Conceptos Básicos de Flotación de Minerales

El proceso de flotación de minerales está basado en procesos fisicoquímicos que ayudan a explicar la afinidad de algunas partículas al aire (esta característica es llamada hidrofobicidad), y también de la afinidad de otras partículas minerales por el agua (esta característica es llamada hidrofilicidad). El objetivo del proceso es tratar de obtener un producto comercial […]
Types of Anionic Collectors of Sulphides
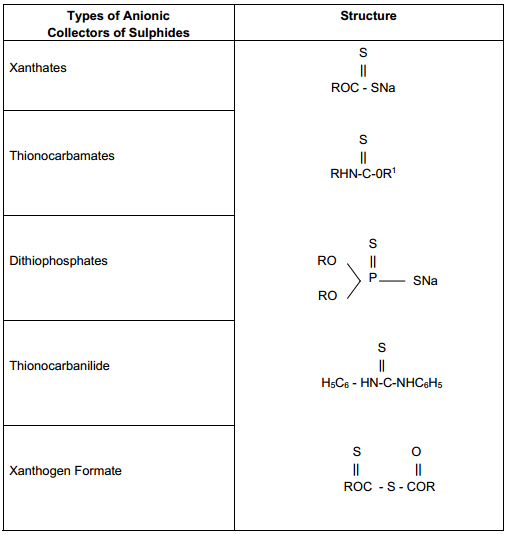
Collectors for sulphide minerals : Anionic collectors are most commonly used for sulphide minerals. By reference to the table (below) it will be note that they are all structurally similar, each having a single sulphur atom double bonded to either a carbon or phrosphorus atom, hence all of the sulphide minerals can be floated with […]
Cassiterite Flotation – Tin Oxide
The nominal size range for cassiterite flotation is between 2 and 100 microns. The top size is variable depending upon the liberation of the cassiterite particles. Cassiterite grains coarser than 100 microns are difficult to float whilst grains finer than 2 microns give selectivity problems. Hence the feed for cassiterite flotation should be reduced to […]
Froth Flotation of Tungsten Ore
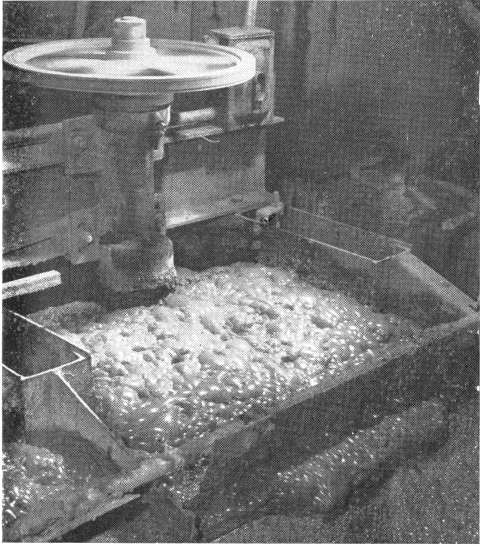

Scheelite (CaWO4) and Wolframite ((Fe,Mn)WO4) are the principal minerals of tungsten, but other important minerals include ferberite (FeWO4) and huebnerite (MnWO4) will also respond to froth flotation. The high specific gravity of these minerals makes many of these ores amenable to gravity concentration methods, however, the fine dissemination of mineral in gangue for some ores […]
Laboratory Flotation Testing
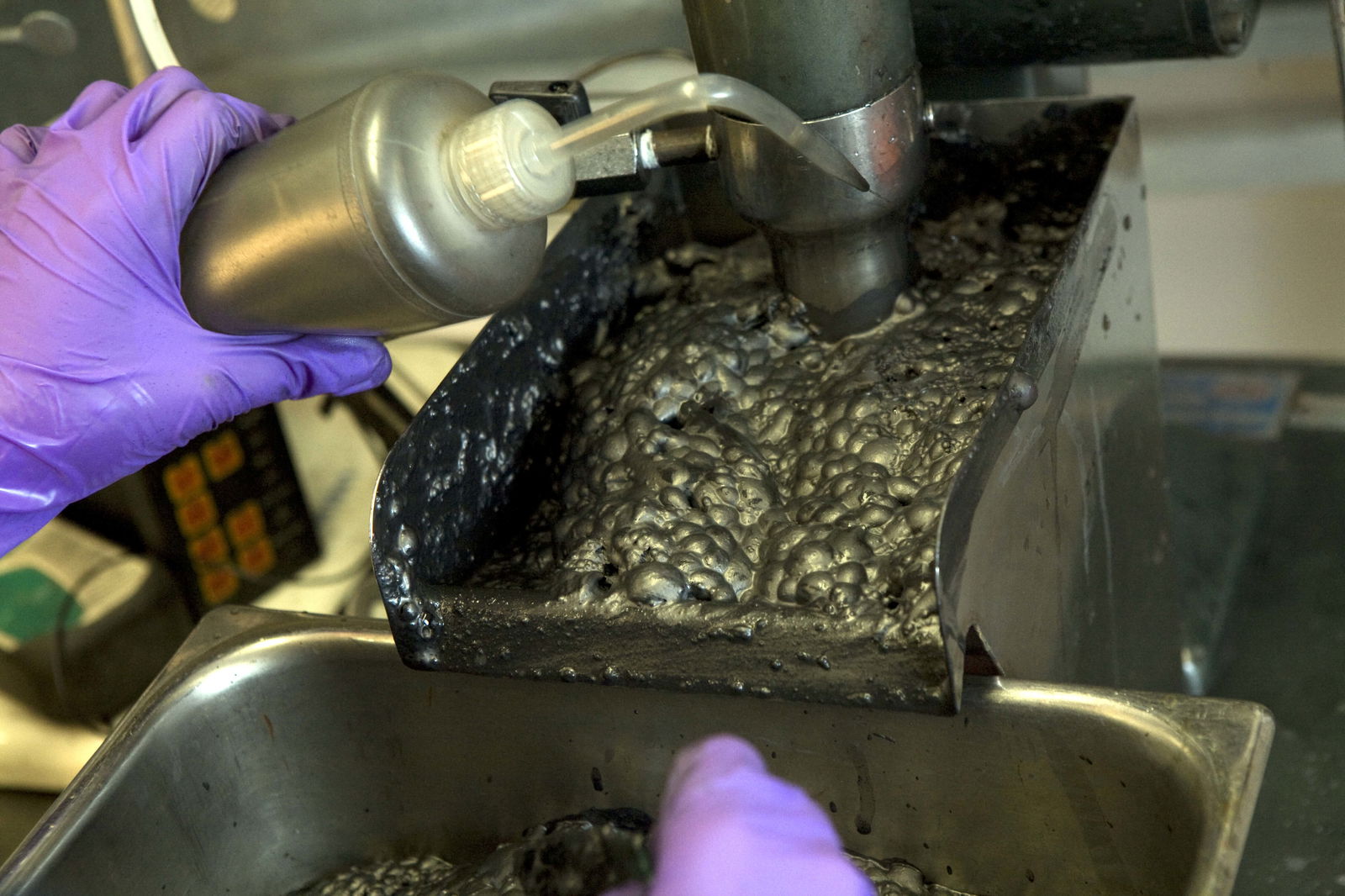

Batch Laboratory Flotation Testing starts from the 3 fundamental types of flotation processes or methods which can be classed as either: Bulk flotation Differential flotation Sequential flotation While all flotation processes are selective or differential in that one mineral or group of minerals is floated away from accompanying gangue, bulk flotation generally refers to separation […]
Agglomeration of Particles
Agglomeration is the formation of aggregate by the sticking together of feed and/or recycle materials, and it includes the formation of agglomerate nuclei. The main objective in agglomerating fines being the conversion of ores, minerals and chemicals of undesirable fineness into agglomerates characterised by a size consistency desirable for subsequent use or processing. In metallurgical […]
Froth Flotation System
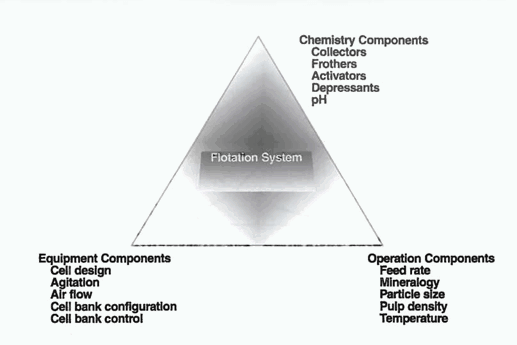
Successful industrial practice has shown that froth flotation sytem needs to be viewed both at the plant level and at the research level as a highly interactive system consisting of equipment, chemistry, and operational factors. A long history of plant tests has shown rather clearly that it is not very fruitful to work in any […]
Flotation Machines

Industrial flotation machines can be divided into four classes: mechanical pneumatic froth separation column air-lift matless As pneumatic and froth separation devices are not commonly used in industry today, no further discussion about them will be given in this module. The mechanical machine is dearly the most common type of flotation machine currently used in […]
Flotation Frothers – Frothing Agents
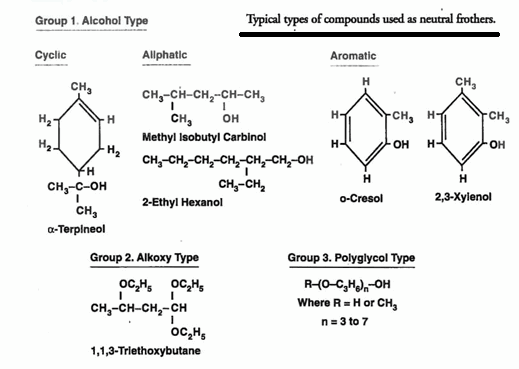
The next reagent that is added is the Flotation FROTHER. The frother strengthens the surface tension of the air that is injected into the flotation cell. As the air rises in the shape of bubbles, they come into contact with the mineral laden collector which attaches itself to the air. The bubble will continue to […]
Flotation Fundamentals
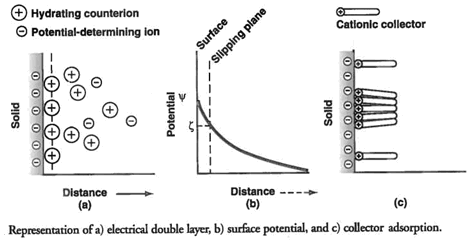
The separation of one component from another by flotation depends on the relative water-wetting ability of the surfaces of the various particle components. Many of the current chemical collectors in use are heteropolar, that is, they contain both a polar charged group and a non-polar uncharged group. When attached to a component surface, these […]
