Dry Gravimetric Methods of Assaying
The methods of assaying are best classed under two heads, Gravimetric and Volumetric, in the former of which the final results are weighed, whilst in the latter they are measured. A commoner and older division is expressed in the terms much used in practice —wet assays and dry assays. Wet assays include all those in […]
Sample Weighing & Measuring for Assaying

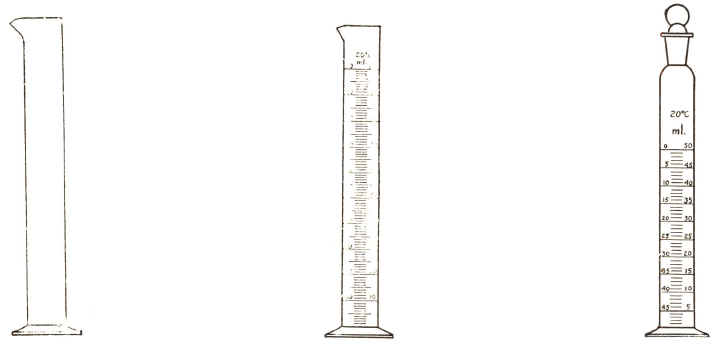
Weighing.—The system of weights and measures which we have adopted is the French or metric system; in this the gram (15-43 grains) is the unit of weight; the only other weight frequently referred to is the milligram, which is 0.001, or 1/1000 gram. The unit of volume is the cubic centimetre, which is approximately the […]
List Assaying Reagents
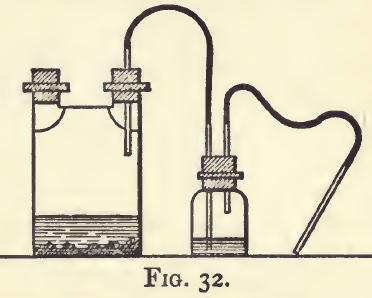
Acetic Acid, HAc or C2H4O2. (sp. gr. 1.044, containing 33 per cent, real acid).—An organic acid, forming a class of salts, acetates, which are for the most part soluble in water, and which, on ignition, leave the oxide or carbonate of the metal. It is almost always used in those cases where mineral acids are […]
Silver Assaying Methods
Silver is widely diffused, and has been found in most mining districts. It occurs native in sufficient quantity to constitute one of the chief ores of the metal. It also occurs combined with sulphur (as in argentite), with sulphur and antimony (as in stephanite or brittle silver ore, and in pyrargyrite or ruby silver), and […]
How to Measure Specific Gravity
The relation of the weight of a substance to its volume should be kept in mind in all cases where both weight and volume are dealt with. Students are apt to imagine that on mixing equal volumes of, say, sulphuric acid and water, an acid of half the strength must be obtained. If the statement […]
Assaying Mercury Determination Method
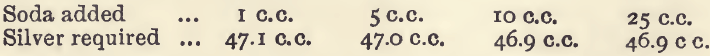
Mercury occurs native and, occasionally, alloyed with gold or silver in natural amalgams; but its chief ore is the sulphide, cinnabar. It is comparatively rare, being mined for only in a few districts. It is chiefly used in the extraction of gold and silver from their ores (amalgamation); for silvering mirrors, &c. Mercury forms two […]
Gold Content Determination Methods
Gold occurs in nature chiefly as metal. It always contains more or less silver, and, in alluvial sands, may be associated with platinum and iridium. Gold is insoluble in hydrochloric or nitric acid, but is dissolved by aqua regia or by solutions of iodine, bromine, or chlorine. It is taken up by mercury, forming an amalgam, […]
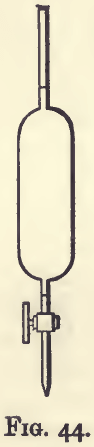
Assaying Copper Determination Method
Copper occurs native in large quantities, especially in the Lake Superior district ; in this state it is generally pure. More frequently it is found in combination. The ores of copper may be classed as oxides and sulphides. The most abundant oxidised ores are the carbonates, malachite and chessylite; the silicates, as also the red […]
Rock Abrasion & Crushers

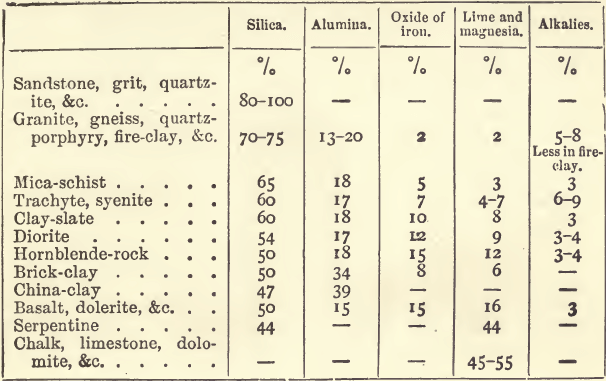
This section of the Paper deals with the abrasive character of rocks affecting crushing machinery. The investigation has followed two courses, firstly, an analysis of the existing data relating to the testing of road-making stones from its bearing on the abrasive wear of crusher-parts, and secondly, an experimental investigation into the correlation of abrasive wear […]
Crushers
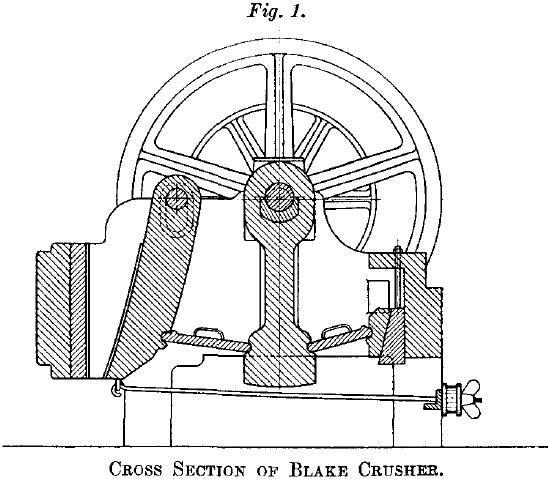
It is difficult to define exactly the meaning of the terms crushing and grinding, or crushing and pulverization; the finer crushing stages may embody a certain amount of pulverizing or grinding, but in the main, crushing may be said to cover the reduction of stones or ores to a size of ½ inch, and in some […]
