How to Remove Quartz & Impurities from Refractory Clays
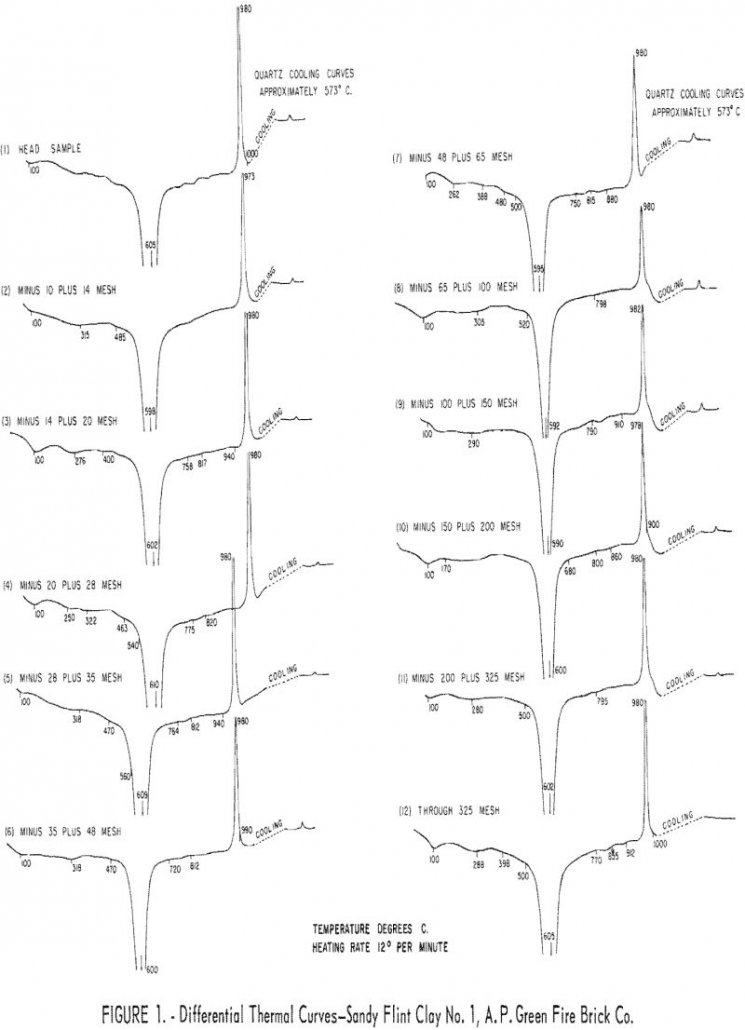
Sandy flint and pyritic plastic clays from east-central Missouri can be beneficiated to good firing quality by ore dressing methods. Quartz and pyrite were the chief contaminants removed by the two gravity concentration methods used in the studies. Most iron-oxide minerals in these clays occur as finely-divided, low-gravity, hydrous material, often in the form of […]
Fine Grain Lead Zinc Sulfides Flotation
This investigation has shown that lead and zinc sulfide minerals, in pulps containing particles all less than 9 microns in size, may be selectively recovered by froth flotation. All but one of the samples yielded lead concentrates-containing at least 57 percent Pb. Selective recovery of lead in the lead concentrate from extremely fine-grained ores was […]
Explosives Explosions and Flames
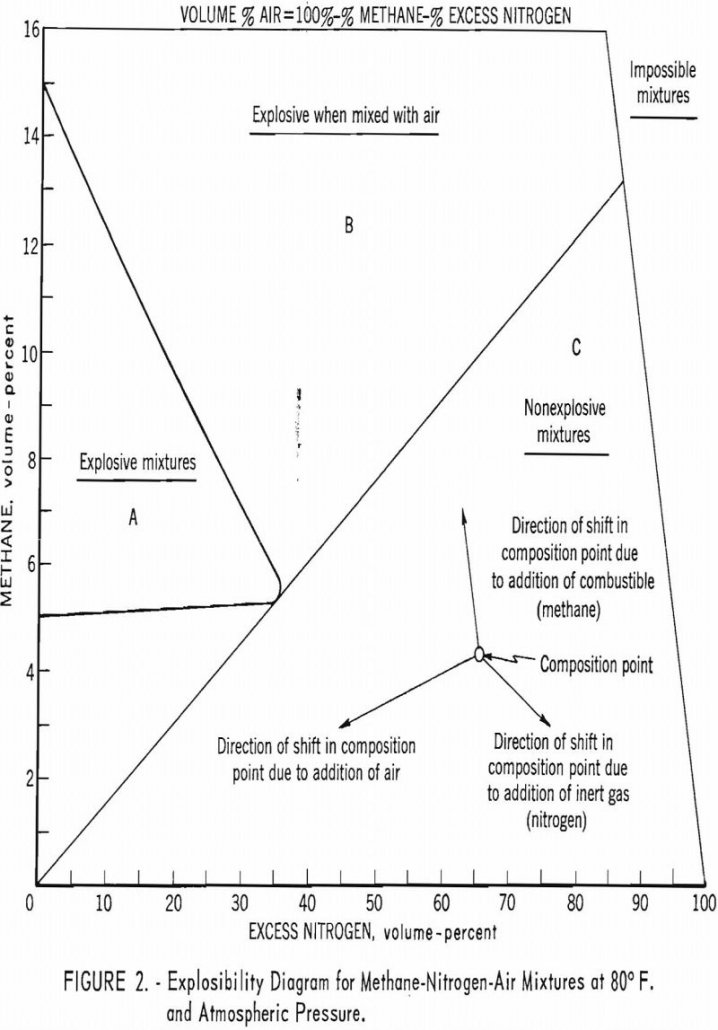
This circular summarizes the research and technologic activities and publications of the Federal Bureau of Mines Division of Explosives Technology during fiscal year 1959 (July 1, 1958-June 30, 1959). Part I briefly describes the programs that were active during the report period and presents a summary of some of the information not published elsewhere. In […]
Spectrograph Analysis of Tungsten
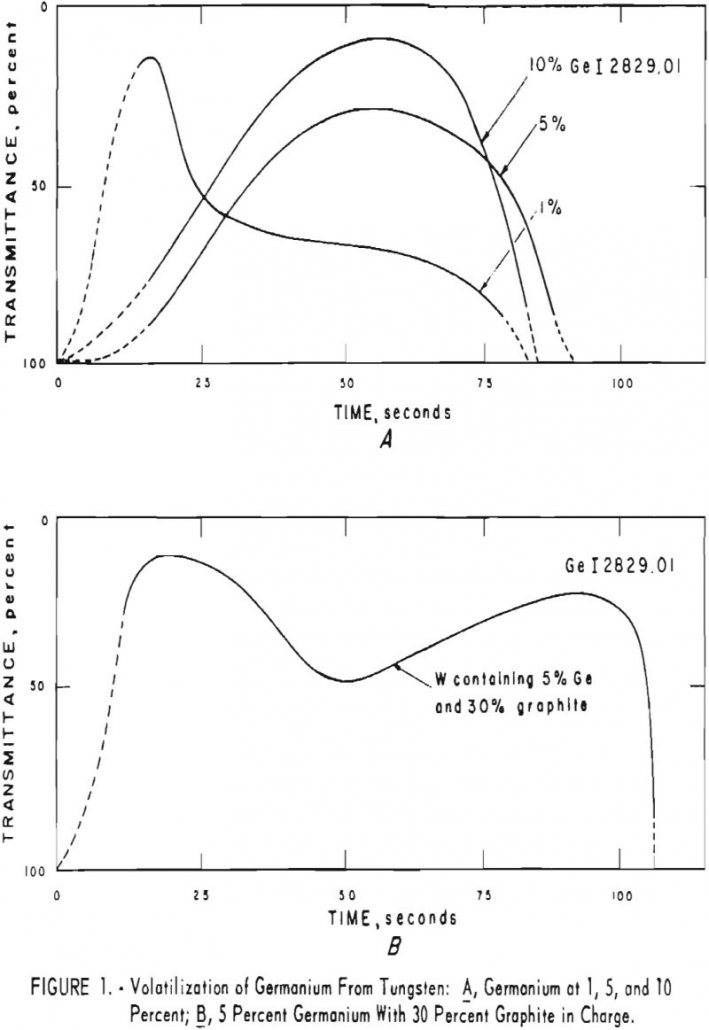
One of the main advantages of this method for estimating impurities in tungsten is that the analysis is performed on the metal. Ideally, samples and standards should be of the same particle size, between 200- and 300-mesh but satisfactory semiquantitative analyses can be made on particles as coarse as 30-mesh. Another advantage is the low […]
How to Separate of Tantalum from Columbium
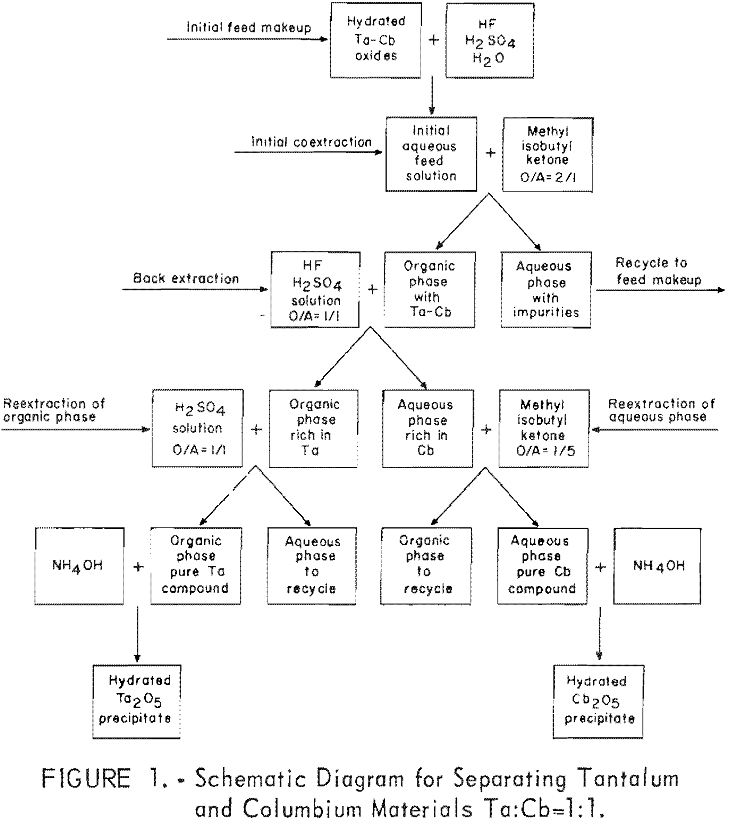
Results of this investigation demonstrate that high-purity columbium and tantalum compounds can be obtained by application of the solvent extraction separation system: Hydrofluoric acid-sulfuric acid-methyl isobutyl ketone. This system is unique in that it not only separates columbium from tantalum, but separates these two metals from other metallic impurities. The system is effective for separating […]
How to Operate a Blast Furnace
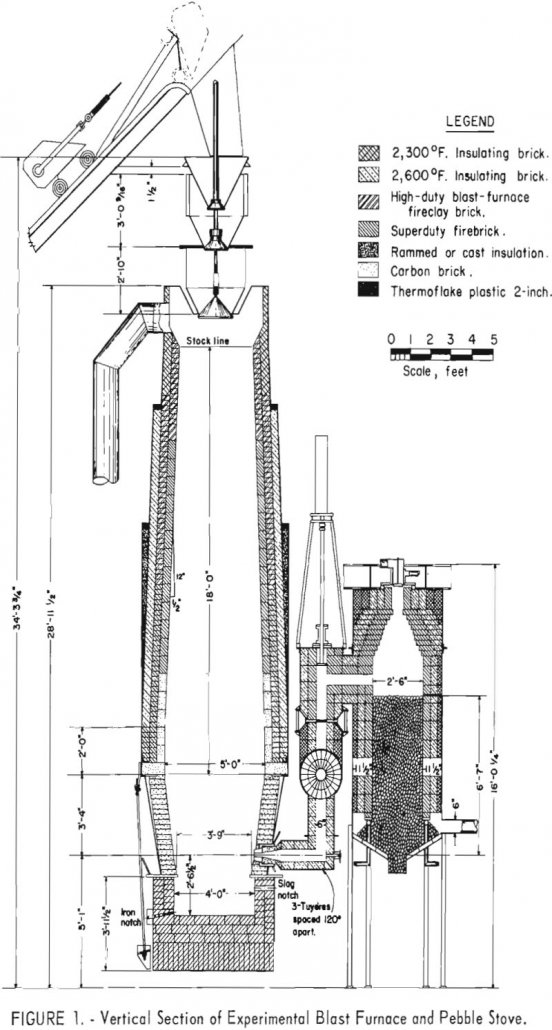
The experimental blast furnace has attracted increasing interest during the past decade as a practical means for investigating a broad range of blast-furnace smelting problems. Under experimental-furnace conditions, information can be obtained with less expenditure of time and raw materials and, therefore, at lower cost than comparable information could be obtained under industrial operating conditions. […]
Phosphorus Pentoxide Content Determination Method
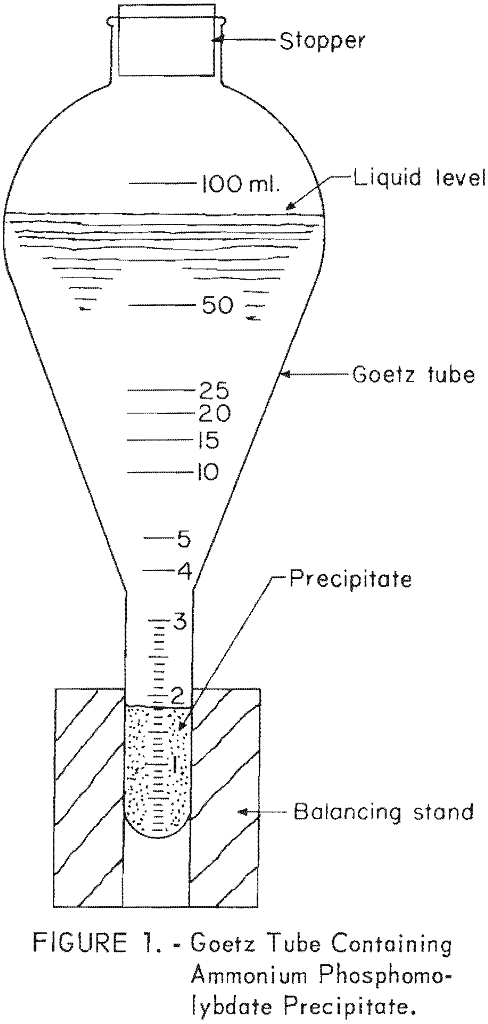
The precipitate method described herein is advantageous because of its rapidity and relative simplicity. This method eliminates the standardization of reagents, second filtration, washing of precipitate, and dissolving of ammonium phosphomolybdate precipitate, all of which are required in the titration step of the usual alkalimetric method. The precipitate method does not approach the accuracy of […]
Nuclear Reactor Simulation
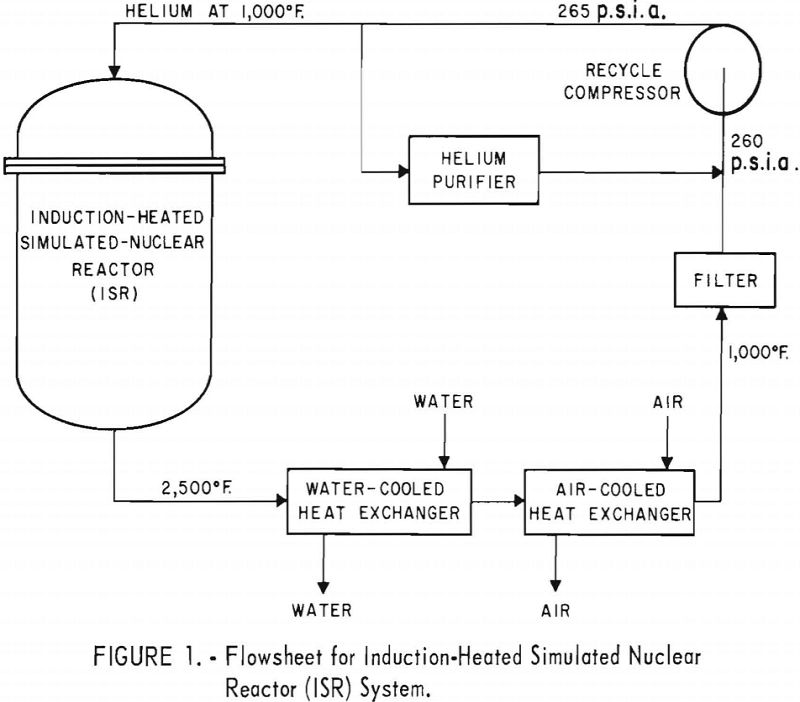
Construction of a 250-p.s.i.g. helium-recycle system to operate with gas temperatures as high as 2,500° F. appears feasible. More development work is required, however, on heat exchangers and compressors. Many problems inherent in large nuclear systems are not present in the pilot-scale ISR system. Although the cooler in the ISR loop operated satisfactorily, thermal expansion […]
Determination of Lithium In Lithium Minerals
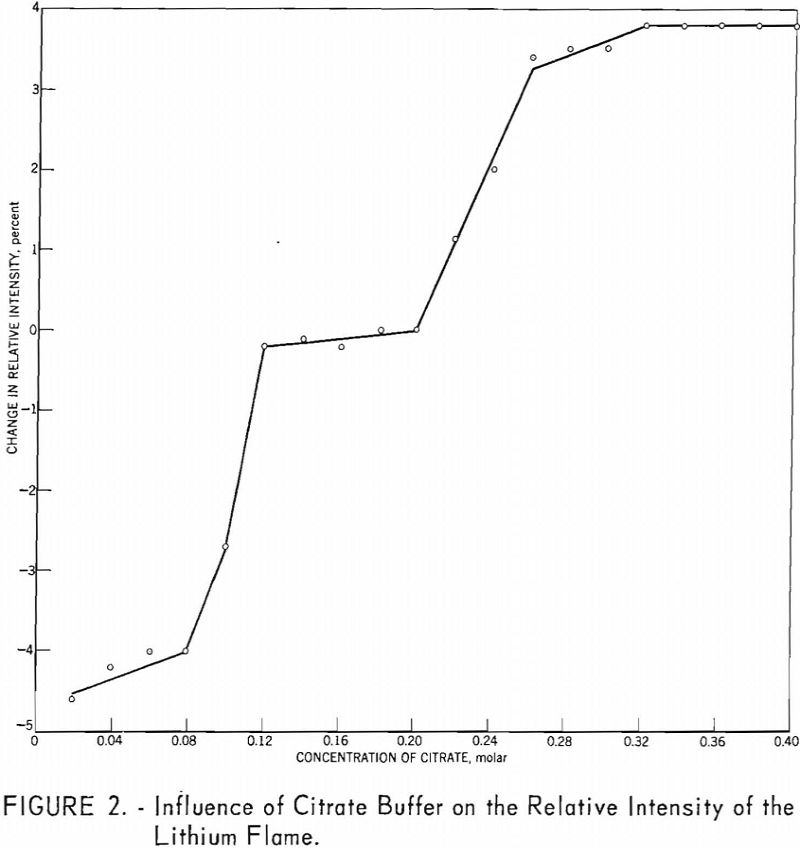
A simplified, routine method for determining lithium in lithium-bearing rock is presented. The sample is decomposed by repeated treatments with nitric, hydrofluoric, and perchloric acids. Since this procedure does not appreciably dissolve beryl, interference by beryllium (the principal interfering cation) is minimized for most samples. The salts are brought into solution with water and enough […]
Asbestos Mining Methods and Costs

This is one of a series of reports prepared by the Federal Bureau of Mines on mining methods, performance, and costs at individual mines in the United States. The primary purpose of these papers is to promote development and conservation of our mineral resources by disseminating technological information on methods, practices, and results that may […]
