Semi-Autogenous Grinding of Copper Ores
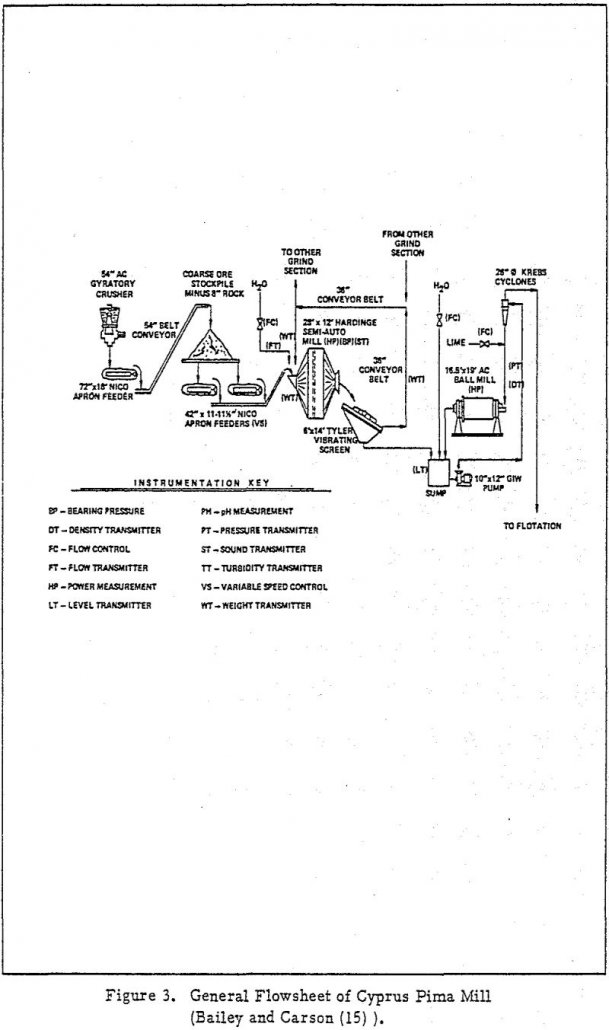
Mechanism of Size Reduction The spectrum of comminution mechanisms in a mill range from shattering of the rock by imposition of a load to abrasion by surface contact with other rocks. Since SAG represents a combination of autogenous and ball milling, a better understanding of the mechanism of the comminution process in a SAG mill […]
Partially Saturated Zone Beneath Tailings Impoundments Seepage
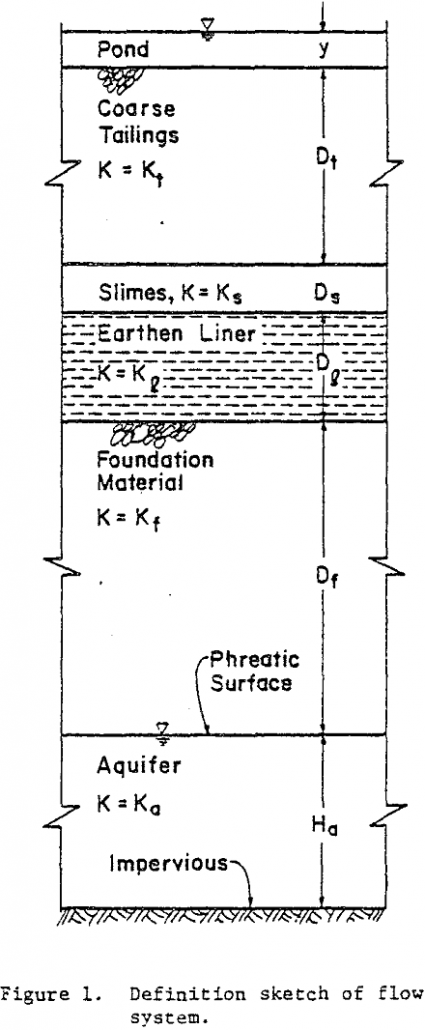
Conventional analyses of seepage through saturated media do not apply when tailings impoundments are located above a partially saturated zone. Three stages of seepage are identified and methods for estimating the seepage rates and duration of each stage, based upon flow in partially saturated and saturated porous media, are demonstrated. The effectiveness of earthen liners […]
Determining Air Requirements for Reverse Air Lift
Numerous large scale drilling projects have made use of reverse circulation air lift methods. Reverse air lift pumping can be established by injecting gas into a column of liquid; the subsequently decreased density of the gas-liquid mixture allows atmospheric pressure outside the lift conduit to establish flow. The rate of flow can be controlled by […]
Predicting Flotation Recovery
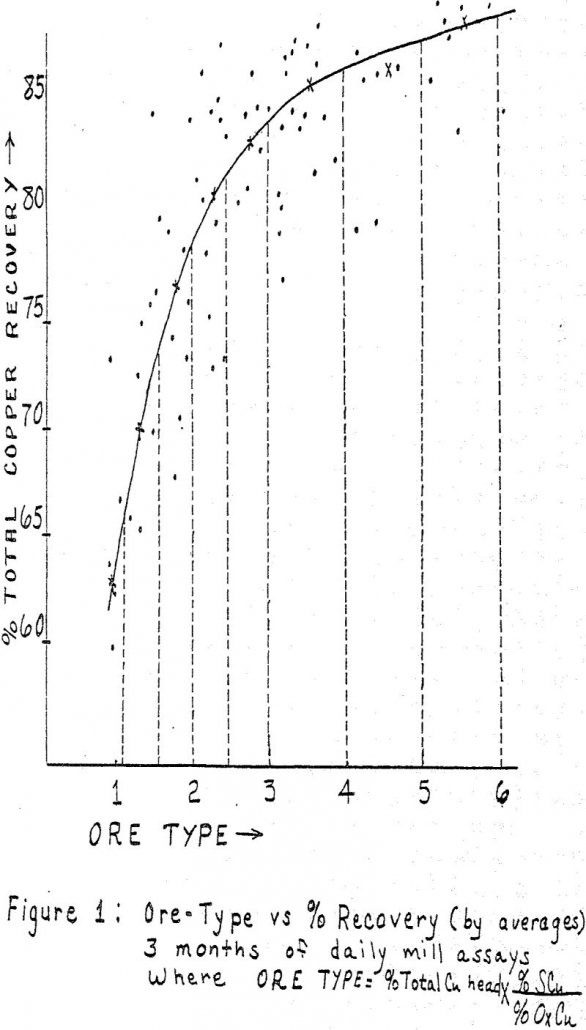
Unfortunately, many milling engineers rely rather heavily on percent recovery as a strict measure of a concentrator’s relative performance. The fallacy of this reasoning is not difficult to see since, by definition, percent recovery is a function of feed assay, tails, and concentrate grade. If copper tailing is constant, and it very nearly is for […]
Factors on the Power Consumption and Capacity of a Mill
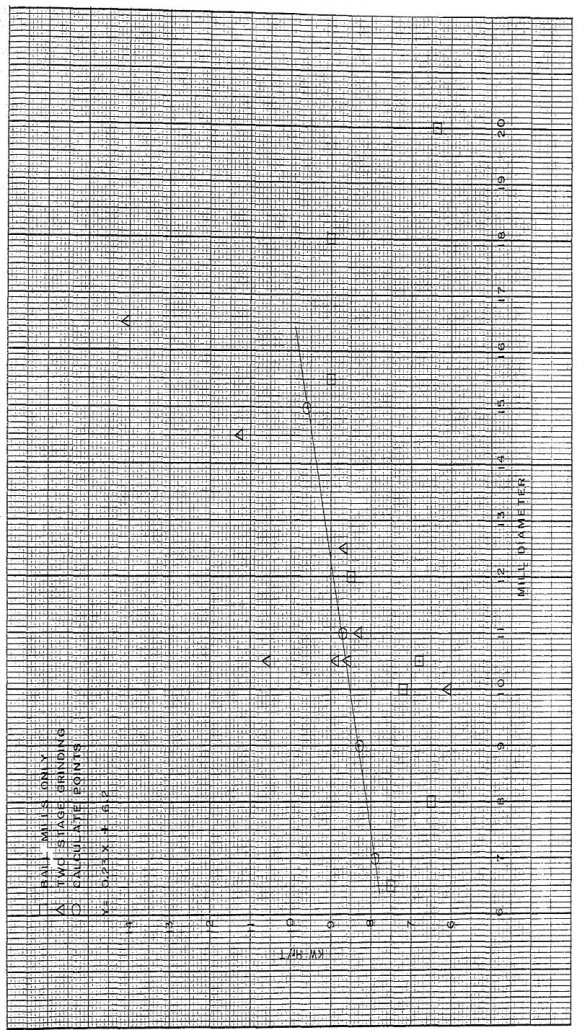
Since man began beneficiating ores, a limited number of factors influenced the type of treatment. The ore itself has always been a factor. The first form of concentration was probably hand sorting, and the grade of concentrate and recovery had to be considered from the start. Five of the principal factors having an effect on […]
Phosphate Rock Beneficiation
Many new mines overseas have also become significant. This includes countries such as Senegal, Togo, Israel, Spanish Sahara, and Jordan. Limited production, often as by-products, has been noted in South Africa, Brazil, and other countries. In recent years, and even recent months, we have learned of many new areas being considered as potential sources of […]
Pellets for Direct Reduction
The iron ores mined by LKAB in the north of Sweden have excellent beneficiation properties. This gives LKAB a favourable position as regards the production of low silica pellets for direct, reduction. LKAB have concentrated on developing and marketing grades of pellets for the Midrex-Purofer-Hyl process group, i.e. such D.R. processes which are carried out […]
Overburden Stripping using Dredge and Draglines
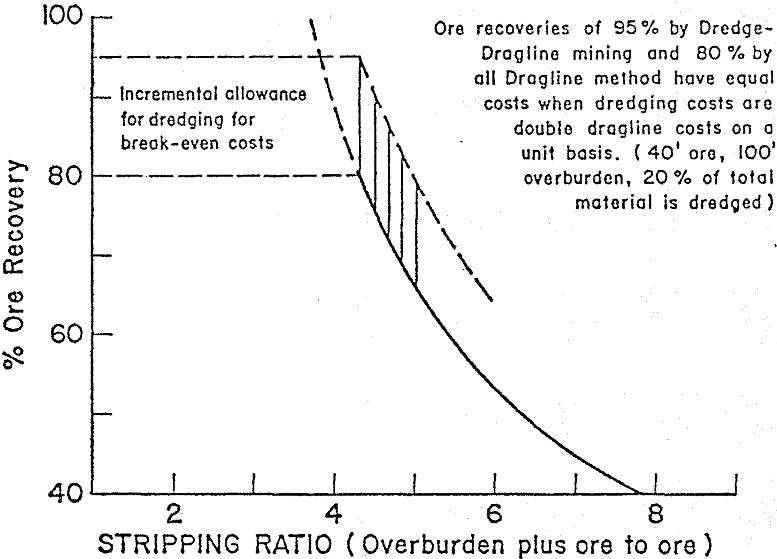
Texasgulf’s Lee Creek Mine in Eastern North Carolina is using a combination Dredge-Dragline method for mining deep phosphate ore at a rate of 3.5 million tons per year. The matrix is thick, uniform in grade, and is processed into agricultural products. As in many other good mineral deposits, there are tough obstacles to overcome in […]
Factors to Optimize Autogenous Grinding Mills
The Stekenjokk plant employs a system with automatic support of the secondary mill with pebbles from the primary autogenous mill. As well as in the Aitik case the Stekenjokk plant has reached its rated capacity and performance after a short running in period. Capacity Variations and Feed Size All of these autogenous installations have been […]
Molybdenite Flotation Operating Variables
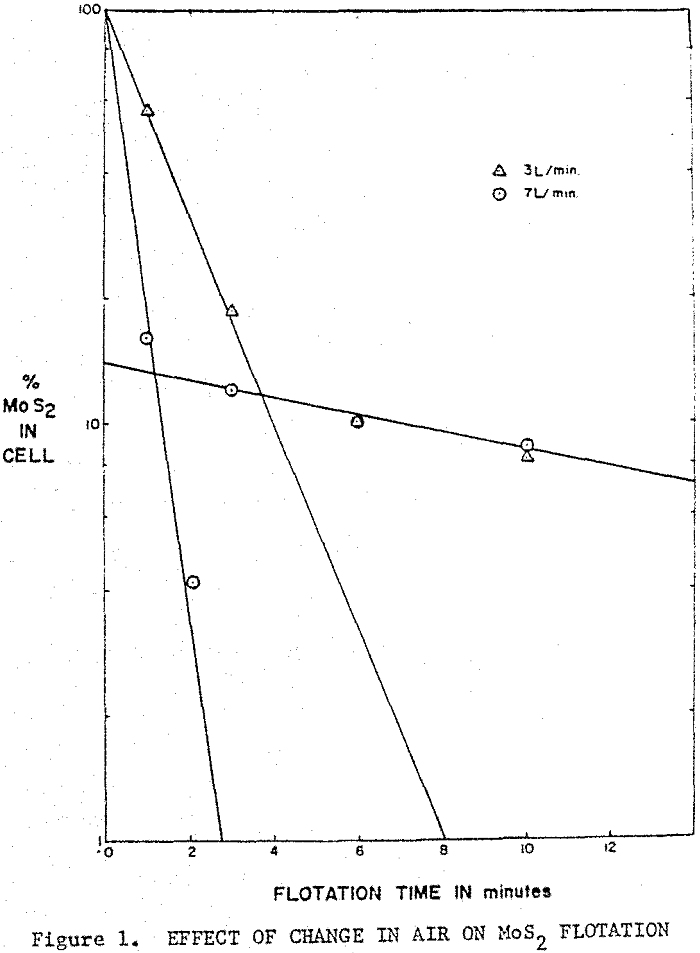
The number of variables which can effect flotation of molybdenite is very large. The analysis of flotation results indicate that molybdenite can be characterized into fast-floating and slow-floating components. The rates of fast-floating components, which do not create a problem in flotation, could be varied by changing agitation of airflow rates. Experimental For the laboratory […]
