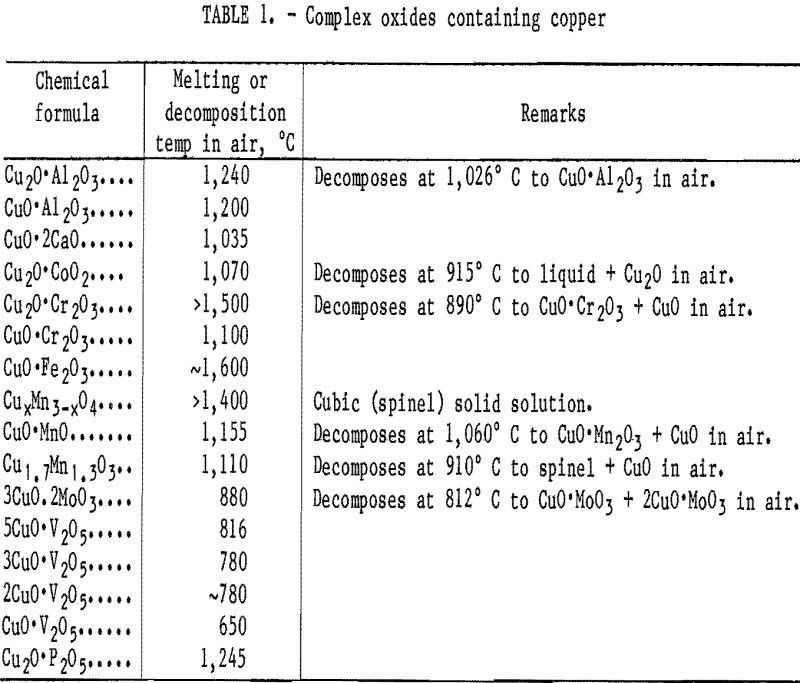
Remove Copper from Molten Ferrous Scrap
The importance of ferrous scrap as a resource in the domestic iron and steel industry has increased significantly during the last two decades owing to the growth of steel production in electric arc furnaces. In 1984, approximately 55 million tons of scrap was consumed in domestic steel mills, of which 56 pct was used in […]
Recover Mercury from Concentrates by Chloride Leaching & Electrolysis
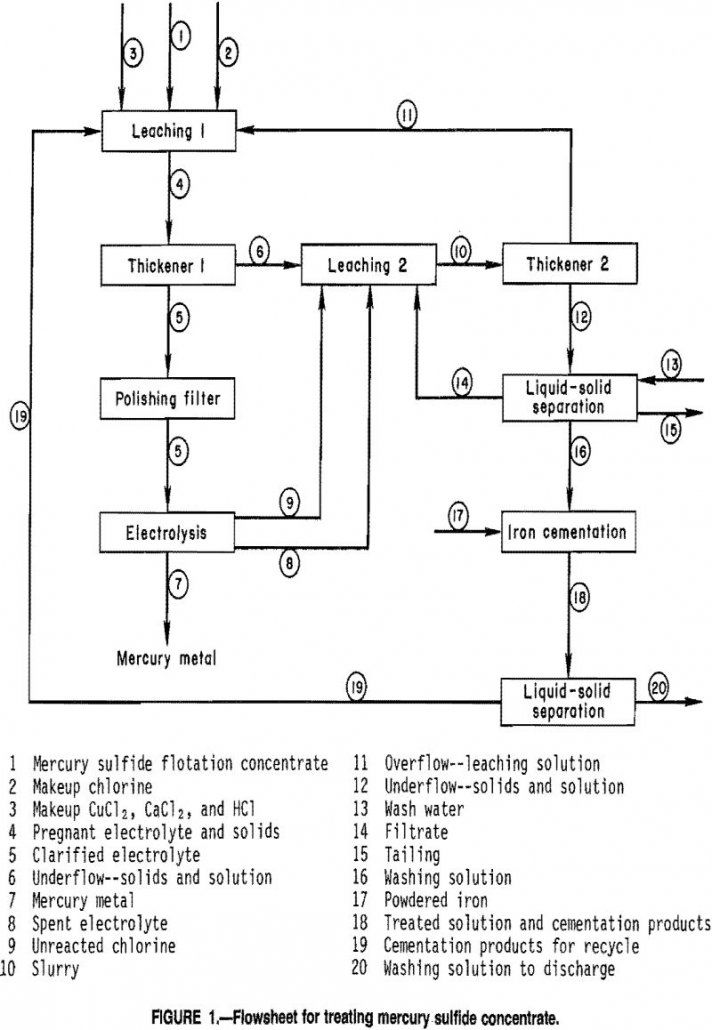
The Bureau of Mines and the Nevada Bureau of Mines have investigated hydrometallurgical methods for recovering mercury metal from sulfide concentrates. Most recently, Atkinson investigated the recovery of mercury from sulfide concentrates by a CuCl2 leaching- electrolysis technique. The concentrate used in the investigation was obtained from the McDermitt Mine, the major mercury producer in […]
Recover Cobalt in Copper Leach Solution by Ion Exchange
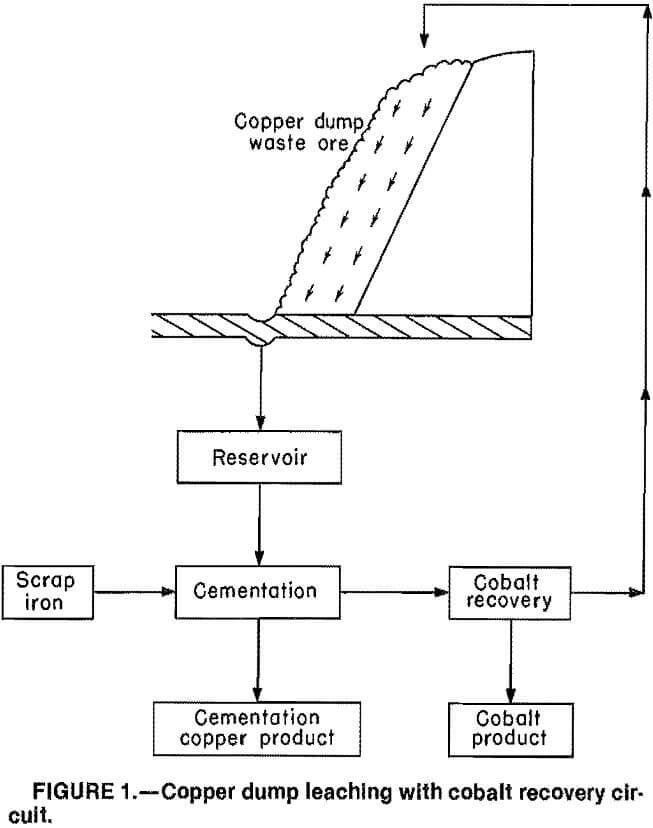
Significant amounts of cobalt, a strategic and critical metal, are present in some secondary sources such as spent copper leach solutions. The United States currently imports over 95 pct of its cobalt supply, much of it from Africa. Development of a process to recover cobalt from readily accessible spent copper leach solutions would help meet […]
Recover Cobalt & Copper from Sulfide Concentrates
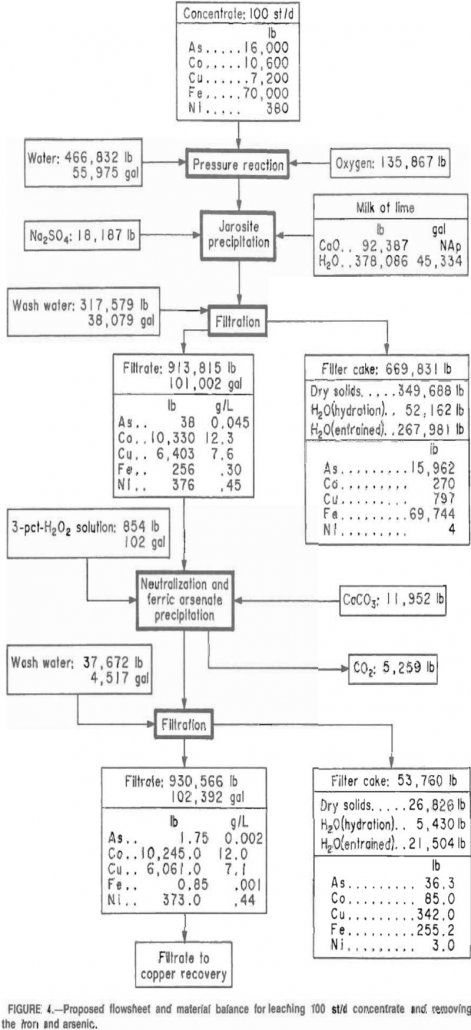
Cobalt is a critical and strategic metal because of its essential defence related uses and the high degree of U.S. import reliance for its supply. Currently, the United States does not produce any cobalt from domestic mines. Most of the U.S. supply of cobalt is imported from the African nations of Zambia and Zaire CO-4 […]
Cobalt Sorption in Ion-Exchange Column
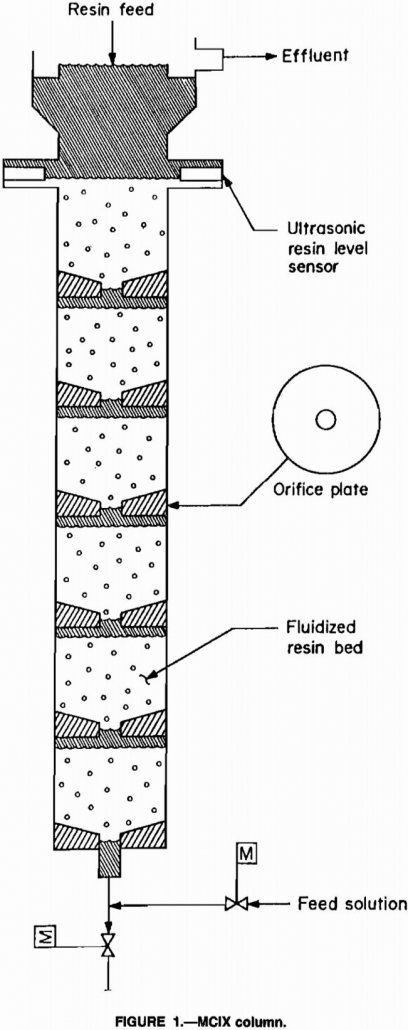
The Bureau has developed a process using ion exchange to extract cobalt, a strategic and critical metal, from domestic copper leach solutions. These solutions are produced by dump or heap leaching of low-grade ores with dilute sulfuric acid and contain significant amounts of readily accessible cobalt. Although the cobalt concentrations in these streams are only […]
Electrogalvanizing using Recycled Zinc
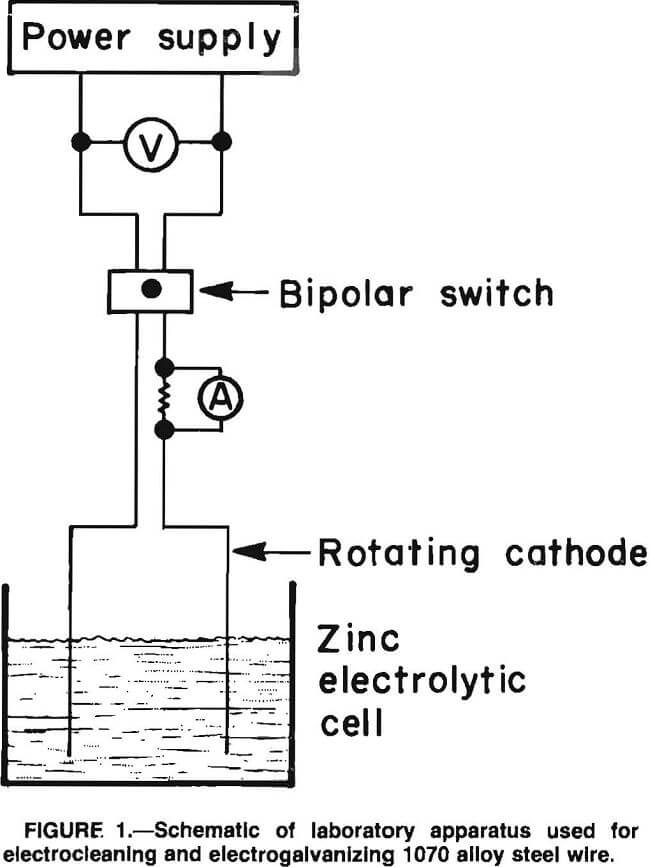
A major problem facing the metals industry in the United States and perhaps throughout the world is the disposition of waste oxide dusts generated at various stages of processing. Storage in landfills has been used most often in the past; but, as more and more of these wastes are being declared hazardous, landfill costs have […]
Flotation of Silicon Carbide
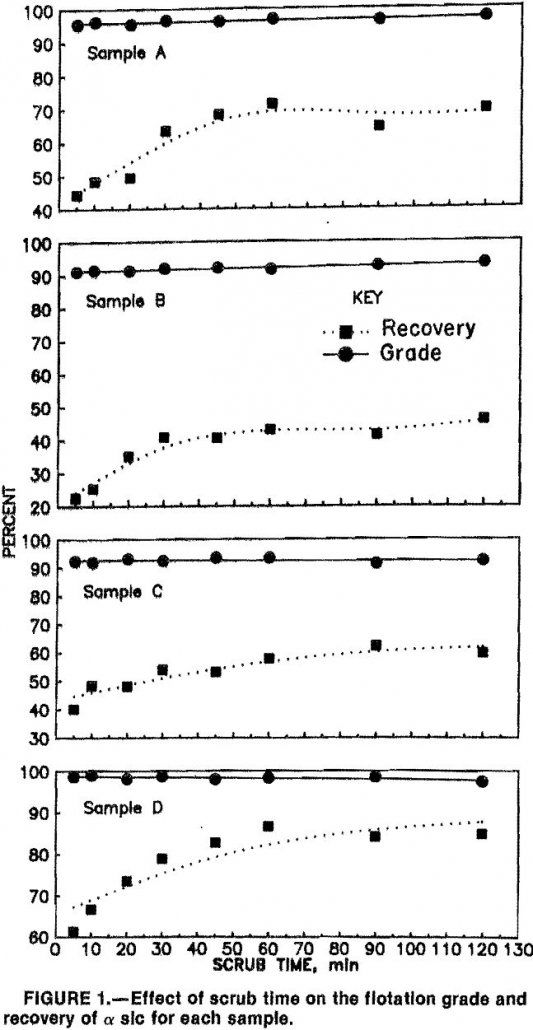
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a synthetic compound which is commercially produced by heating a mixture of metallurgical coke and high-purity silica sand to 2,400° C in an electrical resistance furnace. A method to produce SiC was first discovered in this country by E. G. Acheson in 1891 while studying the reaction of carbon with other […]
Processus d’Extraction de l’OR
Le plant IGR 100 est un système modulaire système autonome de Processus d’Extraction et récupération de l’or. Il utilise la classification et à la gravité accrue pour vous assurer attirent l’or fin et les grosses pépites. Dans le flux de norme de configuration comme suit: Le mineur se nourrit de sable et de gravier dans […]
Extraction de l’or Sans Mercure
Pour l’Extraction de l’or Sans Mercure, le Concentrateur iCON i150est l’iCON de renommée mondiale. Il s’agit d’un concentrateur gravimétrique qui utilise renforcée gravité (G) de concentrer les ‘libres’ de minéraux lourds. Il est également connu comme un concentrateur centrifuge en raison de l’action centrifuge de la cuvette de filage. Le procédé utilise de l’eau seulement, […]
Extraction de l’Or par Gravitation
Récupérer de l’Or avec du Mercure Sans mercure, Pas de Cyanure Balayage / retraitement Tails Hard Rock Publication de traitement des minerais de Hard Rock Concentration des minerais / Tails pour le traitement final régional Alluviales / Placer et travaux de dragage Première transformation lorsque vous savez que votre or est trop fine pour une […]
