Porphyry Copper Blasting
Some are developing fragmentation technology for in situ extraction systems. An in situ extraction system is attractive because it can be applied to deposits that are presently too low grade to be mined by conventional methods, thereby increasing domestic reserves. In situ extraction also reduces exposure of workers to health and safety hazards, minimizes detrimental […]
Nickel Electrowinning

Increasing the relative motion of the electrolyte with respect to the electrode surface has long been recognized as a means by which the mass transport of ions to the electrode can be increased to allow operation at higher current densities. Basic theories and early experiments were discussed by Nernst, Brunner, Lin, Denton, Gaskill, and Putnam, […]
Chalcopyrite Nitrogen Roast & Leaching Electrowinning

Present copper extraction technology is based principally on pyrometallurgical processing of sulfide concentrates in which high-temperature air-roasting and air-smelting generates large quantities of sulfur dioxide. Because of very stringent environmental standards and increasing cost of energy, there has been a renewed interest in hydrometallurgical processes for recovering copper from sulfide flotation concentrates. Potential advantages of […]
How to Recover Mercury from Cinnabar by Electro-oxidation
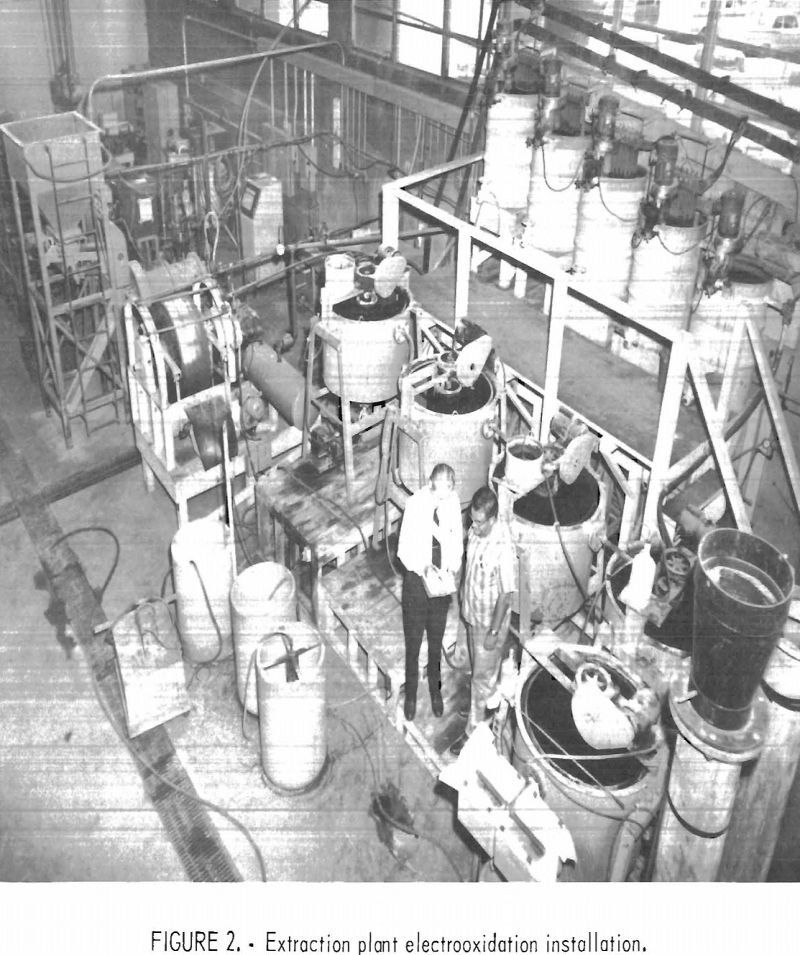

Mercury is customarily recovered from its ores by roasting sulfide minerals and condensing the vapors to obtain the metal. The process is efficient from the standpoint of mercury removal from the calcine; however, vapor and particulate losses in the condensing system, as well as the loss owing to recombination of the mercury with sulfur, can […]
Rock Failure Tilt Precursors
A scale-invariant theory of rock failure has been proposed that predicts precursor effects prior to failure, such as anomalous VP/VS behavior and tilt, will occur in either dry or wet rock. Because the theory is scale invariant, these effects are predicted to occur on the laboratory scale over a time interval of a few milliseconds […]
How to Separate & Recover Molybdenum & Rhenium

Projections for the expanded use of rhenium as a catalyst in the catalytic reforming of gasoline stocks to make low-lead gasoline prompted the Federal Bureau of Mines to investigate techniques for rhenium and molybdenum separation and recovery. In current technology, rhenium is recovered from the roaster gases produced during the oxidation of molybdenite concentrates. The […]
Leach Chalcopyrite using Lime Roasting Process
Most copper is now produced from chalcopyrite flotation concentrate by smelting. While smelting achieves high recoveries of metal values at a reasonable cost, it is responsible for the discharge of large amounts of SO2 to the atmosphere. Roaster gases and, occasionally, converter gases are processed to obtain sulfuric acid, but gases from reverberatory furnaces, which […]
Copper Electrowinning from Chloride Solutions
The object of this research was to investigate procedures for recovering copper from chloride solutions as part of a larger program involving the application of chlorination techniques to copper and other base metal sulfide concentrates. In the first step of the process, a pelletized chalcopyrite concentrate is chlorinated in a vertical shaft countercurrent chlorinator. Molten […]
Composition of Lead Sinter
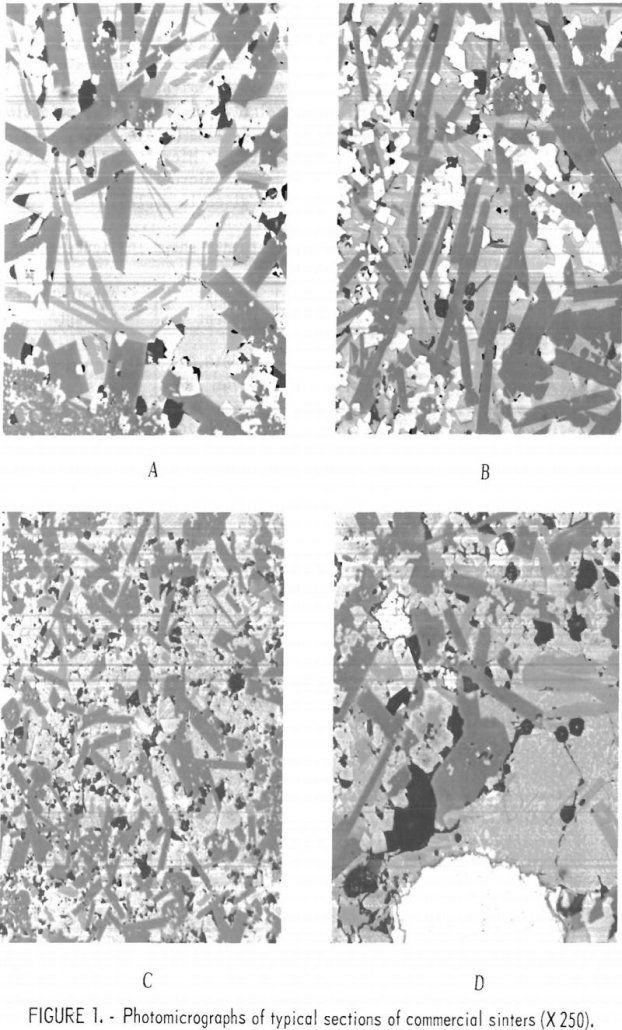
Blast furnace smelting of lead began over 100 years ago. The preparation of feed for the smelting operation always has been an important factor especially the elimination of sulfur by roasting. Over the years roasting progressed from heap roasting to reverberatory roasting, blast roasting in pots, and finally to continuous blast roasting of thin layers […]
Raney Nickel Alloy Melting and Casting
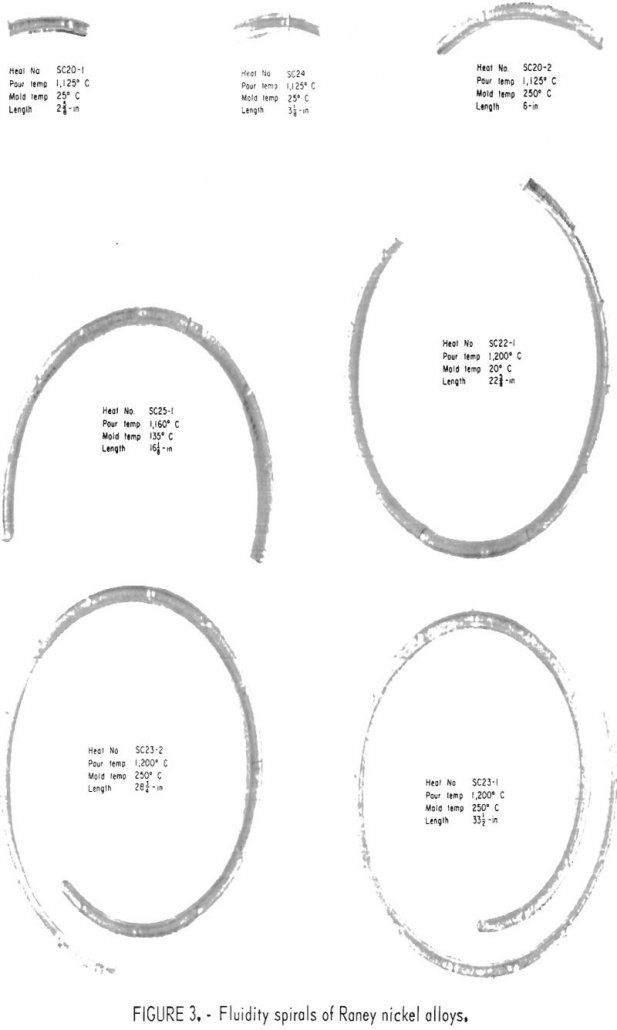
The conversion of coal into a high-Btu gas as a means of augmenting existing supplies of natural gas has been the subject of much research. The Bureau of Mines has played an active role in this area and has developed the Synthane process. The Synthane process consists of reacting coal, steam, and oxygen in a […]
