How to Identify the Surface Texture of Rock
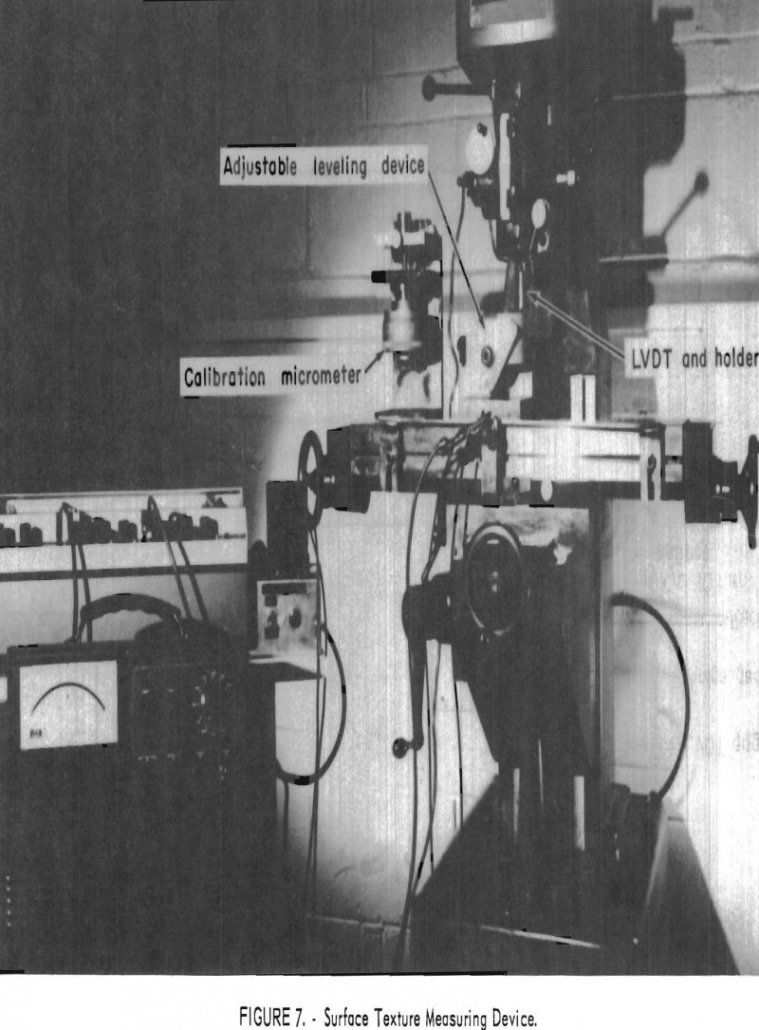
Model studies, using rock, require carefully prepared specimens. Most preparation procedures use some form of grinding or polishing as the last of several steps. During these steps, particularly the final one, the surface formed acquires a configuration defined as texture. Texture is a composite term identifying the physical features called flaws, lay, waviness, and roughness. […]
Electrorefining Yttrium
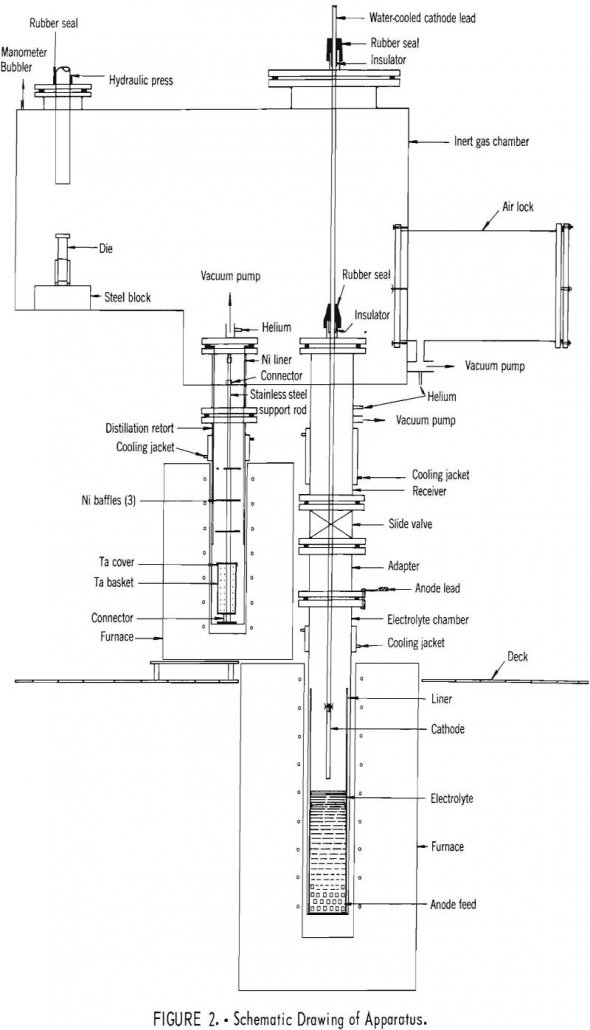
Tests on electrorefining of yttrium were performed in LiCl-YCl3 electrolytes at 710° C, and the deposits were subjected to vacuum-distillation at 880°C to remove salt from the metal. A comparison of the analyses of the anode feed and the product metal indicates that all metallic impurities were substantially lowered, but oxygen was reduced appreciably only […]
Chlorination Of Ferrochromium
Low-temperature chlorination of three types of ferrochromium at 340° to 525° C chlorinated an average of 89 percent of the chromium and 95 percent of the iron contents of the feed materials. From 81.9 to 91.6 percent of the iron was removed by sublimation as FeCl3. The reactor product was a free flowing material which […]
Zinc Copper Titanium Alloys Cast
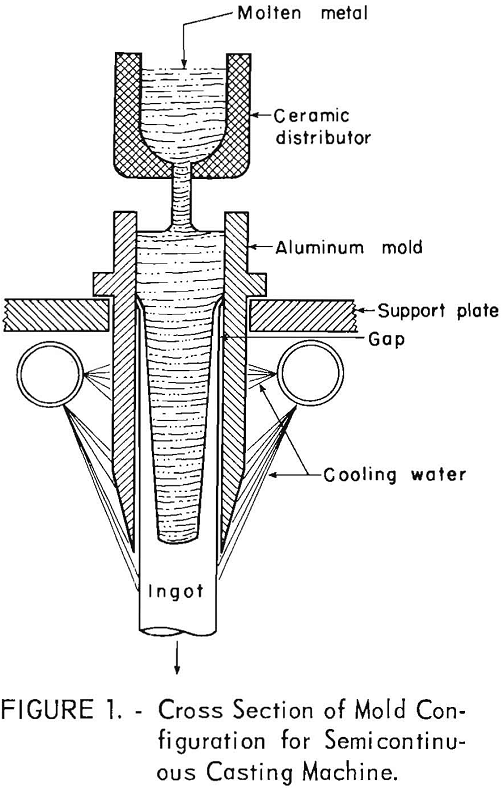
Sound ingots of Zn-Cu-Ti alloys can be semi-continuously cast under appropriate conditions. A modified mold design on a specially constructed, semi-continuous casting stand has permitted casting of ingots having adequate surface quality. With the experimental equipment described, pouring temperatures near 860° F (460° C) produced ingots with better surface quality than when a pouring temperature […]
Ammonium Nitrate ANFO Electric Detonation
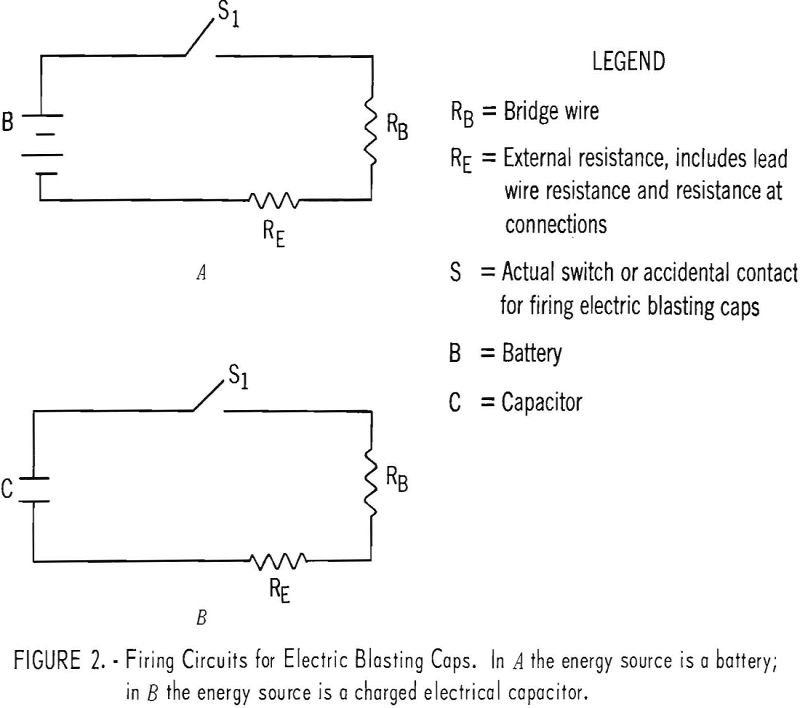
Accidental firings of explosive initiators have occurred occasionally with some uncertain correlation to the pneumatic loading of ammonium nitrate-fuel oil (AN-FO) blasting agents. The exact association, if any, between these firings and static electricity is unknown. This report describes the role of pneumatic loaders in generation or transfer of static electricity and discusses the possible […]
Determining Compressive Strength of Rock
The major conclusion to be drawn from the four series of tests is that reasonable care in preparing specimens and conducting compression tests on a hydraulic machine will provide an acceptable compressive strength value for most applications. For normal uniaxial compression tests, nonparallel ends, end surface texture, steel false end platens, and spherical head friction […]
How to Use Heat to Separate Copper from Steel Scrap
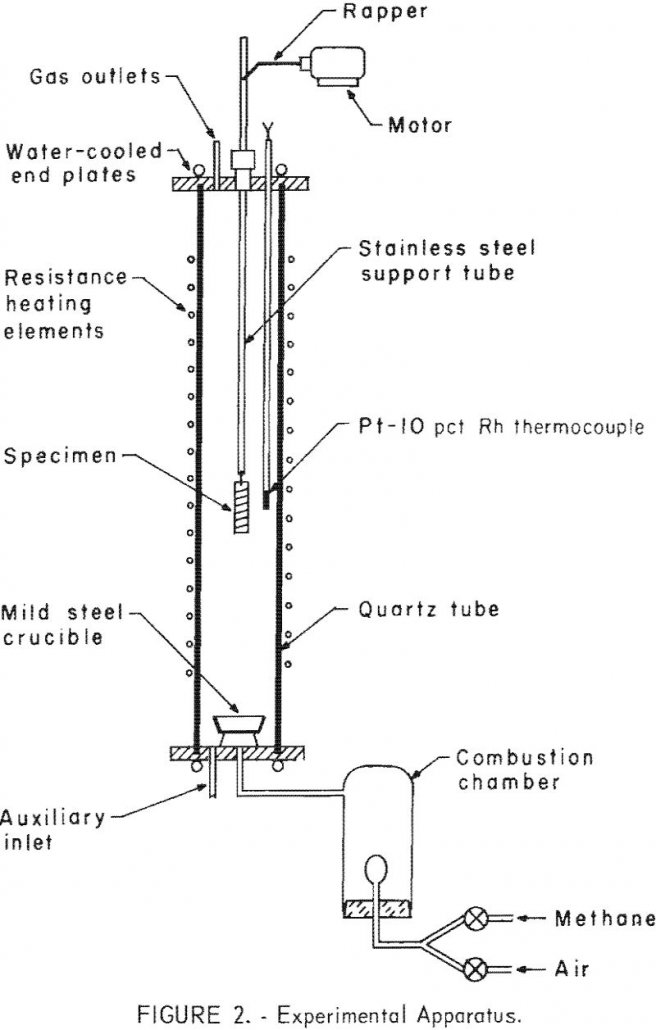
We initiated a program was concerned with the utilization and disposal of steel scrap, as the pollution and unsightliness caused by the accumulation of steel scrap in junkyards. Maybe we could use heat to Separate Copper from Steel Scrap? In the past decade the problem has become increasingly serious; greater amounts of steel scrap are […]
Electrowinning Neodymium
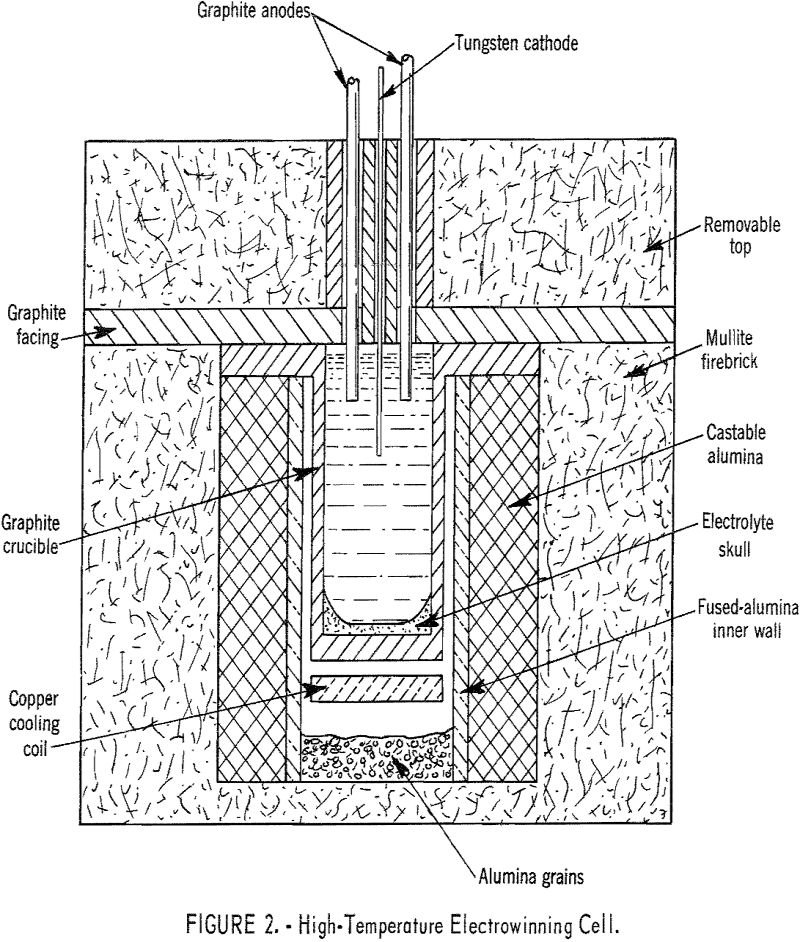
Cells were designed and successfully operated on a laboratory scale for electrowinning high-purity neodymium, praseodymium, and didymium, as well as the higher melting-point metals, gadolinium, dysprosium, and yttrium. The elements were prepared from their oxides, dissolved in fluoride melts, and deposited as liquid metals on a tungsten cathode. Similarly, alloys of these metals and samarium, […]
Separate Nickel and Cobalt by Electrorefining
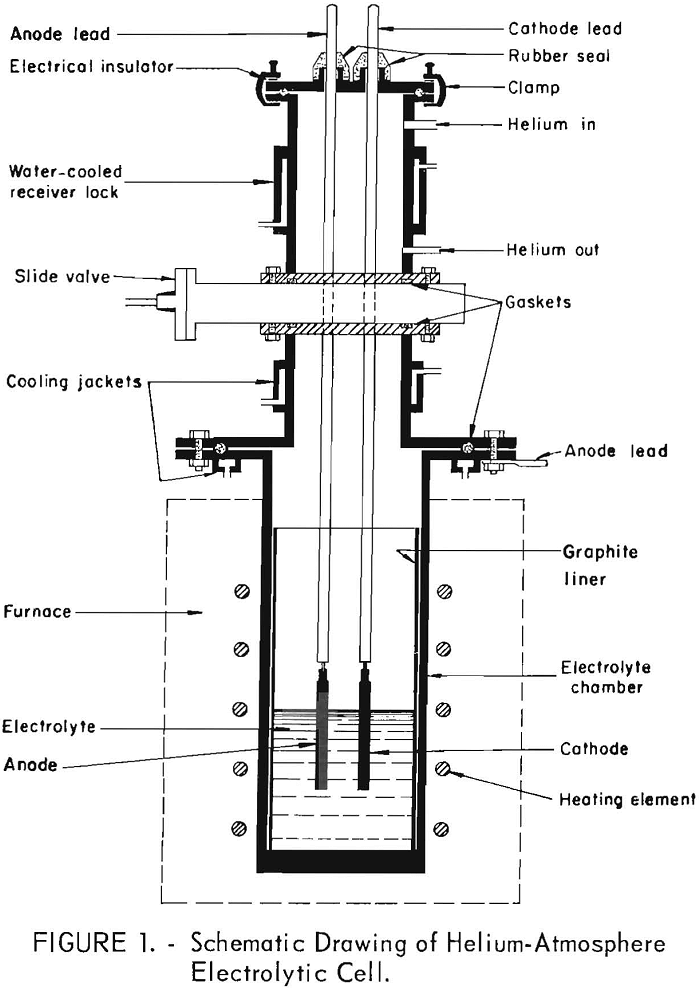
The electrolytic separation of nickel and cobalt by electrorefining in a molten salt electrolyte was shown to be technically feasible. Nickel-cobalt alloys containing up to 5.5 percent cobalt were electrorefined in a KCl-LiCl-NiCl2 electrolyte to a high-purity nickel metal meeting atomic energy specifications. The amount of cobalt transferred to the cathode deposit was found to […]
Copper Hydrometallurgy

Copper hydrometallurgy the leaching of siliceous low-grade copper-bearing ores and waste rock that cannot be processed economically by milling and concentrating is an important low-cost process for recovering copper. In the free world, the United States is the principal user of this process, and in 1965 nearly 10 percent of the U.S. production of primary […]
