Base Metal Ore Processing Plant & Equipment (Copper & Lead+)
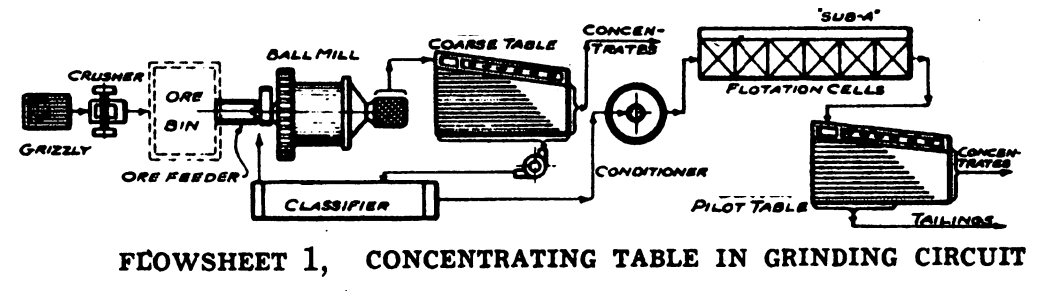
These 5 following estimates on flotation mills cover standard practice as used on base metal and non-metallic ores where the majority of values are recoverable by flotation, and where there is sufficient freed mineral in the ball mill discharge to warrant recovery by means of process Equipment like either a Unit Flash Flotation Cell, a […]
Cyanide Processing Equipment and Plant Configuration Options

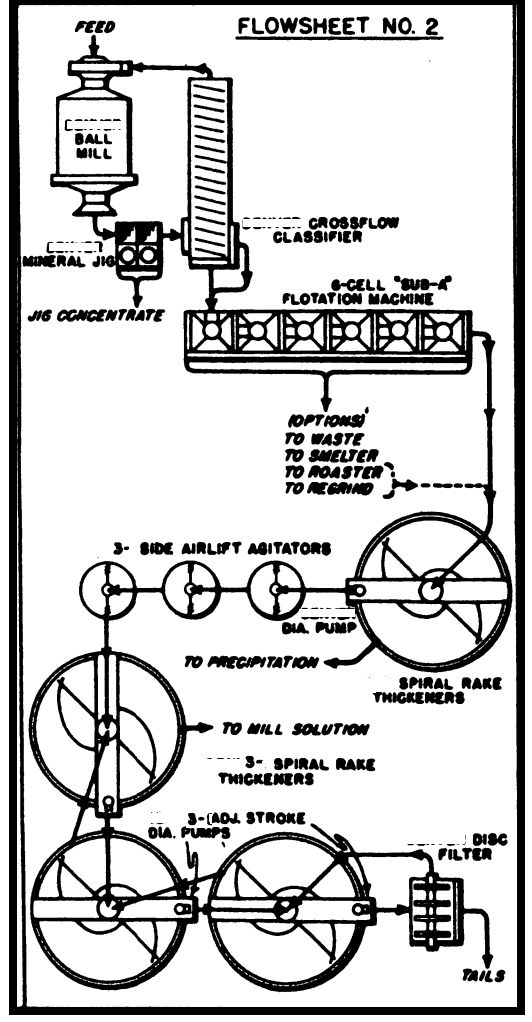
The Jig, placed between the ball mill and classifier, is one of the most valuable and affordable improvements in cyanidation in recent years and was developed by the metallurgical engineering and Mining Equipment Companies. This Mineral Jig has the marked advantage of removing a large portion of the metallic values without excessive dilution, and water […]
Gravity Recovery OR Flotation Circuits ahead of Gold Cyanide Leaching
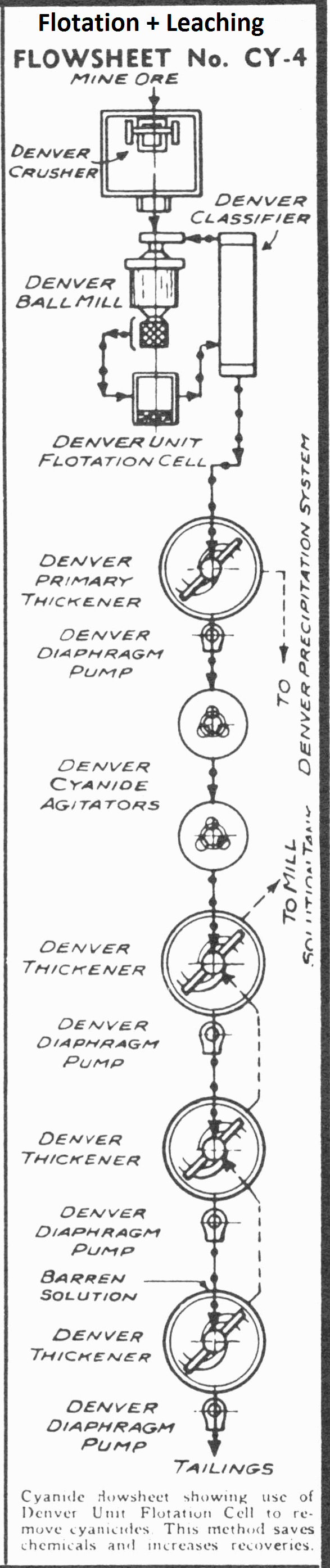
Process Flowsheet NO. CY-3 is shown one of the outstanding improvements made in cyanidation whereby the coarse metallic minerals are removed from the grinding circuit by means of the Mineral Jig. The hutch product from this jig is amalgamated with a Amalgamator or Clean-Up Pan and thus the coarse mineral values, such as metallic gold, are […]
Gold Cyanidation Circuits
The principle of dissolving gold and silver values in solutions of potassium or sodium cyanide is old and has been thoroughly carried out in practice for many years. There have been only a few changes in the chemical procedure and also few changes in the type of equipment used. The gold and silver are dissolved […]
Basic Principles & Variables Affecting Froth Flotation

The basic factors, principles and variables affecting froth flotation are enumerated in condensed form below: Ore. (a) Mineralogical character. (b) Fineness of grinding. (c) Method of grinding. Agents. (a) Principal flotation agent. (“Oil”) α Character. β Quantity. (b) Minor agent. α Character. β Quantity. Water. (a) Quantity with respect to solids, i.e. pulp thickness. (b) […]
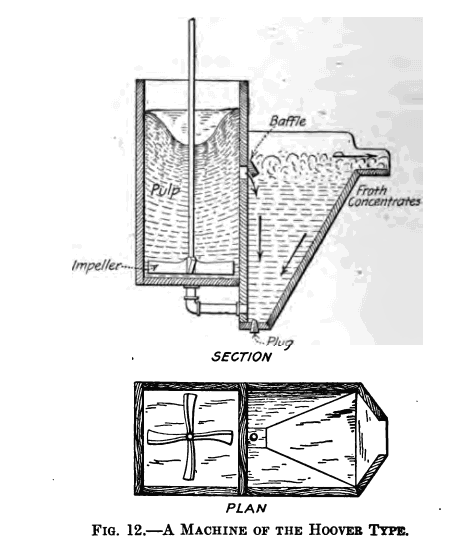
Flotation Principles
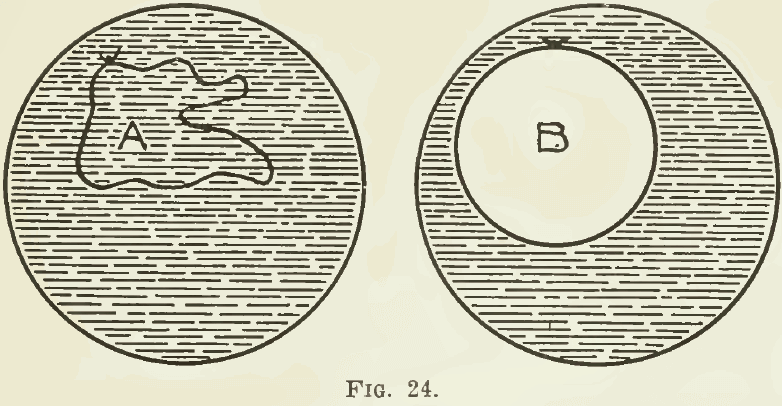
Flotation, in its latest phase, is a process of concentrating ores by frothing. When crushed ore, previously mixed with water and a relatively minute addition of oil, is agitated violently in the presence of air, a froth is formed. This froth, rising to the surface of the liquid mixture, is laden with sulphides or other […]
Flotation Deinking Paper Recycling De-Inking Waste Paper
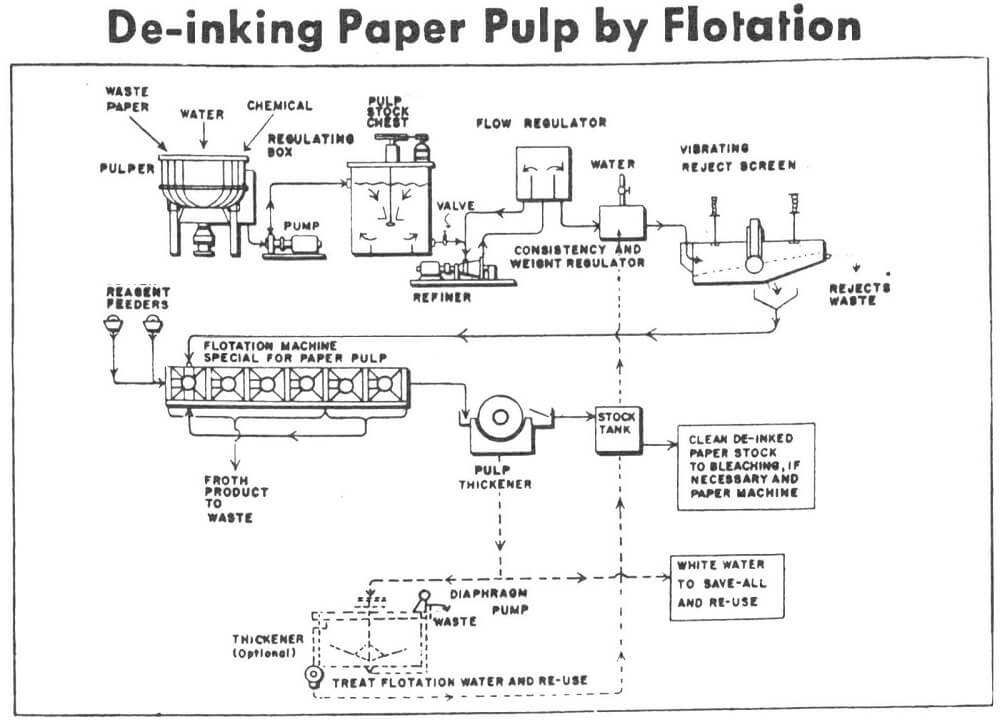
The pulping consisted of disintegration of the wastepaper structure and dispersion of the fibers. The disintegration was accomplished by conditioning 250 grams of wastepaper, under moderate agitation, with hot steam (84 to 90 °C), de-ionized water and reagent as desired. After disintegration the pulp was further dispersed in a high speed blender. All pulping experiments […]
Coal Flotation Machine

Process Plant/Circuit with Coal Flotation Conditioner and Bank of Flotation Cells.
How is Mercury Extracted from Cinnabar Ore
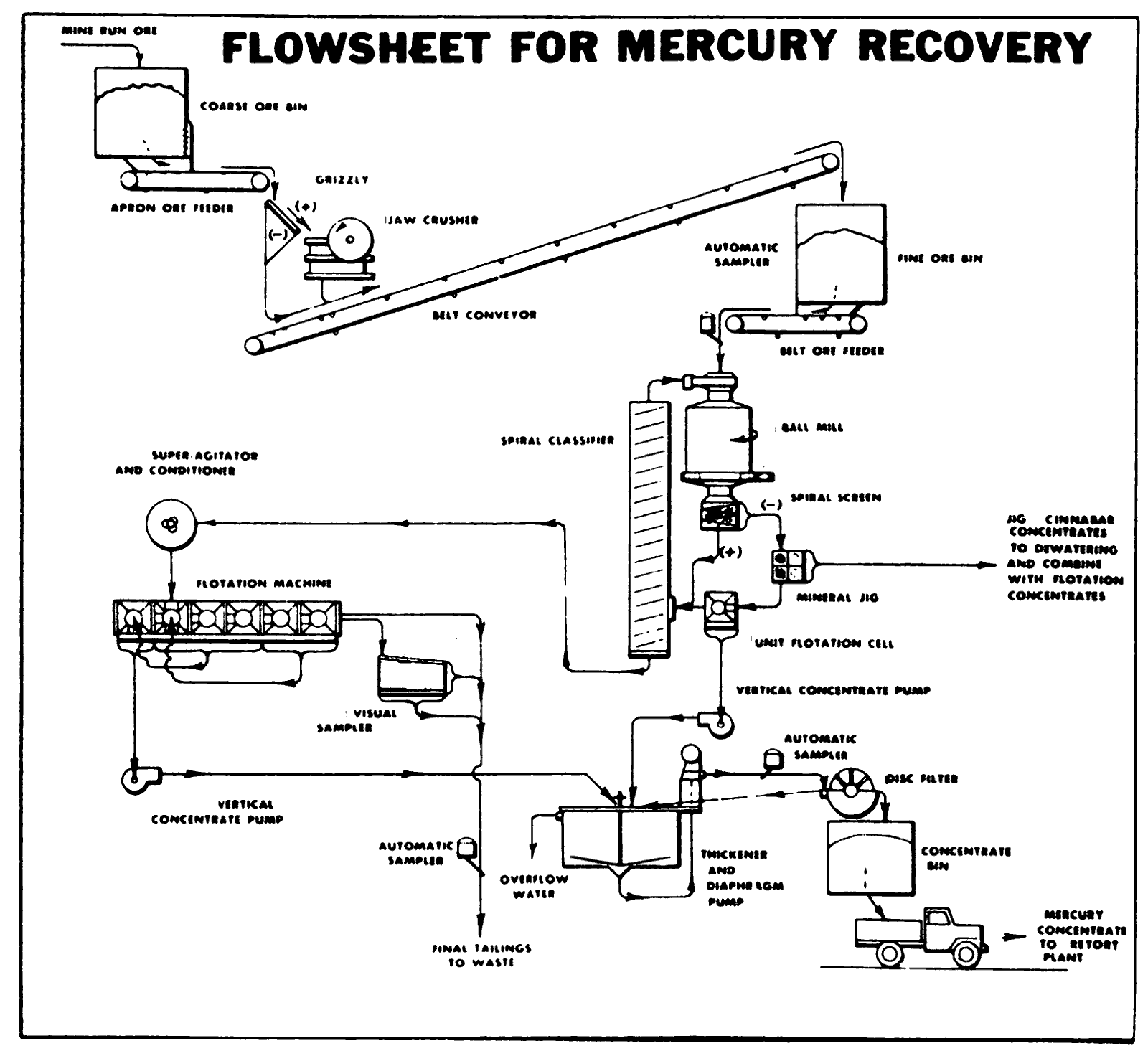
Mercury Process Recovery/Extraction Circuit Flowsheethttps://www.911metallurgist.com/mercury-extraction-process
Woodgrove Flotation Technology