Ferric Chloride Leaching

Primary lead is commercially produced from lead sulfide concentrates by a smelting process consisting of sintering, blast furnace reduction, and refining. The pyrometallurgical method is low cost and requires relatively little energy, but generates gaseous sulfur dioxide and particulate lead, which must be controlled to prevent air pollution. Because of the difficulties in meeting regulations […]
Low Solubility Mineral Flotation
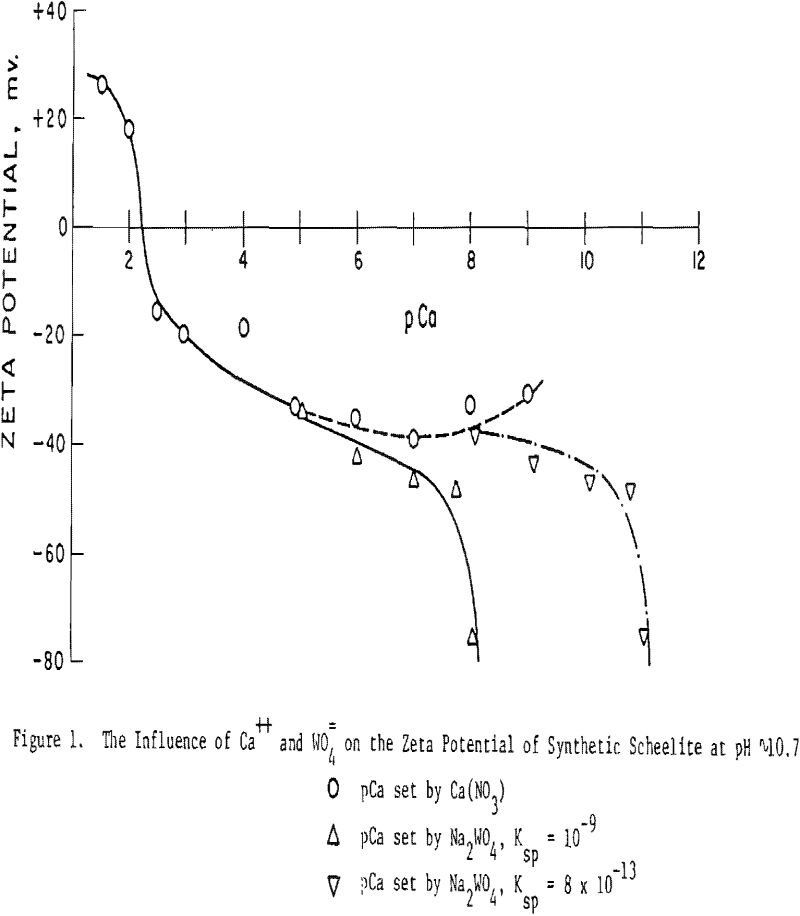
The objective of this study is to evaluate methods to improve the selectivity in flotation of the slightly soluble minerals, typified by calcite, fluorlte and scheelite. The separation of minerals within this class has long been one of the most difficult tasks facing the mineral processing engineer. The slightly soluble mineral class, as defined herein, […]
Vanadium & Uranium Extraction
Addition of vanadium to iron and steel gives improved product properties such as increased strength, improved machinability, reduced distortion, simpler heat treatment, better weldability, increased wear resistance, better control and uniformity of hardness penetration and gradient, smoother and better finishes, and reduced flaking or spalling of carburized surfaces. Consequently, vanadium-steel alloys are used in the […]
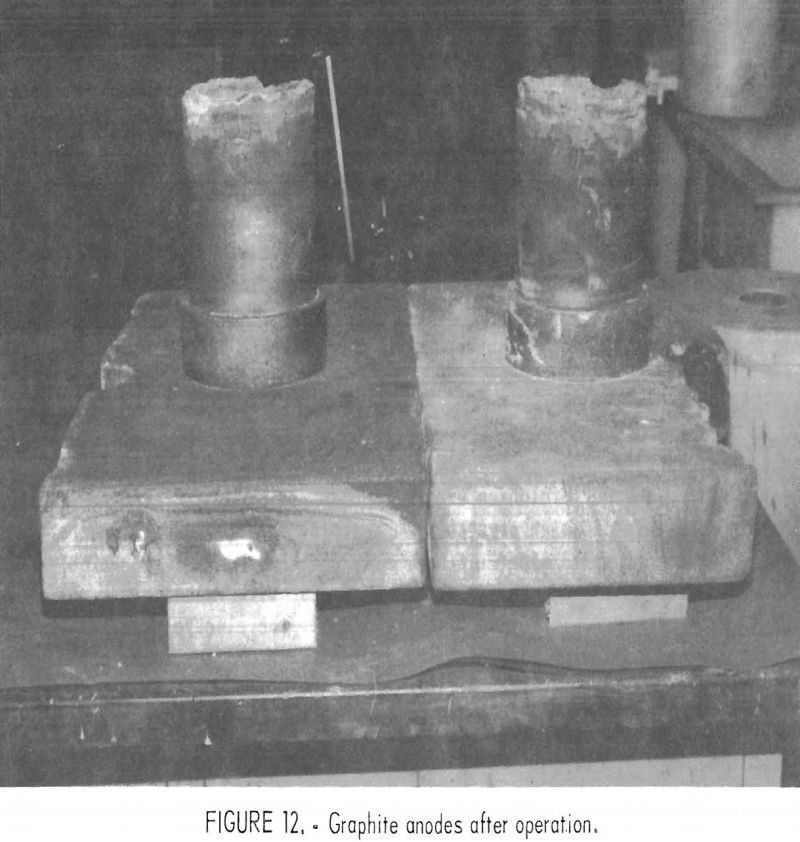
Effects of Impurities on Electrowinning of Lead
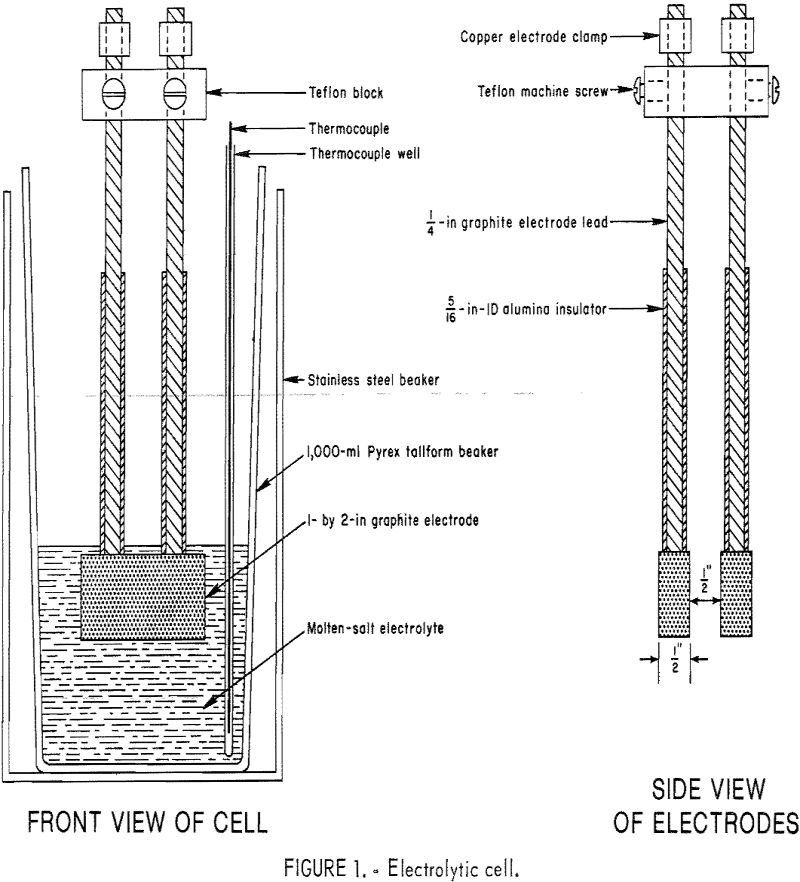
Lead is one of the oldest metals known to man and has been used for hundreds of years. The method for producing lead from galena has changed very little. A lead concentrate is mixed with fluxing agents, roasted to remove sulfur, and heated to about 1,000° C with carbon to obtain an impure metallic product, […]
Electrolytic Method for Recycling Scrap Batteries
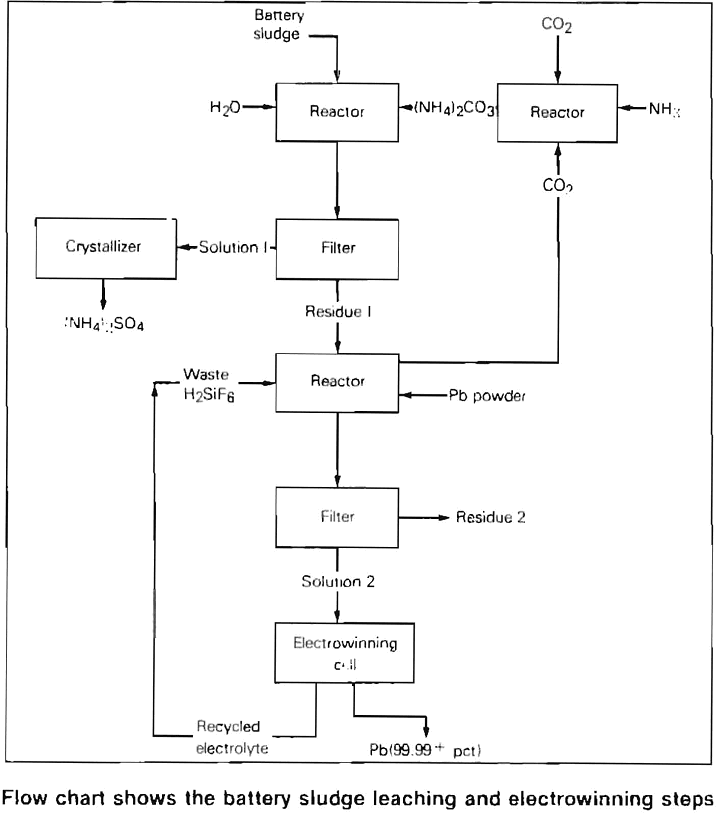
Electrolytic Method for Recycling Scrap Batteries Objective To devise an economical, environmentally acceptable method for recycling scrap lead-acid batteries. Approach A combination electrorefining-electrowinning method for recycling lead metal and sludge from scrap batteries was devised which produces a 99.99 + percent pure lead product and eliminates the lead and sulfur oxide emissions that are […]
Dewatering Talc Slurry
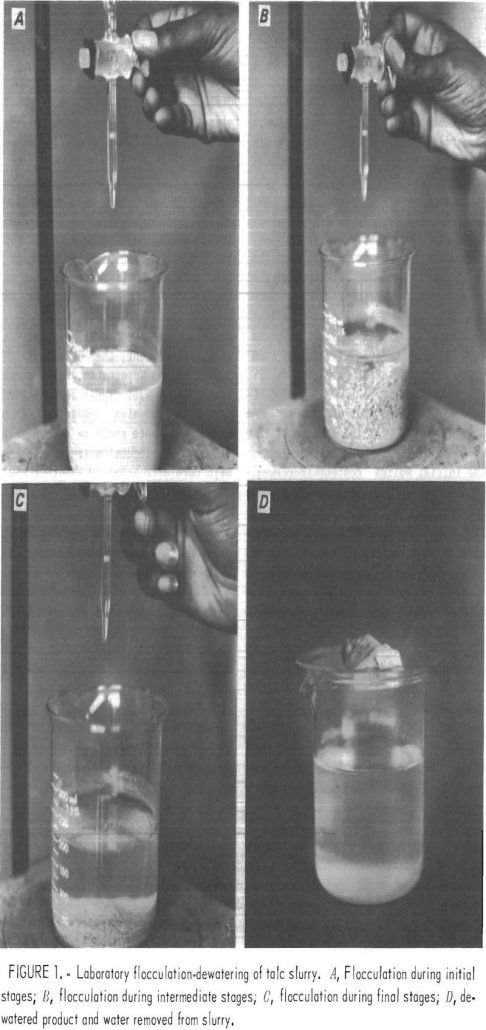
Talc, a hydrated magnesium silicate, is a major constituent of soapstone, which is used in the manufacture of thermal and electrical insulators. Talc also finds applications as filler for use in the paper rubber, and textile industries, in the preparation of soap, cosmetics, lubricating and special polishing agents, as well as in the paint and […]
Microwave Acid Dissolution of Metal Samples
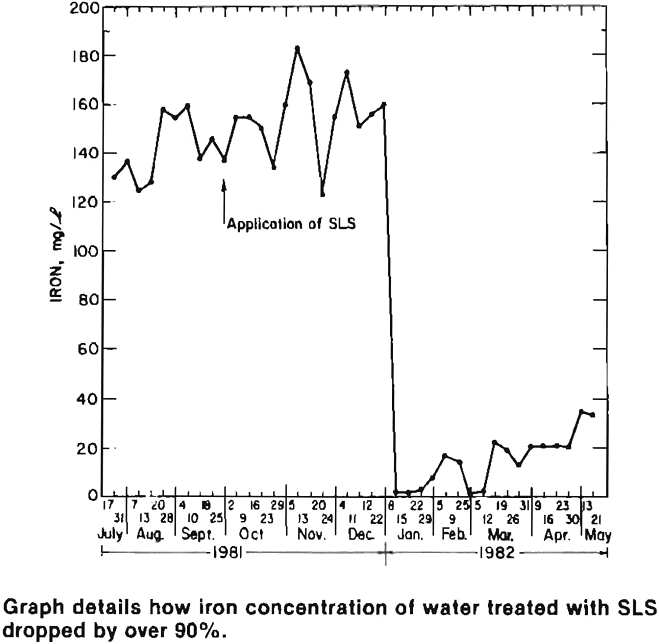
Microwave Acid Dissolution of Metal Samples Objective Reduce or prevent acid mine drainage from coal refuse piles and surface mines by inhibiting the growth of acid- causing bacteria. Approach A dilute surfactant or detergent solution is applied directly to coal refuse piles or overburden using a hydroseeder or road watering truck. The surfactant treatment can […]
Concrete Crib Design
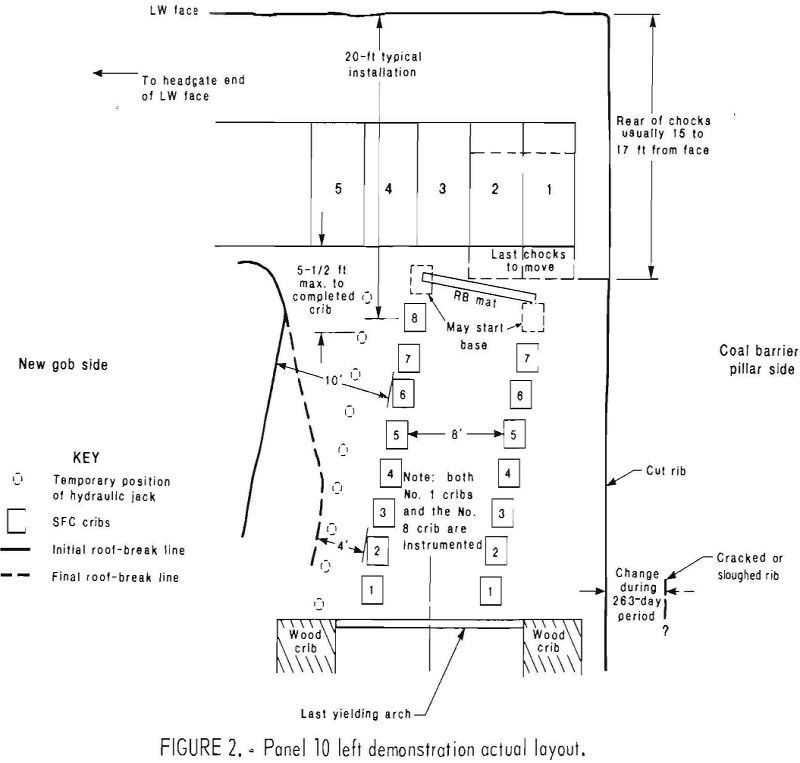
This research is a part of an ongoing effort by the Bureau of Mines to improve health and safety in coal mining as directed by the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1969 and amendments of 1977. The concrete crib design and field testing project has evolved from laboratory research to a verification and […]
Claw Hammer Scaling Tool
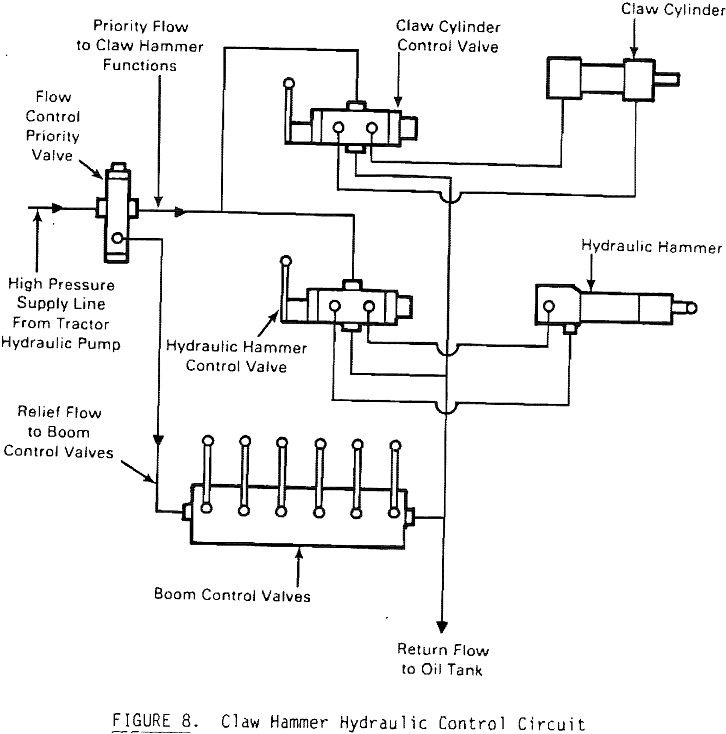
Proper scaling is necessary for safe operation during any underground mining activity. This need is documented in the mandatory regulations for scaling found in 30 CFR 57. In many U.S. mines operating today, scaling is accomplished by manually barring-down the loose material from around the mine opening. Barring-down requires a great deal of physical strength, […]
Wire Ropes & Mine Hoisting
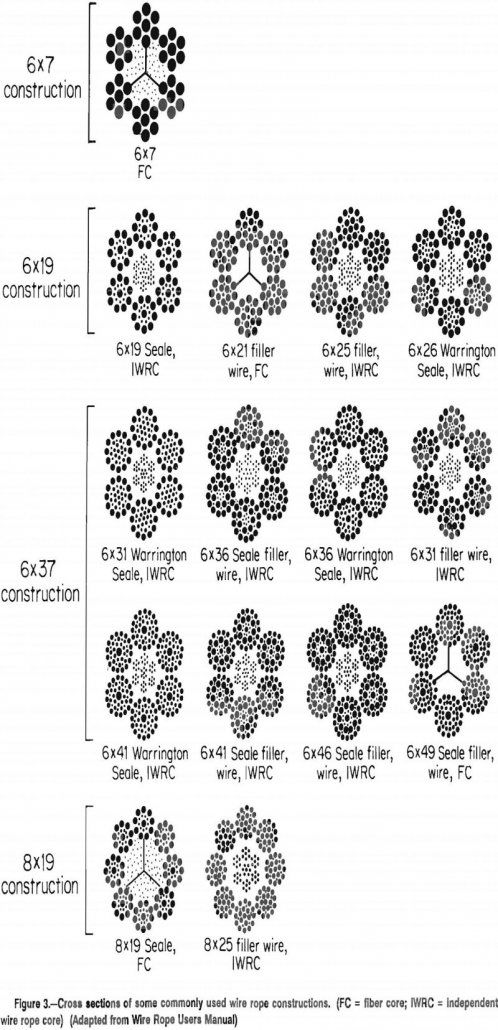
Although wire rope has been in use for over 100 years, it is a complex structure that is still not well understood. Wire ropes are made in diameters from less than 1/32 to more than 7 in and can have as many as 900 individual wires. The mining industry uses a lot of wire rope, […]
