Table of Contents
Carbon dioxide is about one and a half times heavier than air, so it can be collected by downward displacement. Fit up a flat-bottomed flask with a thistle funnel and delivery tube, and set up your apparatus as shown in fig. 31.
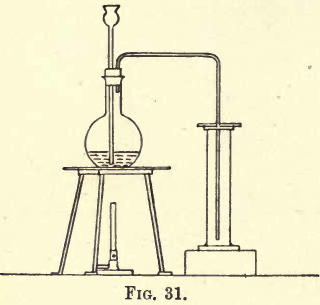
Weigh out about 25 to 30 grams of marble, broken into small pieces, and transfer carefully to the flask; then pour a little water into the flask, and fit in the thistle funnel and delivery tube. Pour down the thistle funnel some strong hydrochloric acid ; a brisk effervescence follows, and the gas is evolved.
CaCO3 + 2HCl = CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Collect three jars of the gas. To test when the jars are full, apply a lighted taper to the mouth of each jar; if it is extinguished, you will know the jar is full.
Laboratory Experiment I
Pour a little clear lime-water into a small beaker, dip the end of the delivery tube into this liquid, and allow the carbon dioxide to bubble through it; the clear solution becomes turbid. Continue to pass the gas, and the turbidity disappears after a time. Remove the beaker and boil the clear solution ; the turbidity soon appears again.
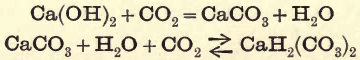
Laboratory Experiment II
Pour a little blue litmus solution into a small beaker and pass the carbon dioxide gas through it; the solution turns a wine-red colour, differing from the red produced by the action of hydrochloric acid on litmus solution. Boil the wine-red liquid and it becomes blue again.
Laboratory Experiment III
Take a jar of the gas, remove the glass cover, and pour the gas on to a lighted taper; the taper soon goes out.
Laboratory Experiment IV
Pour a little water into another jar of the gas, close the mouth of it with the hand and shake well; invert the jar and place its mouth under water in a trough; remove the hand and the water will rise in the jar showing the solubility of the gas.
Laboratory Experiment V
Take the remaining jar of the gas and pour a little sodium or potassium hydrate solution into it; close its mouth with the hand and shake well, then invert it and bring its mouth under water and remove the hand; the water will rush into the jar, showing that the gas has been absorbed by the solution of sodium or potassium hydrate.
2KOH + CO2 = K2CO3 + H2O
Filter the liquid remaining in the flask, transfer to a porcelain dish and evaporate to dryness, stirring it from time to time to prevent the calcium chloride from sticking to the dish.
