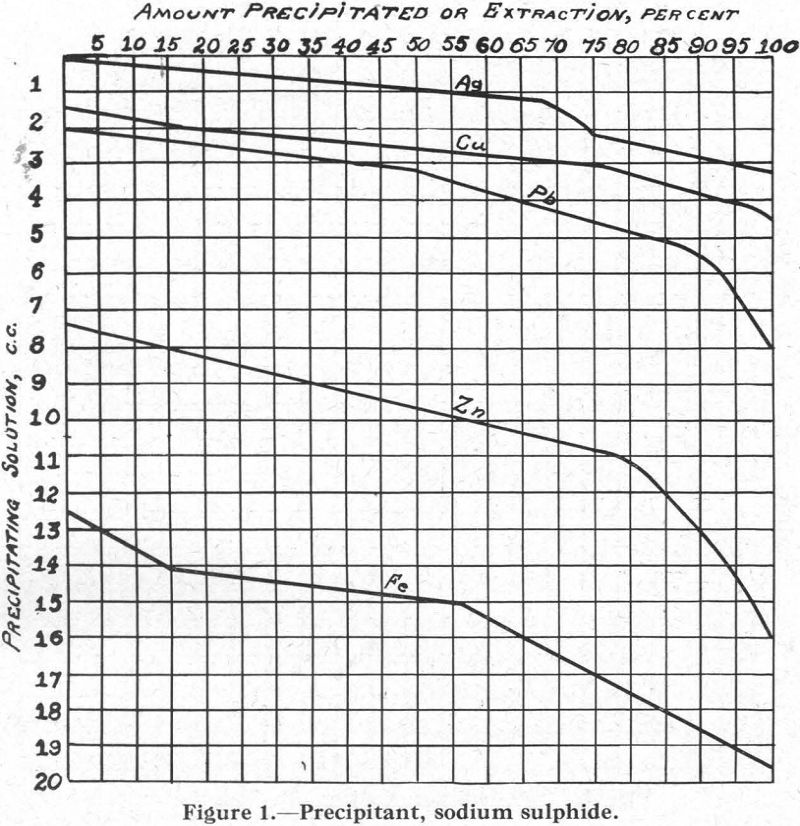
It is generally conceded by flotation men that the condition at the surface of a particle of mineral or gangue is the most important factor controlling its behaviour in a flotation cell. Much research work has been devoted to the study of the forces that are active at the surface of the particle and of […]
Fine Grain Lead Zinc Sulfides Flotation
This investigation has shown that lead and zinc sulfide minerals, in pulps containing particles all less than 9 microns in size, may be selectively recovered by froth flotation. All but one of the samples yielded lead concentrates-containing at least 57 percent Pb. Selective recovery of lead in the lead concentrate from extremely fine-grained ores was […]
Sulfide Oxide Lead Zinc Transitional Ore Treatment Processing Method
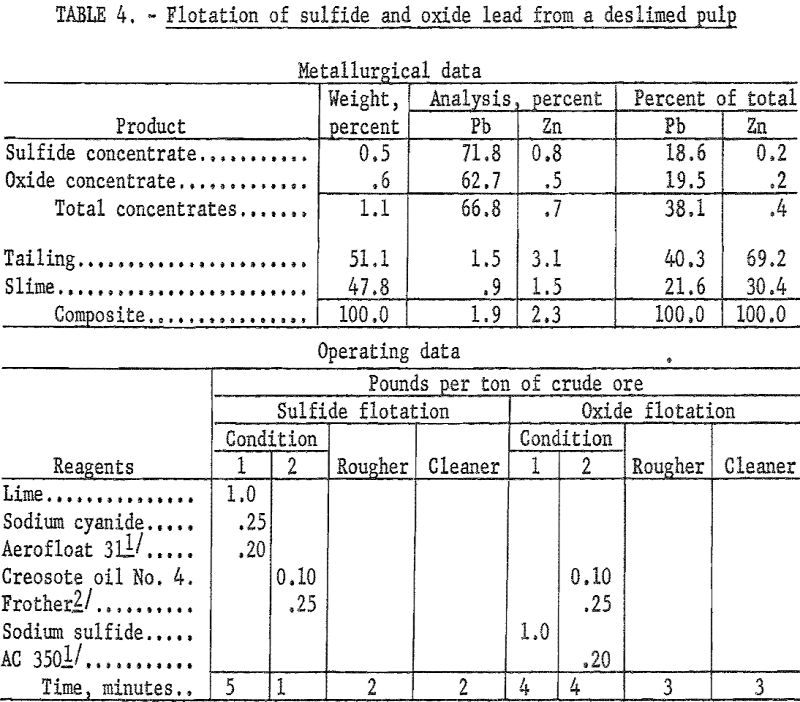
The mineral dressing research here reported is part of a continuing program by the Bureau of Mines to develop new or improved concentration processes for oxidized or partly oxidized lead and zinc ores. A sample of low-grade sulfide-oxide, lead-zinc ore from Jasper County., Mo., containing galena, cerussite, pyromorphite, hemimorphite, smithsonite, and sphalerite was concentrated by […]
Goethite Flotation
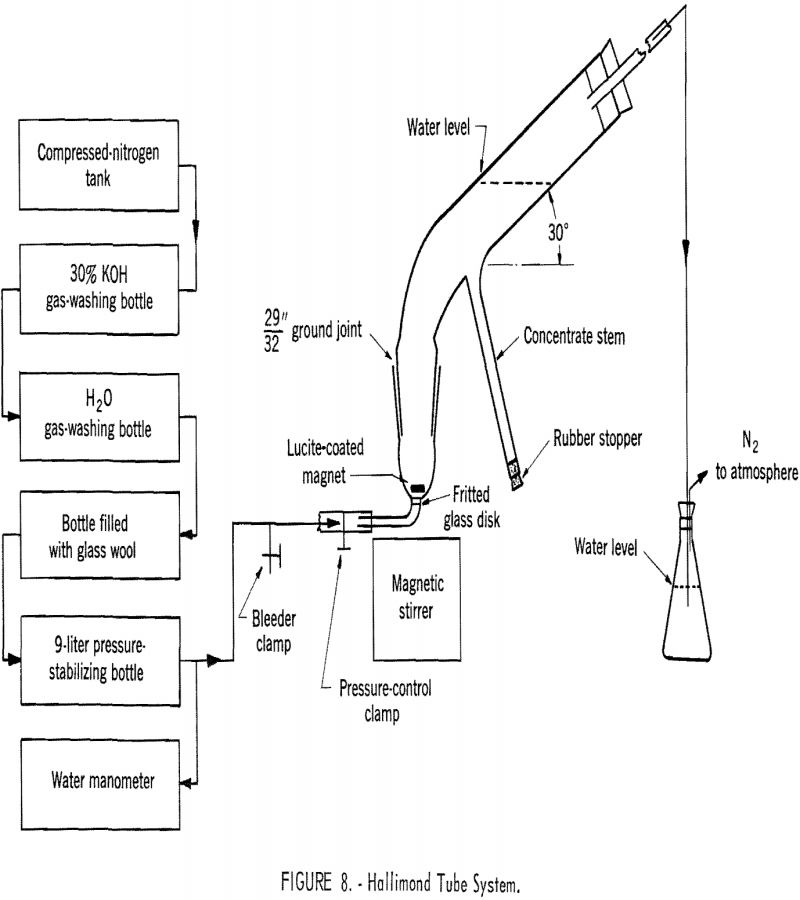
The basic flotation characteristics of goethite were determined by using vacuum flotation, contact angle measurement, and Hallimond tube flotation, and the results have been correlated with information on the electrical condition existing at the goethite-aqueous solution interface. The results have also been used to interpret the batch flotation tests made on an artificial mixture of […]
Recover Chromite by Flotation
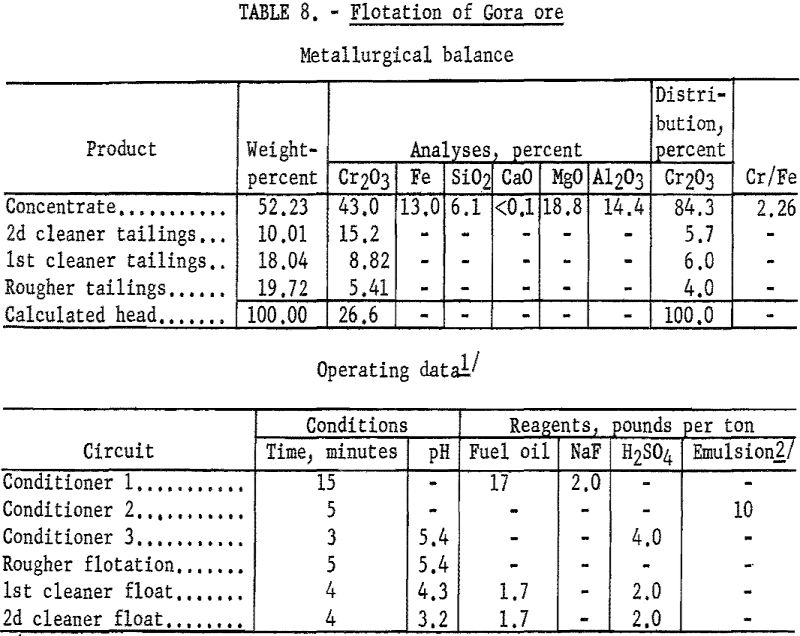
This report describes an investigation by the Bureau of Mines of flotation techniques for the recovery of chromite from fine-grained disseminated ores. Reported work on the concentration of chromiferous materials shows that flotation has been applied almost exclusively to slime-free pulps. Therefore, chromium recoveries that could be obtained by flotation were related to the amount […]
Copper Gold Sulfide Ore – Flotation & Cyanidation Tests
Grinding the ore to minus 100-mesh gave satisfactory liberation of the minerals. Standard flotation procedure with potassium ethyl xanthate, cresylic acid, and lime produced good-grade copper concentrates with over 85 percent recovery of copper and about 60 percent recoveries of gold and silver. This stop was employed in two methods of treatment developed during laboratory testing. […]
How to Measure Flotation Cell Aeration
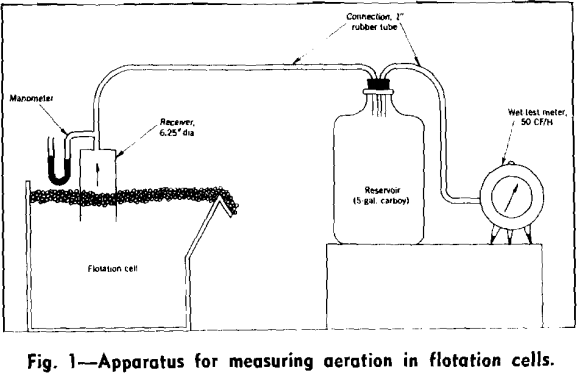
Present flotation processes depend almost entirely on the buoyant properties of air bubbles to effect separations of mineral and gangue, but there is no convenient method for measuring aeration in flotation cells. Consequently the relation between aeration and cell performance has not been definitely established. In connection with a comparative study of kerosene and froth […]
How to Recover Mercury from Cinnabar Stibnite Ore
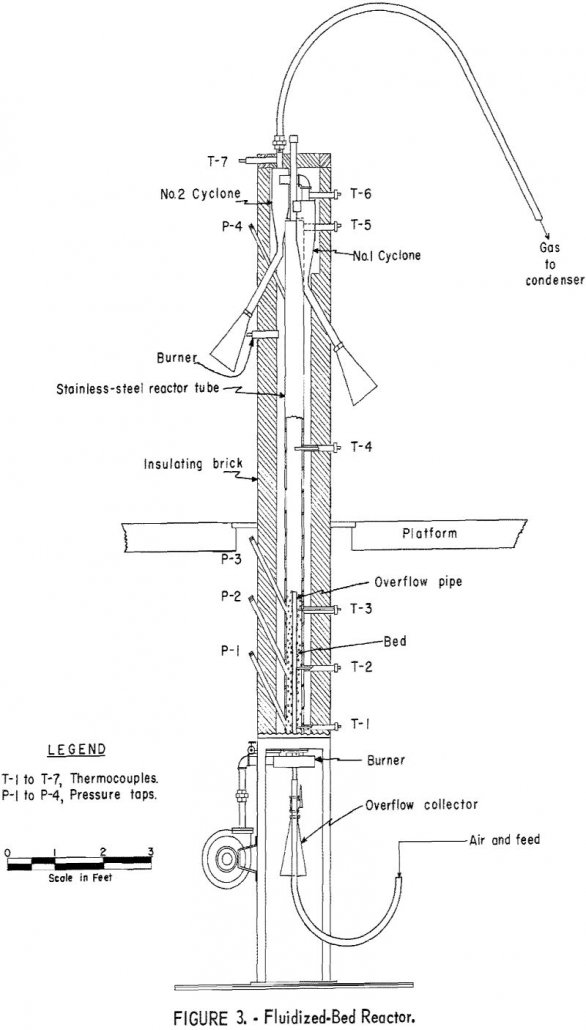
Generalized conclusions cannot be drawn from the laboratory studies about the economic feasibility of extracting mercury by a combined flotation and fluidized-bed roasting process. The 94 percent mercury recovery indicated in the laboratory compares favorably with the 90 to 95 percent recoveries usually reported by mercury-plant operators. Grinding the entire ore to liberation size, plus […]
Columbium Tantalum Flotation
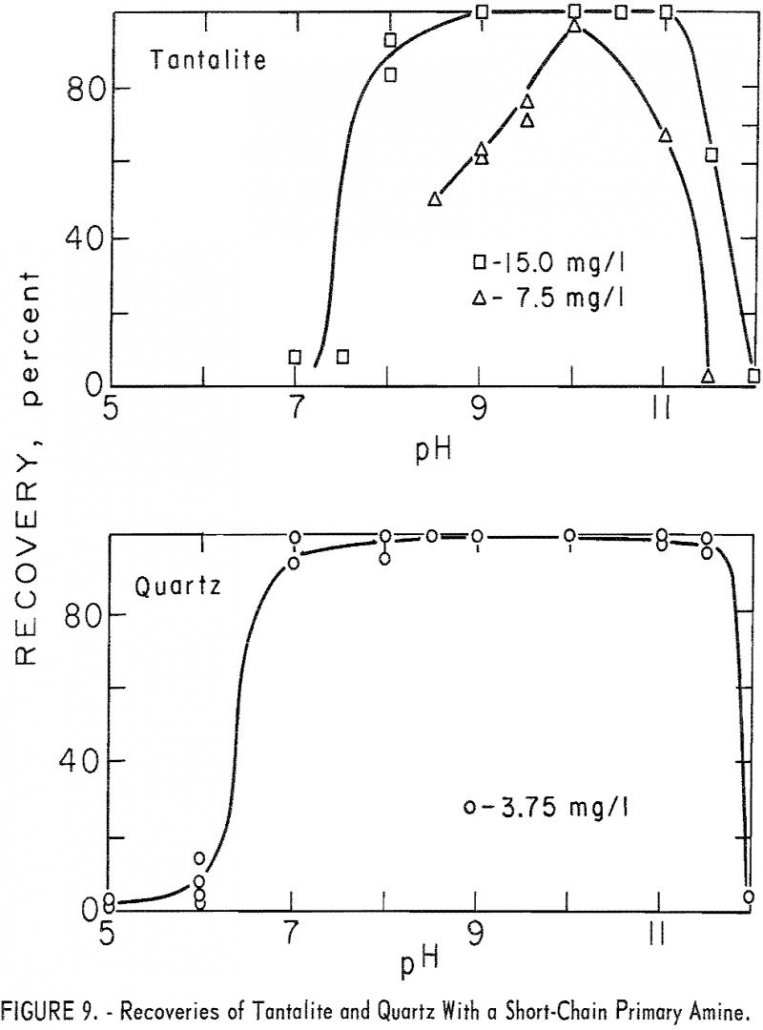
The purpose of this investigation was to determine the flotation characteristics of important columbium / tantalum ore minerals as a guide for the practical concentration of low-grade columbium ores. Placer deposits amenable to gravity concentration have been the major source of columbium; however, these deposits are limited. Therefore, the future of columbium is dependent upon […]
Chrysoberyl Flotation
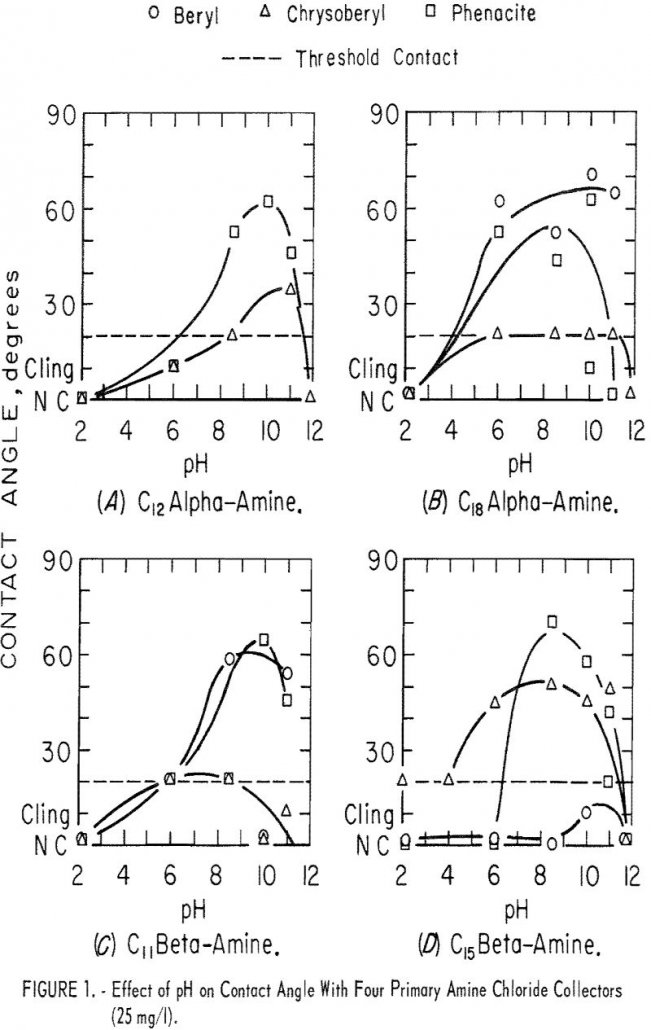
In contact-angle research, 10 of the 17 surfactants evaluated proved to be collectors for Chrysoberyl Flotation. With eight of the nine surfactants evaluated as collectors, microflotation recoveries of beryl, feldspar, and topaz were equal to or greater than recoveries of chrysoberyl. Ore-gangue mineral selectivity of all collectors evaluated, except isooctyl phosphate, will be low. Further […]
