Rock Failure Tilt Precursors
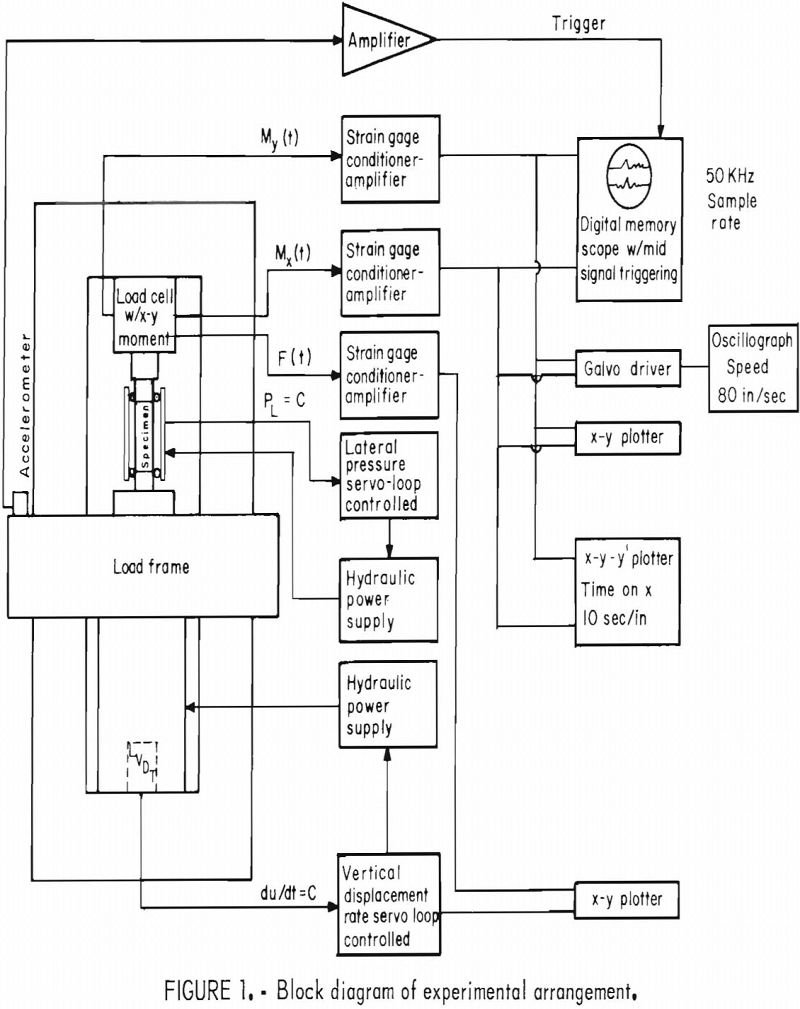
A scale-invariant theory of rock failure has been proposed that predicts precursor effects prior to failure, such as anomalous VP/VS behavior and tilt, will occur in either dry or wet rock. Because the theory is scale invariant, these effects are predicted to occur on the laboratory scale over a time interval of a few milliseconds […]
How to Separate & Recover Molybdenum & Rhenium
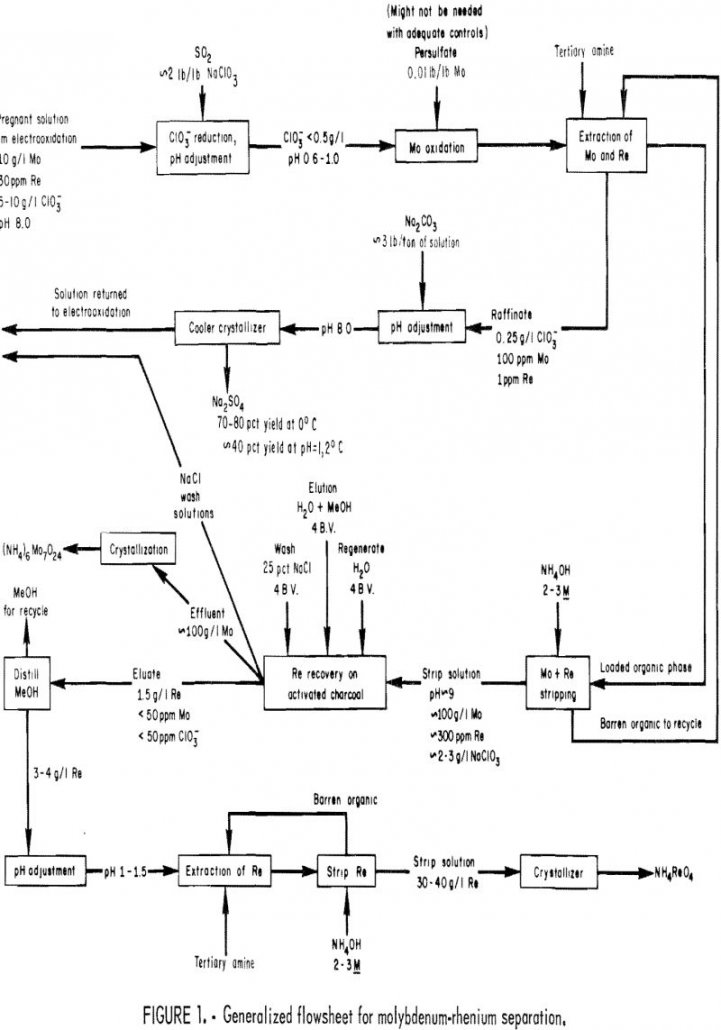
Projections for the expanded use of rhenium as a catalyst in the catalytic reforming of gasoline stocks to make low-lead gasoline prompted the Federal Bureau of Mines to investigate techniques for rhenium and molybdenum separation and recovery. In current technology, rhenium is recovered from the roaster gases produced during the oxidation of molybdenite concentrates. The […]
Leach Chalcopyrite using Lime Roasting Process
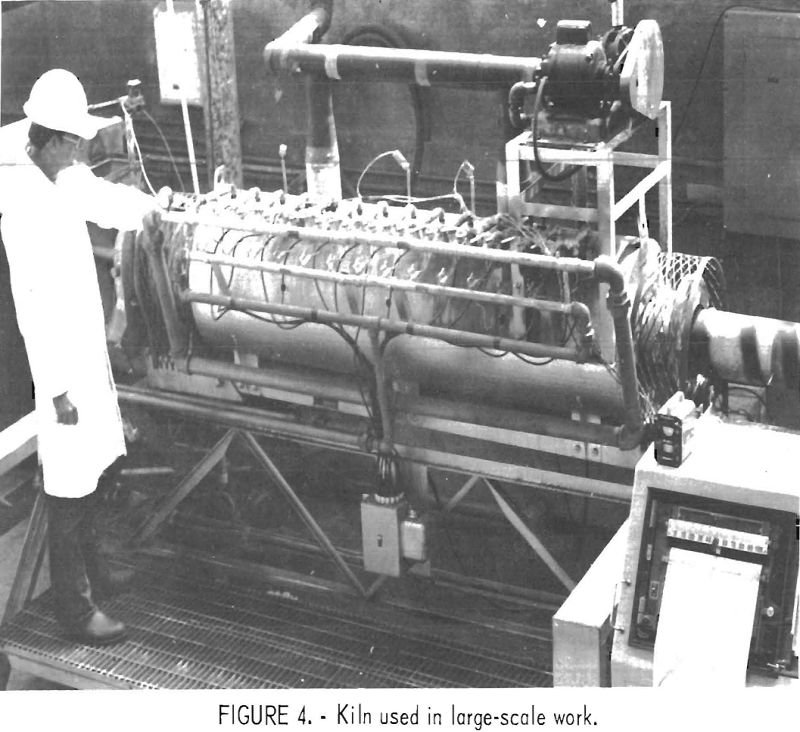
Most copper is now produced from chalcopyrite flotation concentrate by smelting. While smelting achieves high recoveries of metal values at a reasonable cost, it is responsible for the discharge of large amounts of SO2 to the atmosphere. Roaster gases and, occasionally, converter gases are processed to obtain sulfuric acid, but gases from reverberatory furnaces, which […]
Copper Electrowinning from Chloride Solutions
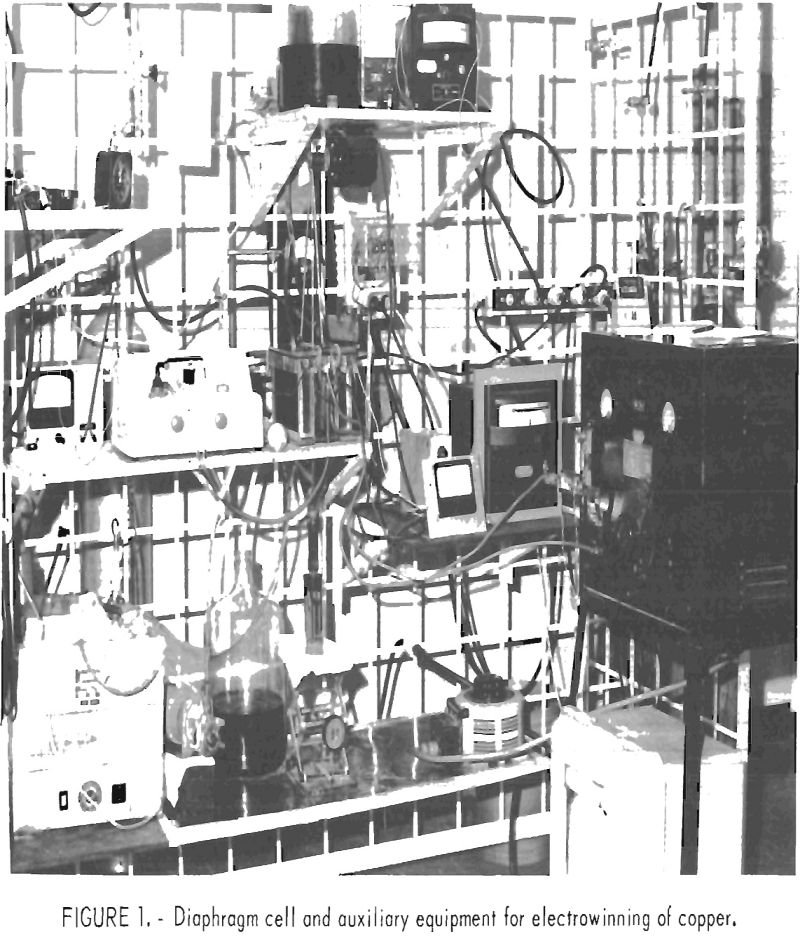
The object of this research was to investigate procedures for recovering copper from chloride solutions as part of a larger program involving the application of chlorination techniques to copper and other base metal sulfide concentrates. In the first step of the process, a pelletized chalcopyrite concentrate is chlorinated in a vertical shaft countercurrent chlorinator. Molten […]
Composition of Lead Sinter

Blast furnace smelting of lead began over 100 years ago. The preparation of feed for the smelting operation always has been an important factor especially the elimination of sulfur by roasting. Over the years roasting progressed from heap roasting to reverberatory roasting, blast roasting in pots, and finally to continuous blast roasting of thin layers […]
Raney Nickel Alloy Melting and Casting
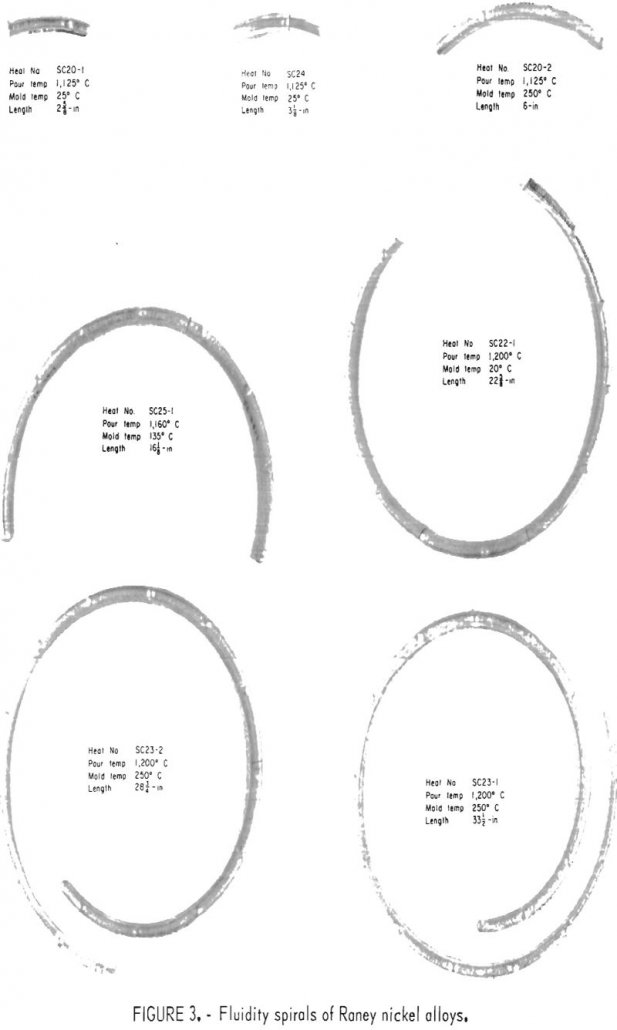
The conversion of coal into a high-Btu gas as a means of augmenting existing supplies of natural gas has been the subject of much research. The Bureau of Mines has played an active role in this area and has developed the Synthane process. The Synthane process consists of reacting coal, steam, and oxygen in a […]
Chalcopyrite Electrowinning Process
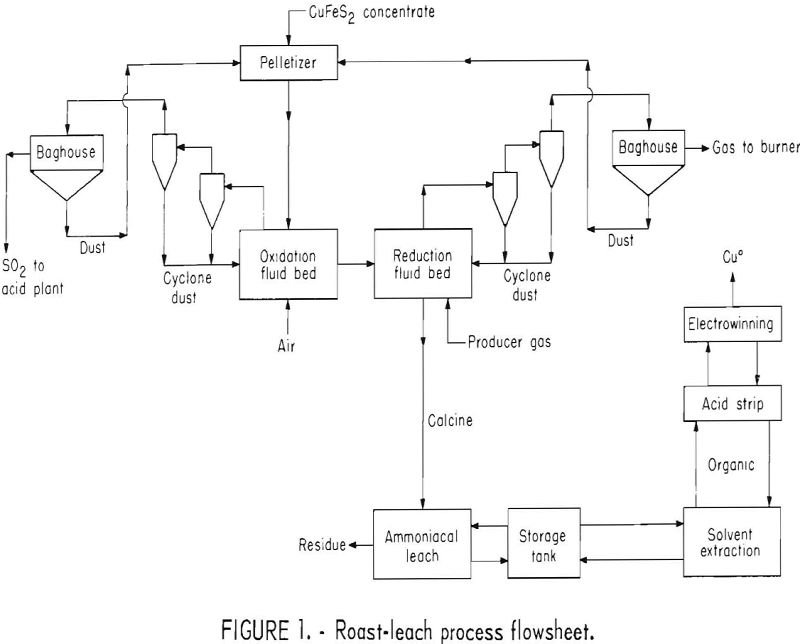
About 85 percent of the copper produced in the United States is derived from copper sulfide ores by flotation, smelting, and electrolytic refining. Chalcopyrite is the predominant copper sulfide mineral in vein and disseminated porphyry-type deposits. Projected production of chalcopyrite concentrates from copper deposits now being developed and from expanded operations will soon exceed existing […]
How to Convert Stainless Steel Dust – Waste to Alloy
The manufacture of stainless steel results in a variety of wastes; the number, quantity, and composition are dependent on the manufacturing method used, the alloys produced, and the manner and degree of finishing of the metal products. A single domestic plant using conventional electric arc furnaces in conjunction with the argon-oxygen process, and producing finished […]
Heat Capacity Enthalpies of Cuprous and Cupric Sulfides
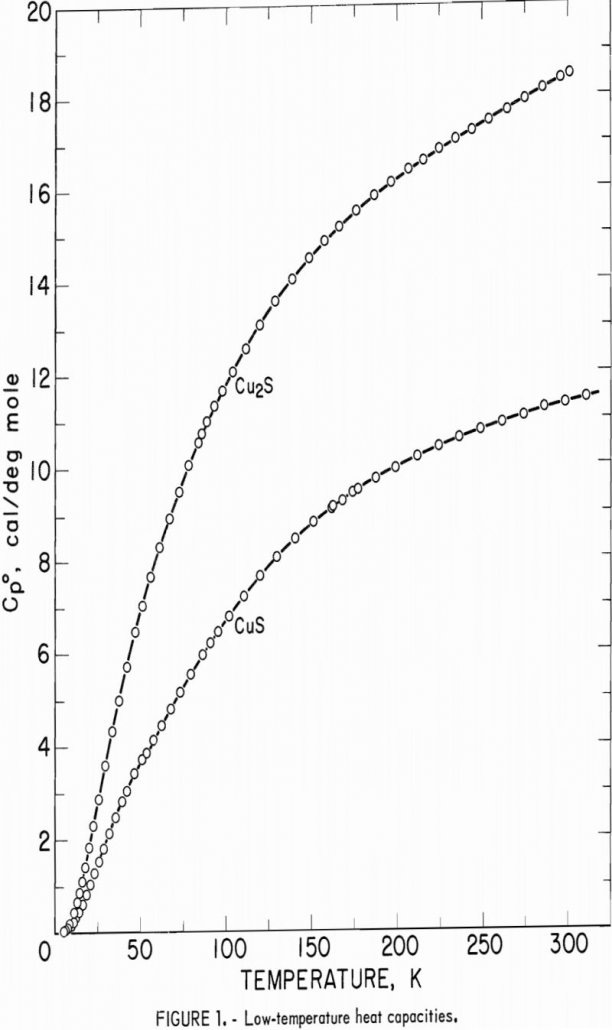
The present investigation of the low-temperature heat capacities and high-temperature enthalpies of synthetic cuprous sulfide and cupric sulfide is one in a series of thermodynamic studies by the Bureau of Mines on metallurgically important copper compounds. Despite the importance of cuprous and cupric sulfides in the processing of copper, thermodynamic data for these substances are […]
Use Sulfuric Acid to Recover Zinc
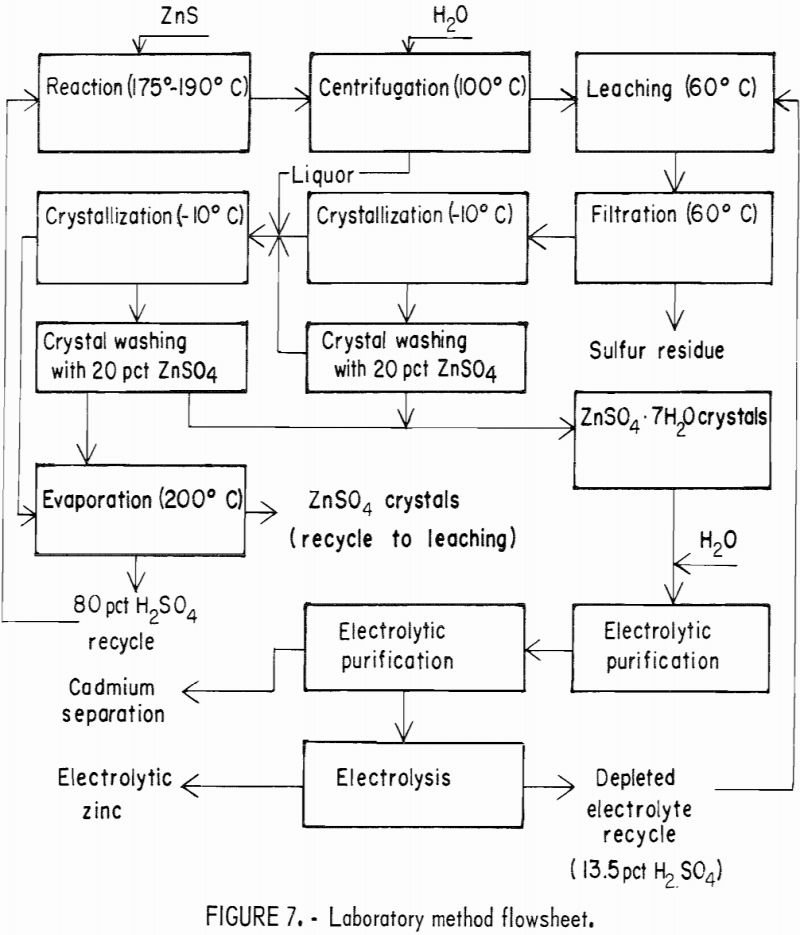
This investigation was conducted by the Bureau of Mines in support of its overall goals of helping to maintain an adequate supply of minerals and metals for future national needs with minimum waste and environmental degradation. The objective of the investigation was to develop a hydrometallurgical method of producing zinc from ZnS (sphalerite) concentrates without […]
