Froth Flotation Rule of Thumb
Here is a list of Rules of Thumb often used in Froth Flotation: Clean metallic gold particles (free gold) finer than 200 microns (65 mesh) float readily with appropriate reagents. Gravity separation is desirable for larger particles. Source: Mining Chemicals Handbook (Cyanamid). When designing the flotation circuit for a proposed mill, the scale-up factor for flotation retention times […]
Chrysocolla Flotation
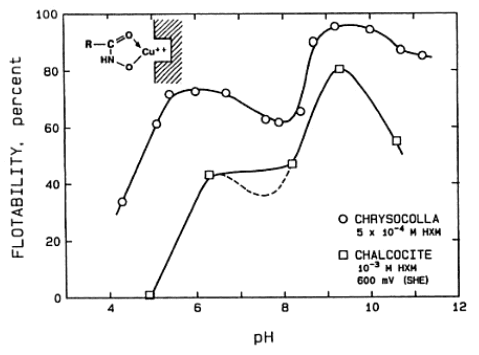
The effect of pH on the flotation response of Chrysocolla and chalcocite with potassium octyl hydroxamate as collector. The potential for the chalcocite system is slightly oxidizing. A detailed electrochemical investigation of chalcocite with a collector that does not oxidize, namely a chelating compound, potassium octyl hydroxamate shows the pH dependence of the floatability of chrysocolla (a hydrous […]
Flotation Tests
Batch and continuous flotation tests are the quickest, safest, and most economical method of determining flotation and other ore dressing problems. Best use an ore testing facilities under the direction of experienced metallurgical engineers. Tests eliminate errors and are moderate in cost. Laboratory equipment is available for complete tests covering grinding, flotation, gravity concentration, amalgamation, leaching, […]
Flotation Flowsheets: Key Types and Benefits in Mineral Processing
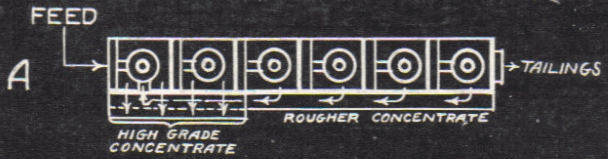
A flotation flowsheet should be as simple and flexible as possible, because changes in the ore often necessitate changes in treatment: the more flexible the flotation machine, the easier and quicker the changes can be made, not only in regard to flexibility in arrangement of cells, but also the ability to treat coarse as well as […]
Flotation Cells

More ores are treated using froth flotation cells than by any other single machines or process. Non-metallics as well as metallics now being commercially recovered include gold, silver, copper, lead, zinc, iron, manganese, nickel, cobalt, molybdenum, graphite, phosphate, fluorspar, barite, feldspar and coal. Recent flotation research indicates that any two substances physically different, but associated, […]
Flotation Cell Design
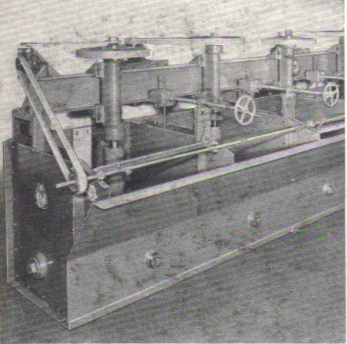
The task for the “Sub-A” Flotation Machine-Cell design is solid as it is made of heavy steel joints are electric welded both inside and out. Partition plates are furnished with gaskets and arranged for bolting to partition channels so that if necessary all of the plates can be changed at any time in the field […]
Flotation Agitators

pH Ranges for Sequential Cu Pb Zn Flotation | Separation
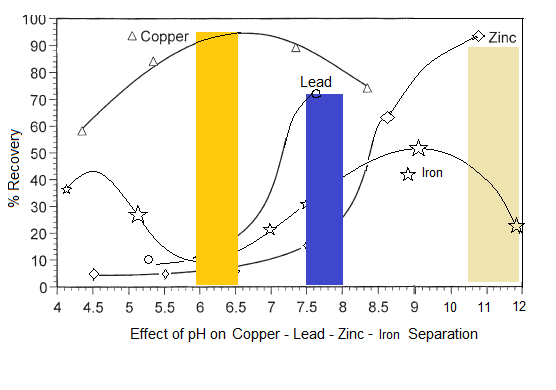
To understand froth flotation, first read that article and come back to read about sequential flotation of Copper, Lead and Zinc. Given a baseline amount of frother and collector, these curves are the approximate/relative rate of flotation recovery of Copper (Chalcopyrite/Bornite/Chalcocite/Covellite/Tennantite/Enargite/Tetrahedrite /Freibergite ), Lead (Galena) and Zinc (Sphalerite) as well as iron (pyrite/arsenopyrite) minerals VS […]
Effect of Collector and pH on Pyrite Fe Selectivity Flotation/Depression
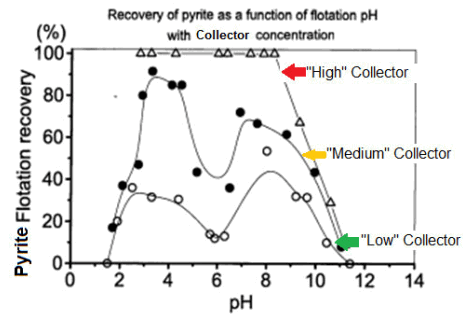
The curves below show how pH 5.5-6.5 is where conditions are optimum for iron depression. Shown on the previous chart but not these curves is this same pH 5.5-6.5 is also the optimum for Pb depression. Note on the graph how iron recovery increases as collector dosage increases. Even at optimum pH 6, over dosage […]
Determinacion pH Optimo en Flotacion
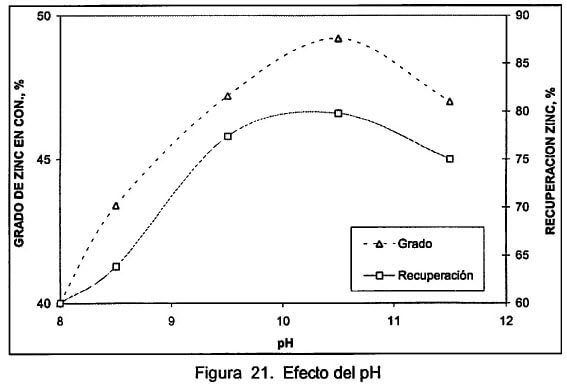
Para la determinacion de este parametro, se realizan pruebas variando el pH, adicionando cal, a continuacion se muestra la determinacion del pH el circuito de Zinc del mineral de La Negra. De la tabla anterior se establece un pH de 10.5 ya que es donde se obtiene el maximo grado y recuperacion de Zinc.
