FORGE 4-TAP HYDRATION STATION – Portable Water Dispenser
An Industrial Hydration Station for Remote Mining Operations Ensuring reliable access to clean, cold drinking water is a critical safety requirement on modern mining sites. The
An Industrial Hydration Station for Remote Mining Operations Ensuring reliable access to clean, cold drinking water is a critical safety requirement on modern mining sites. The
Are you looking for a motor crusher or a crusher motor? This difference is significant. The first is if you want to crush motors, while
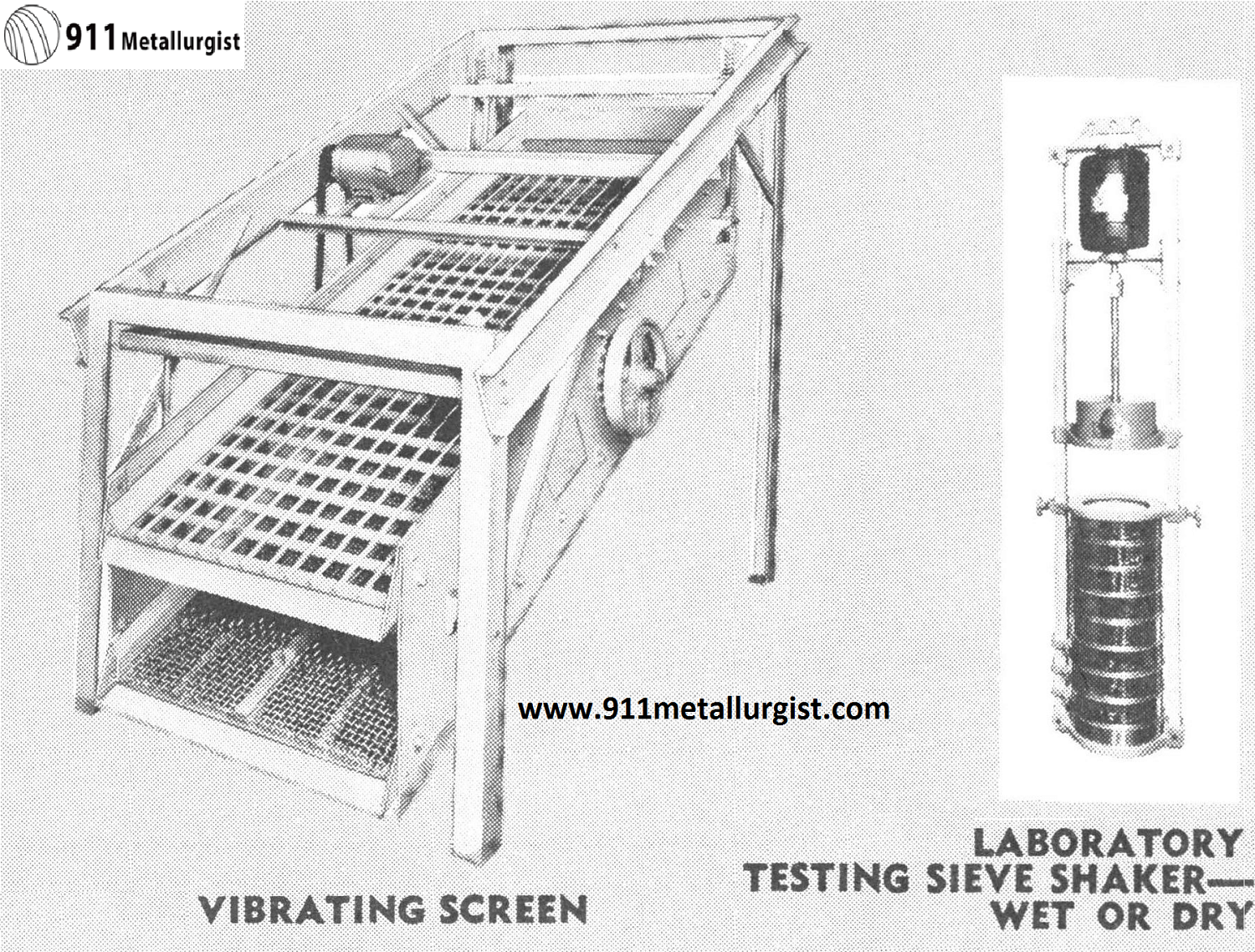
For efficient wet or dry screening—Hi-capacity, 2-bearing design. Flywheel weights counterbalance eccentric shaft giving a “true-circle” motion to screen. Spring suspensions carry the weight. Bearings
How do Seawater Greenhouses Work? A seawater greenhouse is a type of greenhouse technology that utilizes seawater to grow crops in arid or desert regions.
Balancing Resource Extraction and Water Sustainability Lithium, a key component in batteries that power electric vehicles and store renewable energy, has become increasingly vital in
Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) is an innovative method of extracting lithium from brine or other lithium-rich sources without the need for traditional evaporation ponds. Unlike
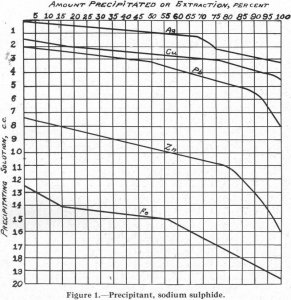
It is generally conceded by flotation men that the condition at the surface of a particle of mineral or gangue is the most important factor
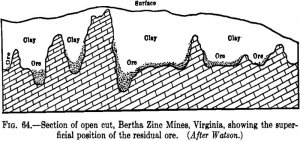
In the examination of an undeveloped prospect a decision must be arrived at from an inspection of the outcrops and the exposures in a few
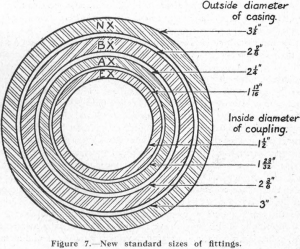
In approaching the subject of diamond-drilling practice, a brief history of the origin and development of the diamond drill may be of interest. The use