Extract Aluminum from Aluminum Silicon Alloys
The following conclusions are drawn from the results of these investigations: The reflux leaching method is an effective means for extracting aluminum from crude Al-Si alloy. Aluminum obtained by this method will contain from 1 to 6 percent silicon, 0.04 to 0.8 percent iron, and 0.01 to 0.9 percent titanium. With only minor changes in […]
How to Make Zirconium Diboride Directly from Zircon
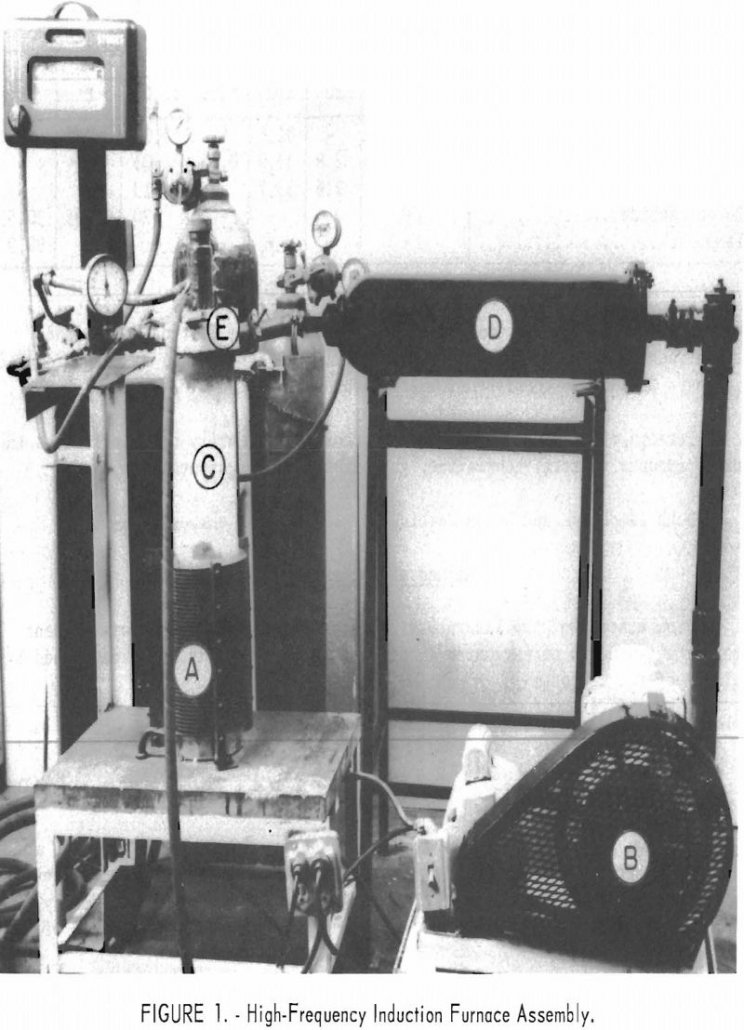
Zirconium diboride of a quality comparable to that produced commercially from zirconium dioxide may be synthesized directly from zircon. The quantities of residual carbon and silica are not excessively high, but it is believed that some refinements in procedure may lower these percentages. The grain size of the final product has been demonstrated to be […]
Zirconium Gadolinium Equilibrium Diagram
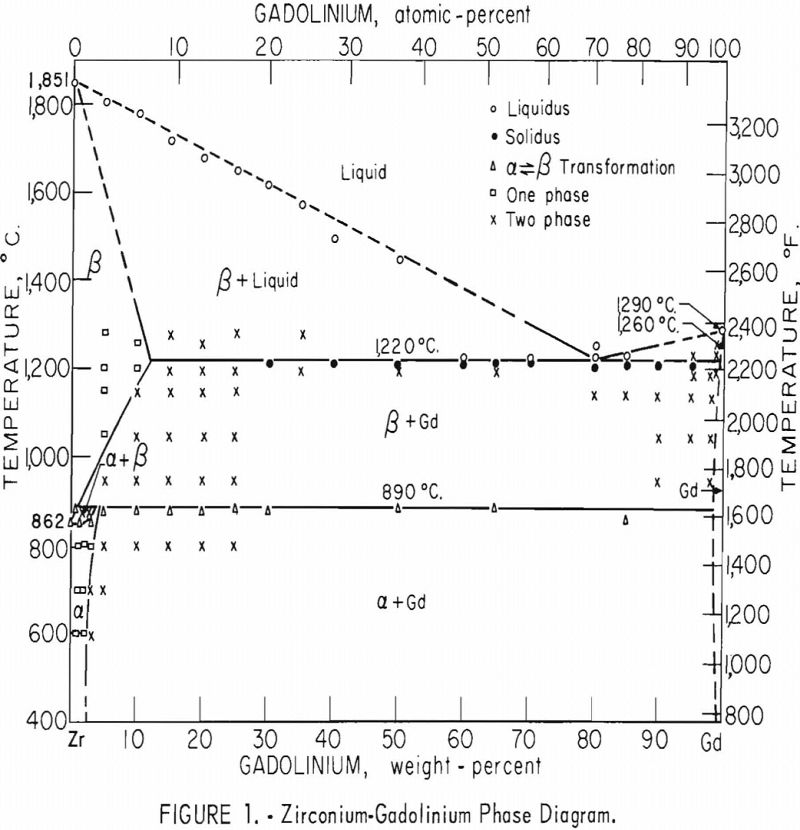
The investigation of the zirconium-gadolinium equilibrium diagram revealed a eutectic system with limited terminal solubilities and one peritectoid reaction. The eutectic point occurs at about 82 percent gadolinium. The eutectic isotherm, at 1,220° C., extends from about 12 to 99+ percent gadolinium. The peritectoid isotherm, at 890° C., involving the alpha-beta transformation of zirconium, extends […]
Sulfide Oxide Lead Zinc Transitional Ore Treatment Processing Method
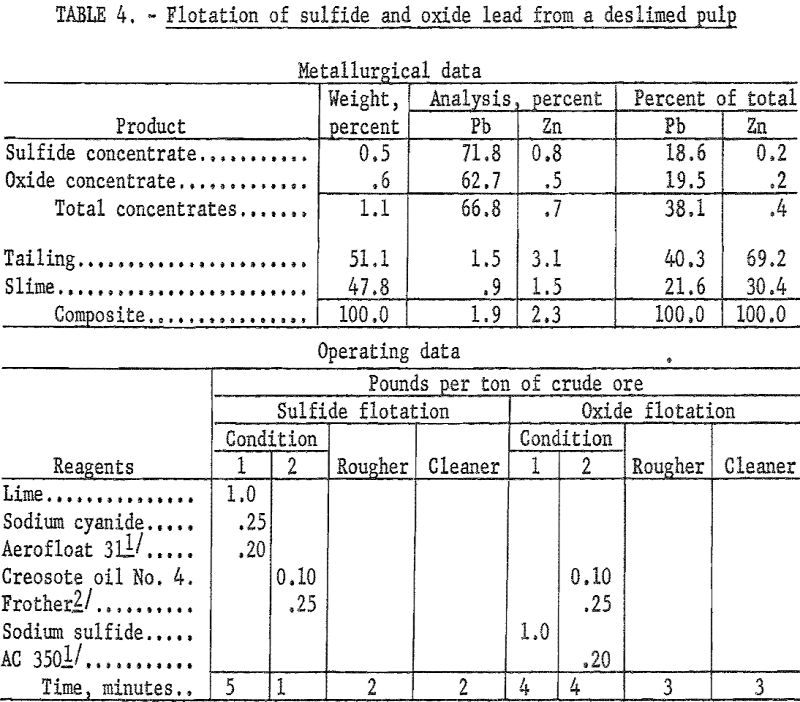
The mineral dressing research here reported is part of a continuing program by the Bureau of Mines to develop new or improved concentration processes for oxidized or partly oxidized lead and zinc ores. A sample of low-grade sulfide-oxide, lead-zinc ore from Jasper County., Mo., containing galena, cerussite, pyromorphite, hemimorphite, smithsonite, and sphalerite was concentrated by […]
Casting Titanium Zirconium and Hafnium
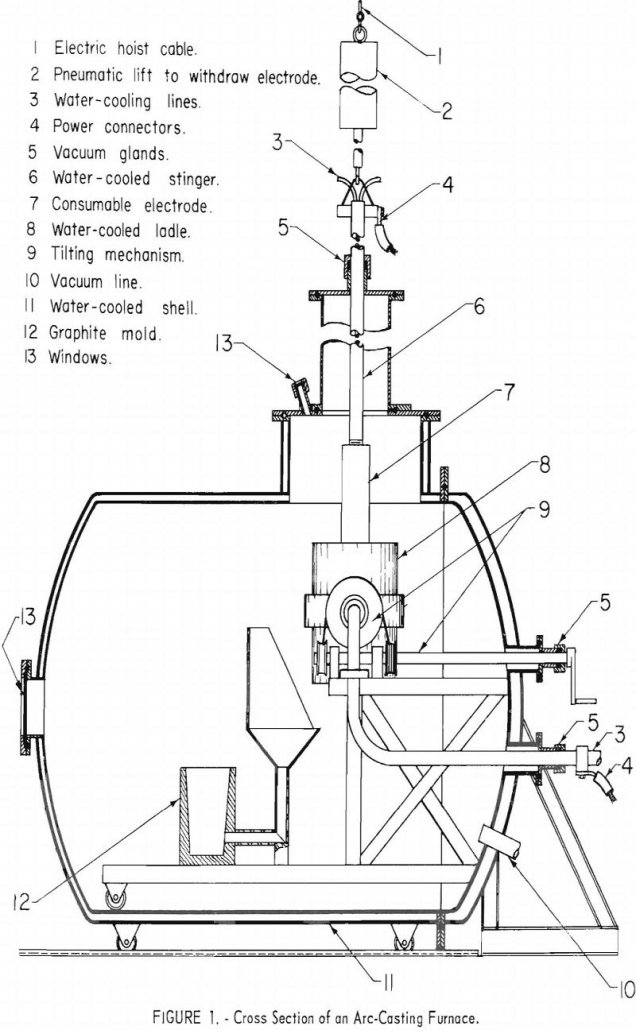
The work covered in this report is a continuation of an earlier feasibility study by the Federal Bureau of Mines and points out improvements in the skull-melting method for casting reactive metals such as titanium, zirconium, and hafnium. Machined graphite molds with laminated sections can be reused many times. Large tube sections can be produced […]
Volatilization of Tin Chlorides
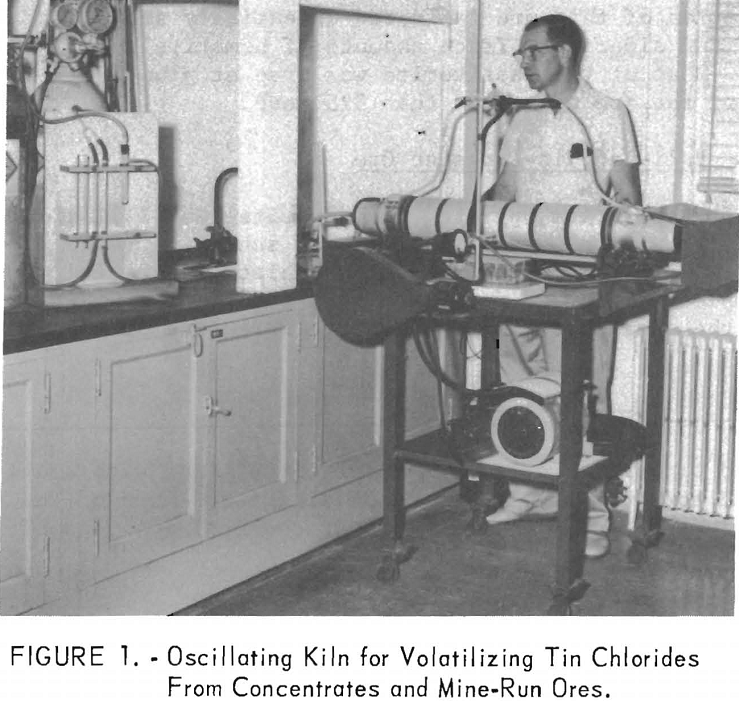

More than 95 percent of the total tin in Bolivian mine-run ores can be volatilized and recovered as tin chlorides at temperatures ranging from 520° to 565° C. Equally high percentage recoveries of tin can be obtained from low-grade Bolivian concentrates at temperatures of 565° to 600° C. Minus 35-mesh ores and concentrates can be […]
Crushing Chestnut to Produce Buckwheat
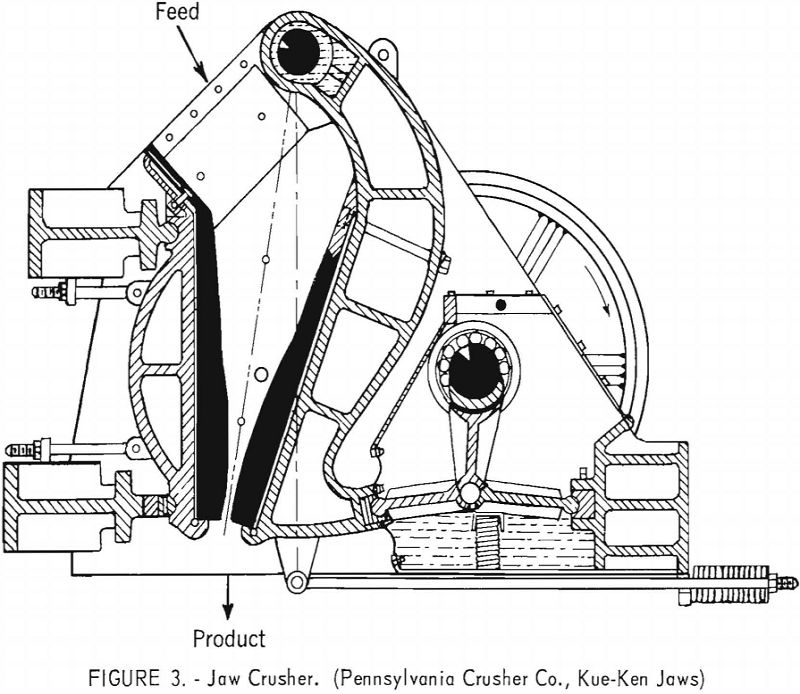
The crushing of chestnut-size (1-5/8 by 13/16 inch) Pennsylvania anthracite in four commercial crushers (impact, jaw crusher, hammer mill, and gyratory types) was studied by the Bureau of Mines to determine which could produce the largest proportions of buckwheat Nos. 1 and 2 sizes (9/16 by 3/16 inch). Single pass dry and wet crushing techniques […]
Radioisotopes Applications
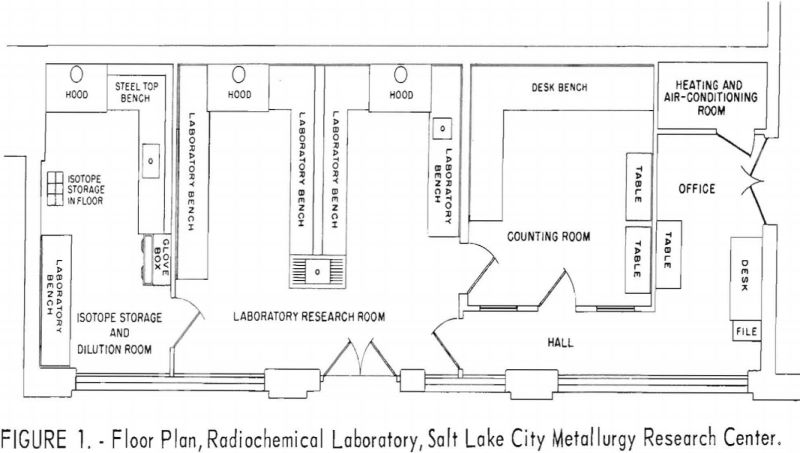
Many factors contributed to the decision to build a radiochemical laboratory at the Salt Lake City Metallurgy Research Center to investigate the application of radioactive isotopes and chemical compounds in extractive metallurgy. These reasons included the notable success achieved in biological sciences with radioisotopes, the development of reliable instruments and methods for identifying the isotopes […]
How to Determine Trace Impurities in Helium
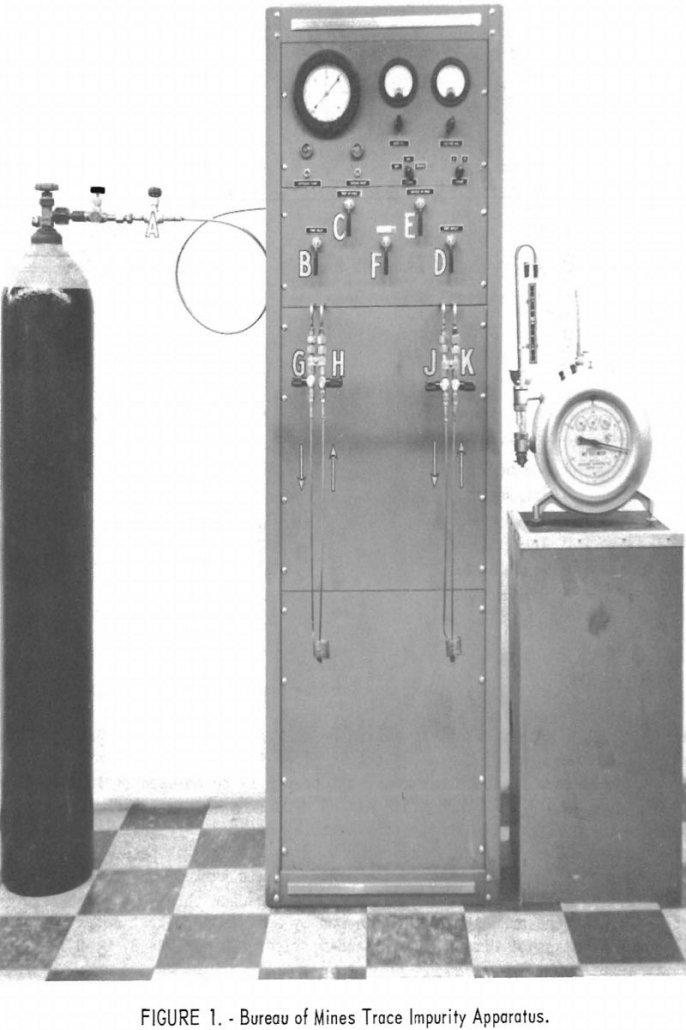
An apparatus for determining trace impurities in Grade-A helium by mass spectrometer methods was designed and built by the Federal Bureau of Mines. Grade-A is the designation for helium commercially produced by the Bureau. Its nominal purity is 99.995 percent. The device, following a suggestion by Deaton, concentrates the impurities in the helium by freezing […]
How to Design an Underground Mine Opening in Rock
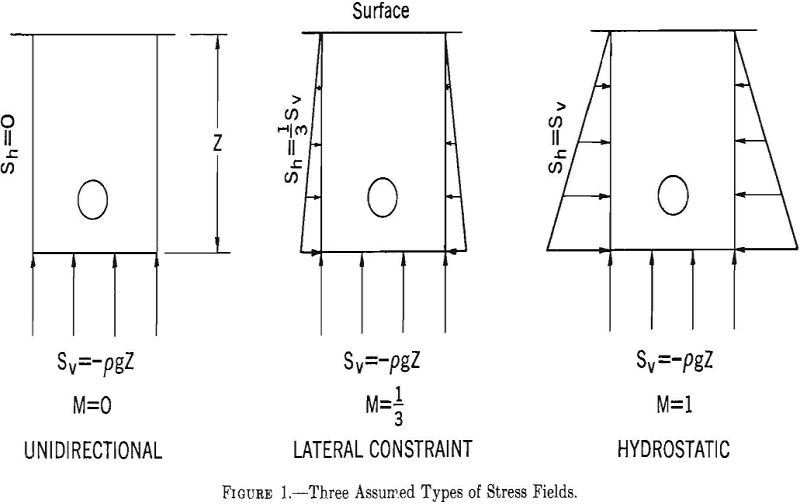
The design and stability of underground openings are problems of paramount importance in mining. Insuring the safety of employees, protecting equipment, mining in a prescribed and efficient manner, and (in mineral mining) achieving an optimum recovery from the deposit depend upon the ability of engineers to design and excavate underground openings that will remain open […]
