Flotation Process Development in Laboratory
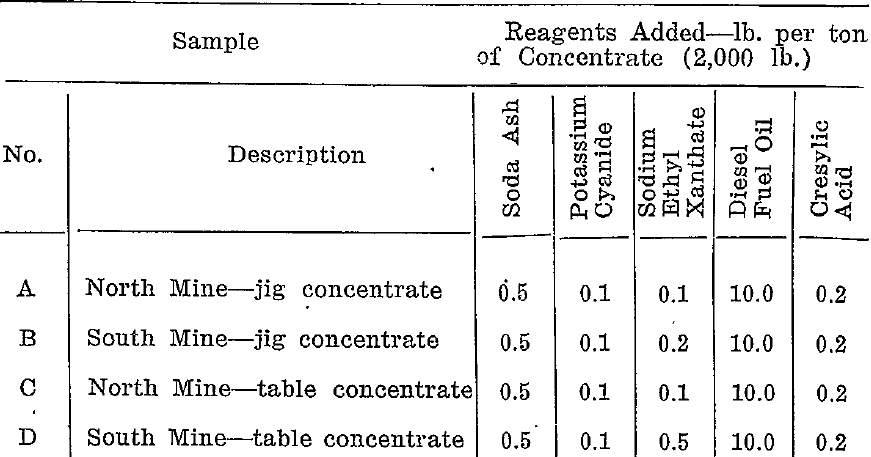
Differential and preferential flotation The pressing problems in differential and preferential flotation of ores are (1) the separation of lead sulphide from zinc sulphide, and (2) the separation of zinc and copper bearing sulphides from sulphides of iron. Methods seeking separation of one sulphide from another by flotation are of two classes, viz.: (1) those in which a difference […]
Metallurgical Testwork for Process Development
Mineralogy & Microscopy Amenability of an ore to flotation is best tested for by a microscopic examination of the ore followed by a few laboratory flotation tests. As stated in Chapter I, most ores containing minerals of metallic, resinous or adamantine luster associated with minerals of earthy, vitreous, or pearly luster, can be divided by froth flotation […]
Flotation Equipment and their Test Procedures
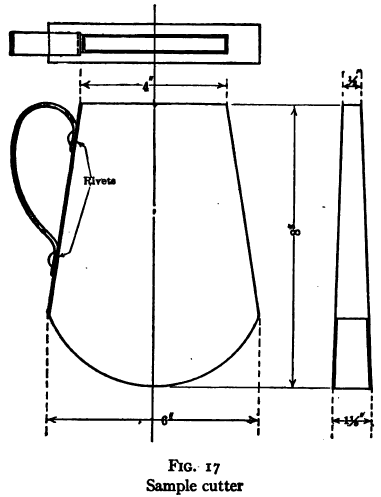
Practice in testing ores for flotation varies, of course, in its detail, from practice in testing work for other purposes, but in this as in other such work certain general principles apply. These principles would seem to be so obvious that they should not need to be enunciated, but the writer has found in going over the results of […]
Laboratory Flotation Equipment & Testing
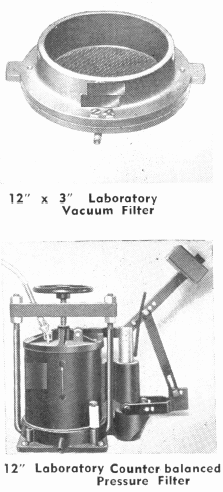
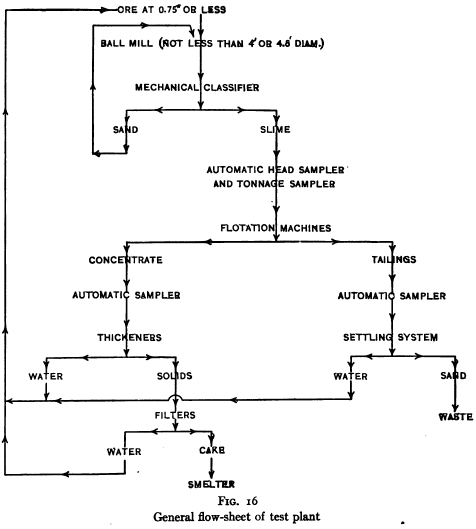
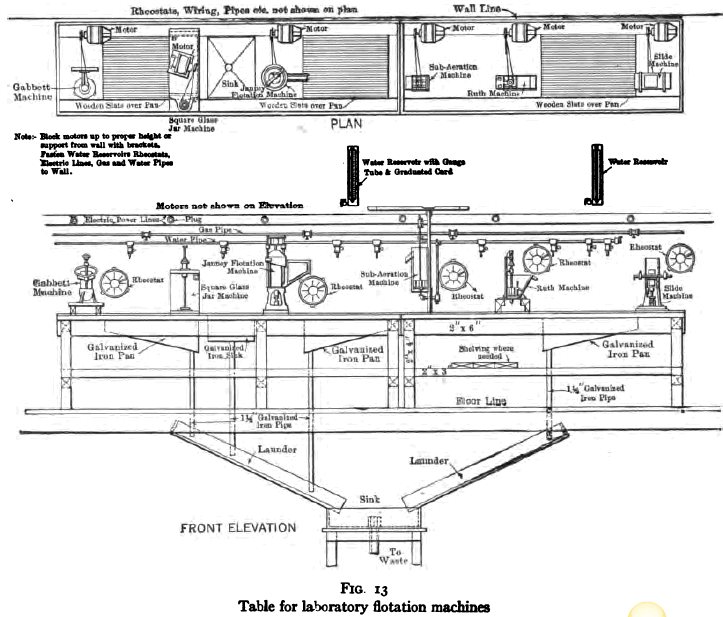
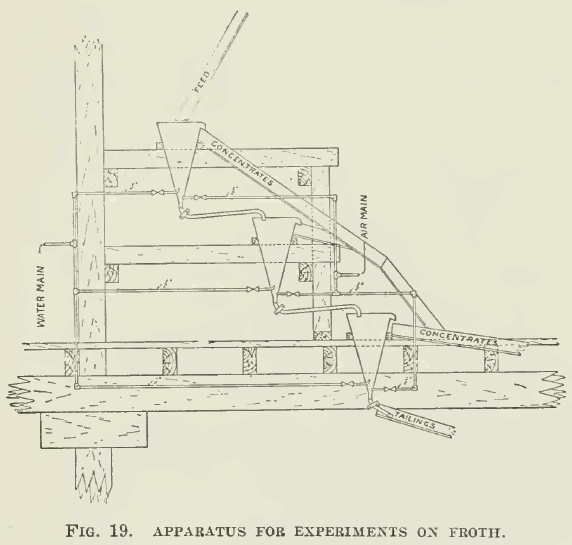
The apparatus listed in the following pages comprises the equipment necessary for complete and thorough testing of flotation processes. Some of it can be omitted where the problems to be studied are of a special character. It is urged, however, that such omission be of the actual flotation machines themselves rather than in the apparatus listed for preliminary […]
Froth Flotation Handbook

What is Flotation Flotation, as the term is applied to ore concentration, means the separation of one of the constituents of an ore from the remainder by causing it to float at or above the surface of a pulp consisting of the finely pulverized ore and water. Minerals that float Minerals that float have a […]
Explaining the Process of Froth Flotation
The flotation process for the concentration of ores is a method by means of which one or more of the minerals in the ore (usually the valuable ones) are picked up by means of a liquid film and floated at the surface of a mass of fluid pulp. Here they are separated from the other […]
Remove Arsenopyrite from Galena
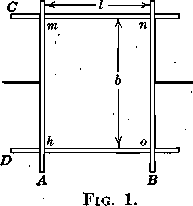
This paper deals with the application of table flotation to two unusual mineral dressing problems. Both problems involved the removal of interfering minerals at sizes too coarse for normal froth flotation. The first problem was the removal of arsenical minerals from Broken Hill gravity concentrates without further size reduction. Table flotation without grinding of the […]
A Glossary of Flotation

Absorb. To drink in, suck up, like a sponge. Adsorb. To condense and hold a gas on the surface of a solid, particularly metals. From L. ad, to, and sorbeo, suck in. Agitation is the act or state of being shaken, stirred, or moved with violence. From L. agitatus, agito, the frequent of ago, to […]
Froth Science
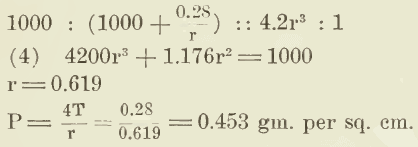
The little book on ‘Surface Tension and Surface Energy’ by Willows & Hatschek shows how the elastic film analogy in the study of froth will get one into no end of trouble if not handled with care. It is the characteristic of analogies to break down when pressed too far, though they are useful up […]
How Froth Flotation was Discovered and Developed
While concentrating the galena in the lead ore produced from the Central mine, a valuable by-product was obtained in the form of slime assaying 18% lead, 20% zinc, and 16 oz. silver per ton. This came from an ore in which quartz and rhodonite were the chief gangue-minerals. In the course of ordinary operations, it […]
