Diamond Flotation

Experiments in the flotation of small diamonds from both kimberlite and alluvial deposits indicate the following conclusions: Water-repellent diamonds: Satisfactory flotation of —16 mesh diamonds, which are naturally water-repellent, may be accomplished using either Aerofloat 25 together with cresylic acid, or Du Pont B23 as frother together with kerosene as auxiliary oily conditioner or froth […]
Effects of Alkalinity on Lead Flotation
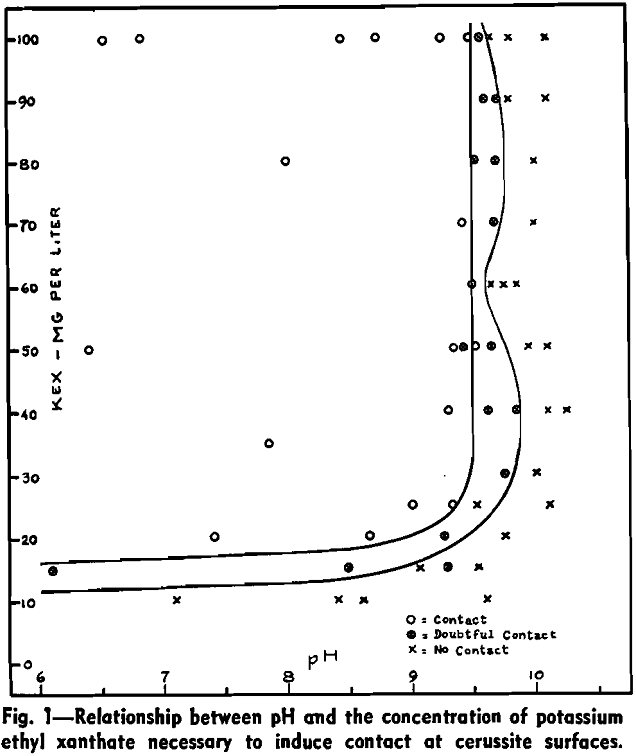
Critical pH has been defined by Wark as that pH value below which a mineral will float and above which it will not float in solutions containing a given concentration of collector but free from other depressants or activators. The relationship between mineral, collector concentration, and pH is expressed in the form of a critical […]
Pine Oil for Flotation Frother
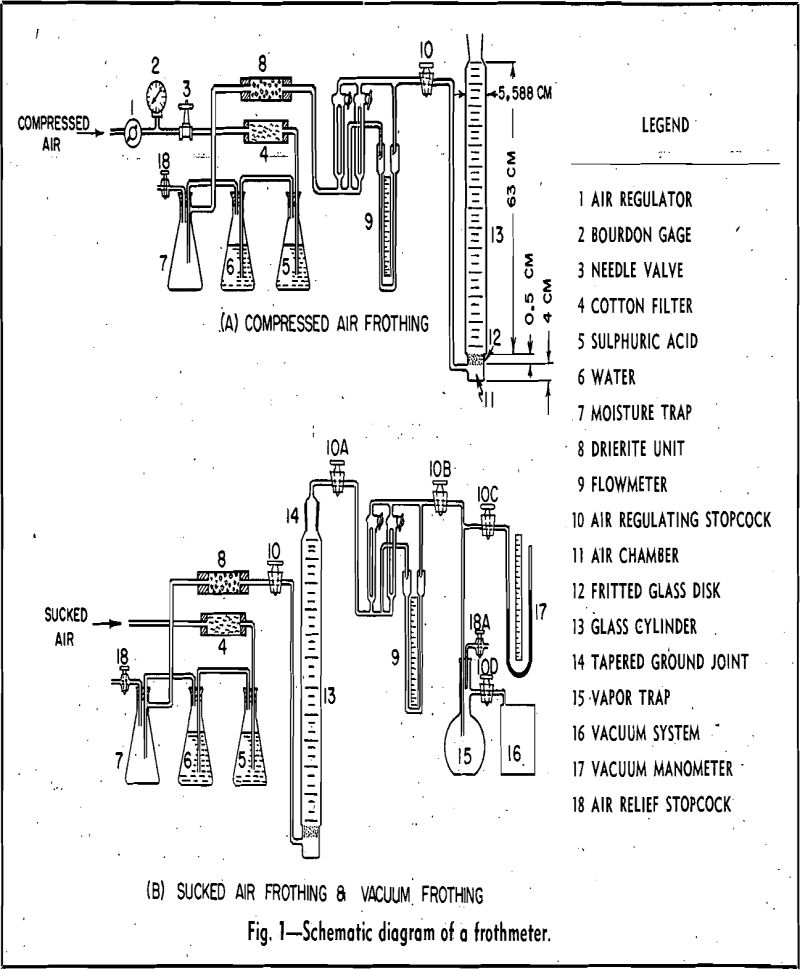
This paper presents the design and operation of a frothmeter capable of measuring the frothing characteristics of pine oils and other frothing reagents. The experimental data show that the frothability of pine oil is governed by: 1—rate of aeration, 2—time of aeration, 3—height of liquid column, 4—chemical composition of pine oil, 5—pH value of solution, […]
How to Control Flotation Reagents
Reagent control in flotation is more an art than a science. Operators vary the amount of reagents used according to the metallurgy obtained. The amount of collector may be increased, for example, if tailings losses are high and decreased if concentrate grades are low. Often control decisions are based on only one assay, such as […]
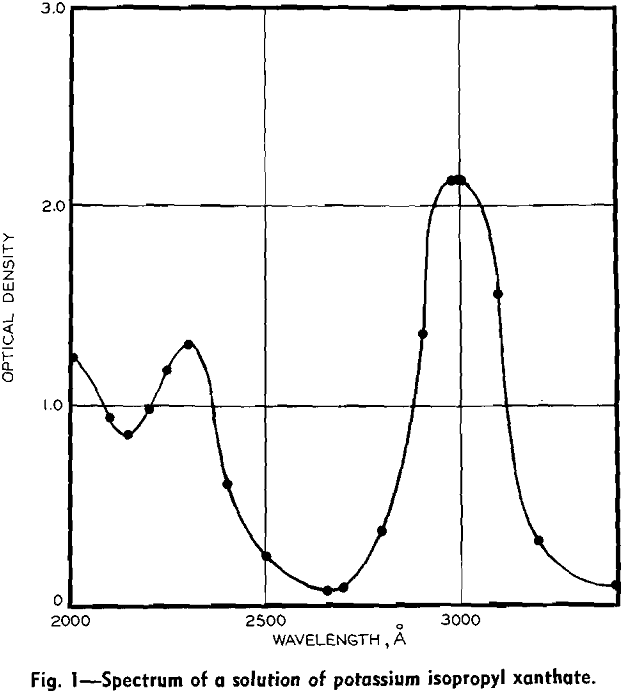
Metal Ethyl Xanthates Solubility
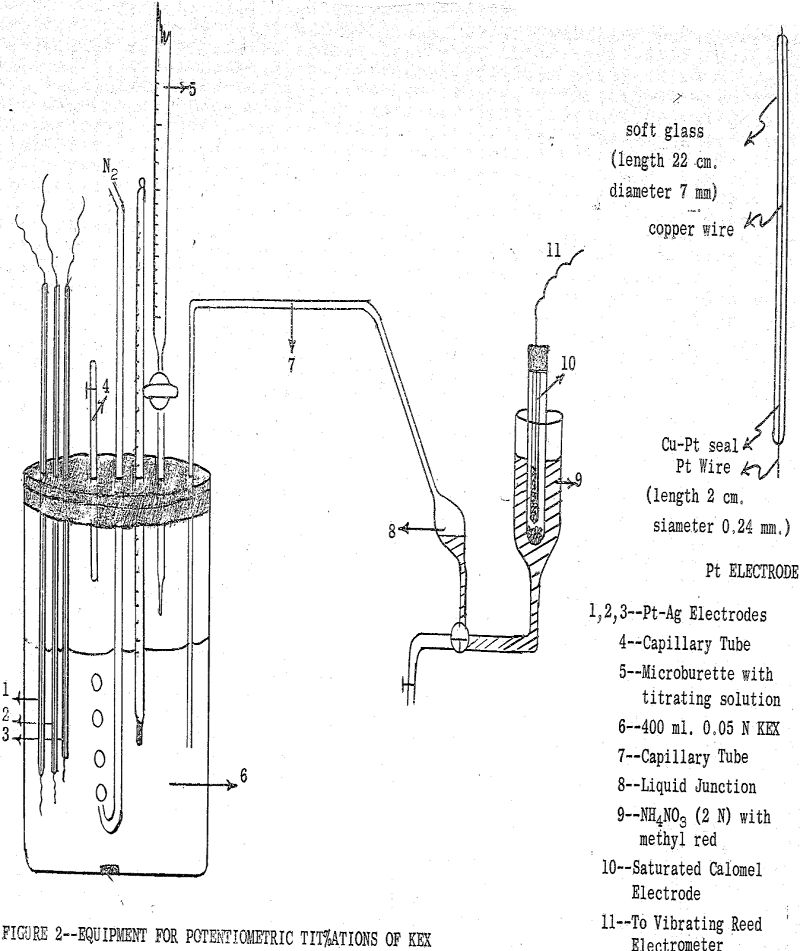
The flotation system is usually distinguished from other physical chemical systems by the importance of interactions at the solid-liquid and solid-gas interfaces. In recent years, numerous quantitative studies have been made of the distribution of common collectors between the solid and aqueous solution phase. Although in flotation the main emphasis is placed on the adsorption […]
Dithiophosphate in Selective Flotation of Lead and Zinc
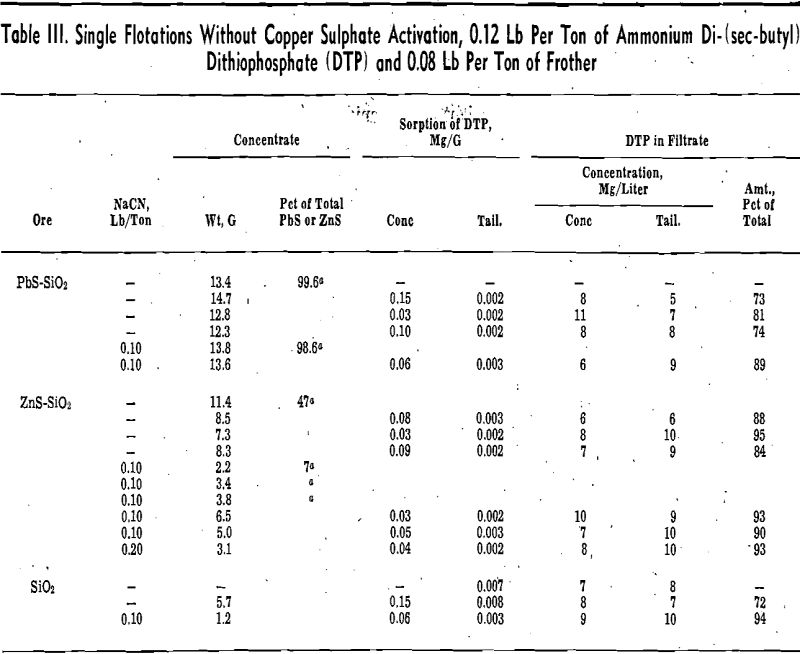
Dithiophosphate collectors are commonly used in the flotation of sulphide minerals. Studies of the interaction of a typical dithiophosphate collector with galena surfaces have been previously reported from these laboratories. These fundamental studies were carried out by employing phosphorus labeled radioactive dithiophosphate. Radioactivity determinations then could be used to measure readily and accurately the small […]
Mineral Flotation with Ultrasonically Emulsified Collecting Reagents
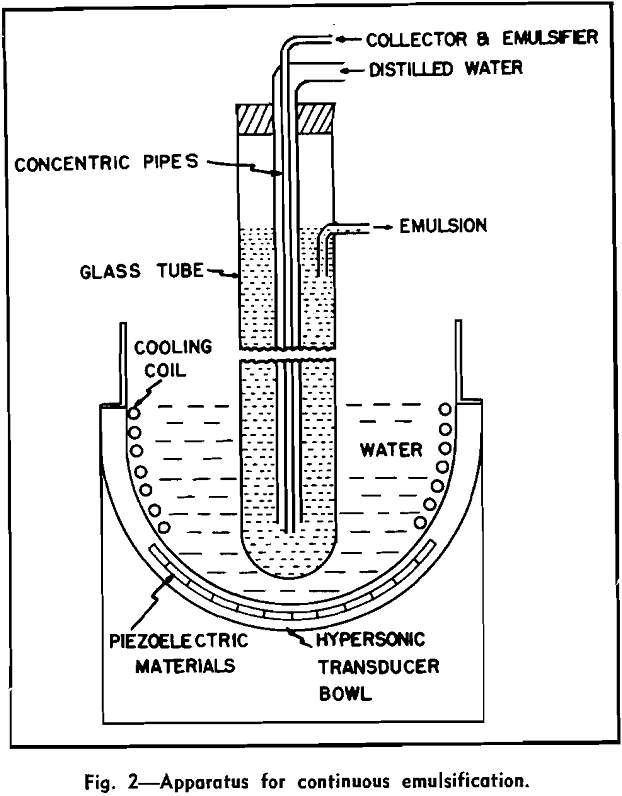
An emulsion is a two-phase system consisting of two incompletely miscible liquids, the one being dispersed as finite droplets in the other. The dispersed liquid is known as the internal or discontinuous phase, and the surrounding liquid is termed the external or continuous phase. Apparatus and Experimental Procedure: Ultrasonic emulsification was performed in three steps, although […]
Contact Angles and Flotation Rate
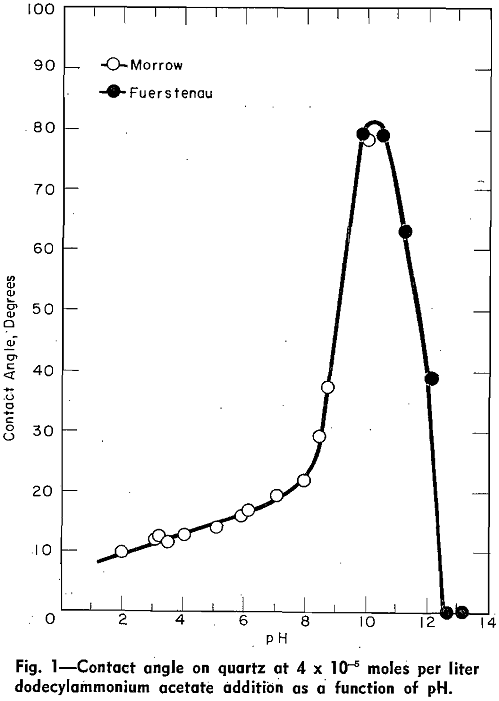
The object of this article is to point out the experimental relationship which exists among contact angle, adsorption density, zeta potential, and flotation rate data. In each of the experiments discussed in this article, the surface properties of quartz, as a function of pH, were measured in solutions to which constant quantities of dodecylammonium acetate […]
Morenci Reduction Works – Milling Practices
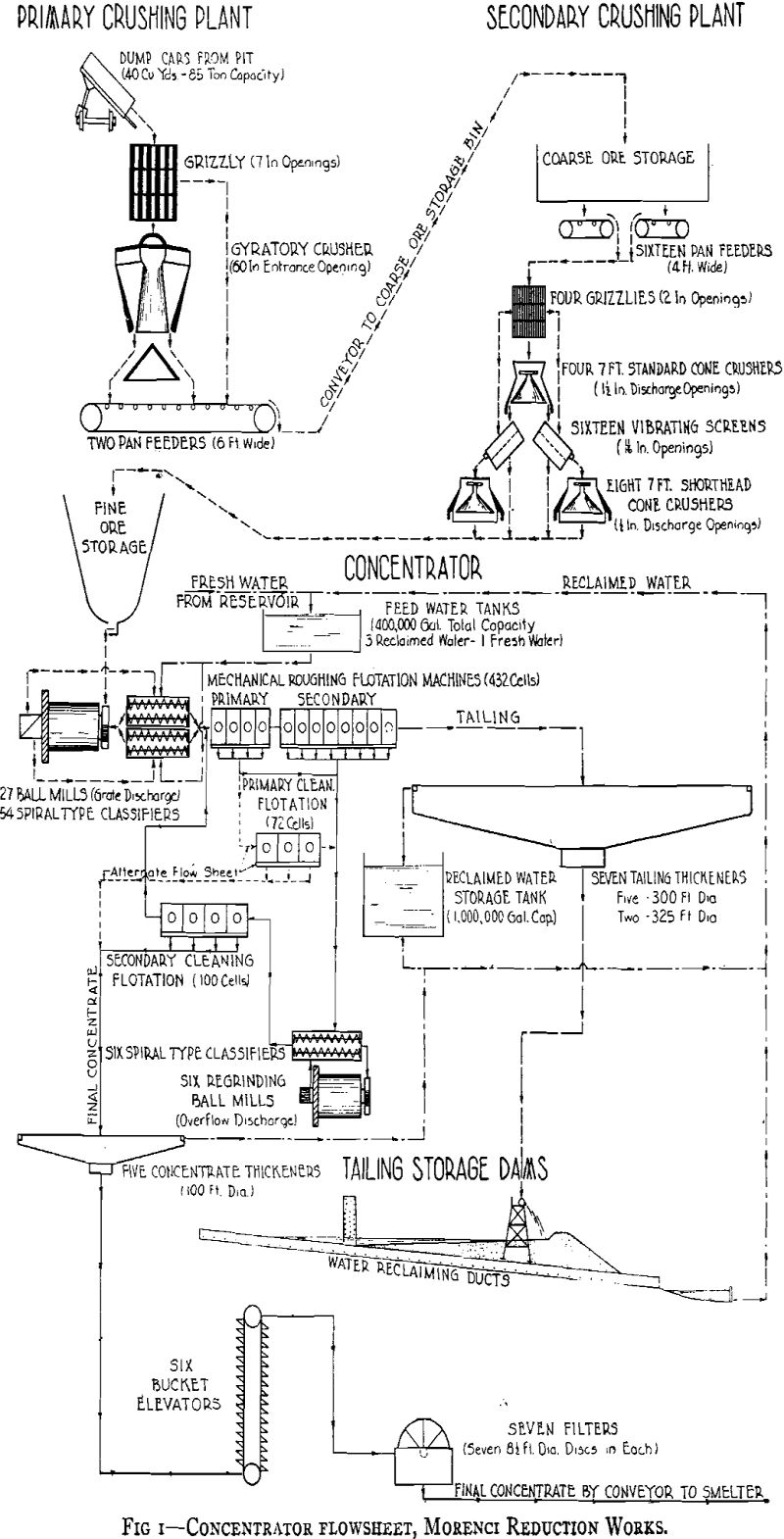
The Morenci concentrator of the Phelps Dodge Corporation is a part of the project that was completed after five years had been spent in development of the open-pit mine, equipment and process testing in the former No. 6 concentrator, and construction of the reduction works. The reduction works, of which the concentrator is a part, […]
Mining in Rhodesia

The Roan Antelope concentrator was originally designed with a nominal milling capacity of 6000 tons of copper ore per day but this was subsequently considerably exceeded. In broad outline the plant consisted of two No. 30 McCully gyratory crushers for coarse crushing, five 5½-ft Standard Symons crushers in open circuit for secondary crushing, ten No. […]
