Electric Smelting Lead Zinc
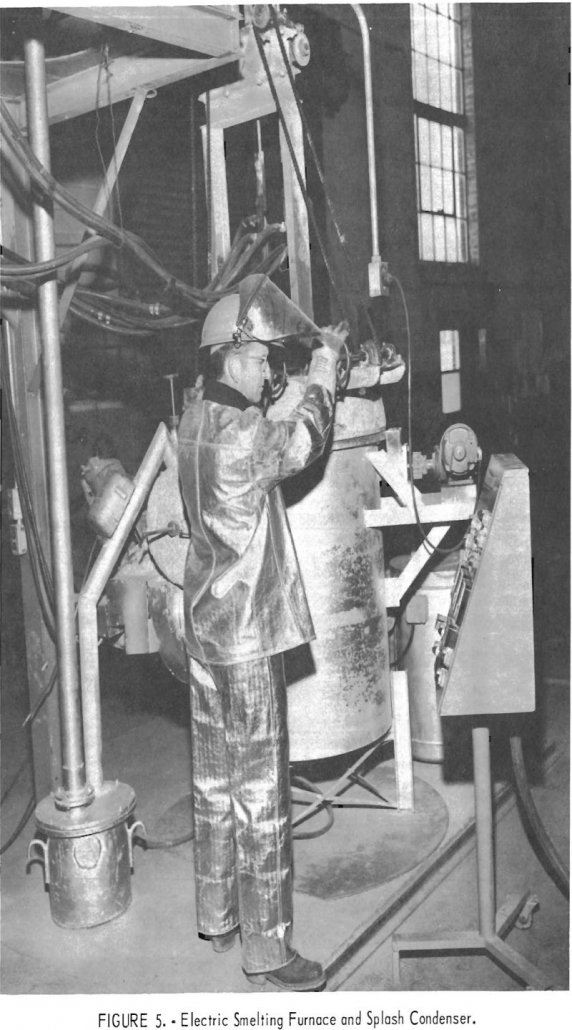

Based on the results obtained during this investigation, slag-resistance, open-bath electric smelting of complex lead-zinc sinter is not considered feasible. Inherent characteristics of electric smelting promote and permit excessive transfer of iron, lead, and volatile slag constituents to the condenser when smelting normal lead-zinc sinter. Reaction of these constituents with zinc causes its degradation. Consequently, […]
Mine Sampling Assays
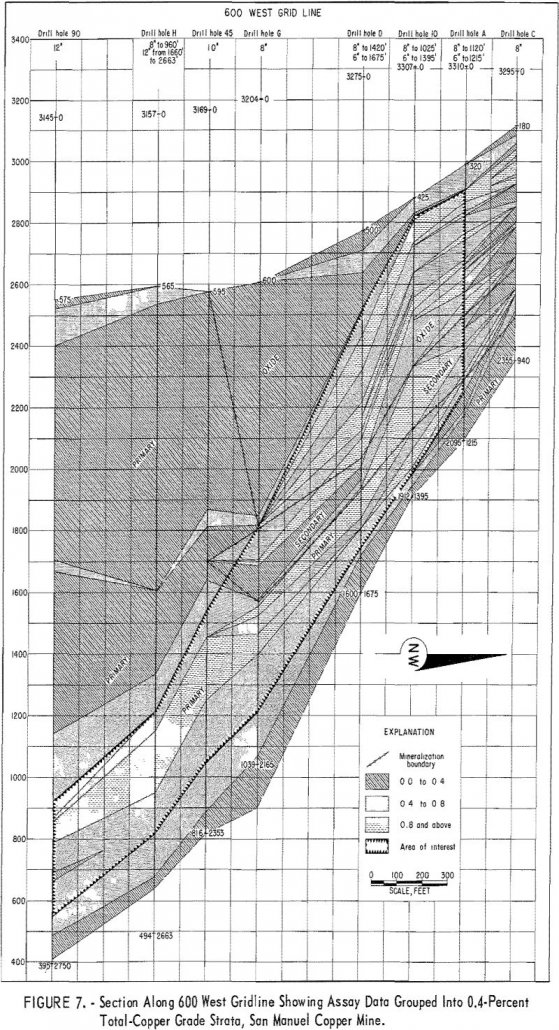
A continuing problem in mine evaluation, planning, operations, and production scheduling is the necessity of assigning some value for the grade of mineralization which occurs in the area lying between two sample points. This problem is particularly prevalent in evaluating ore deposits because of the usual wide-spaced drilling and sampling in the exploration phase of […]
Recover Hydrofluoric Acid from Fluosilicic Acid Waste
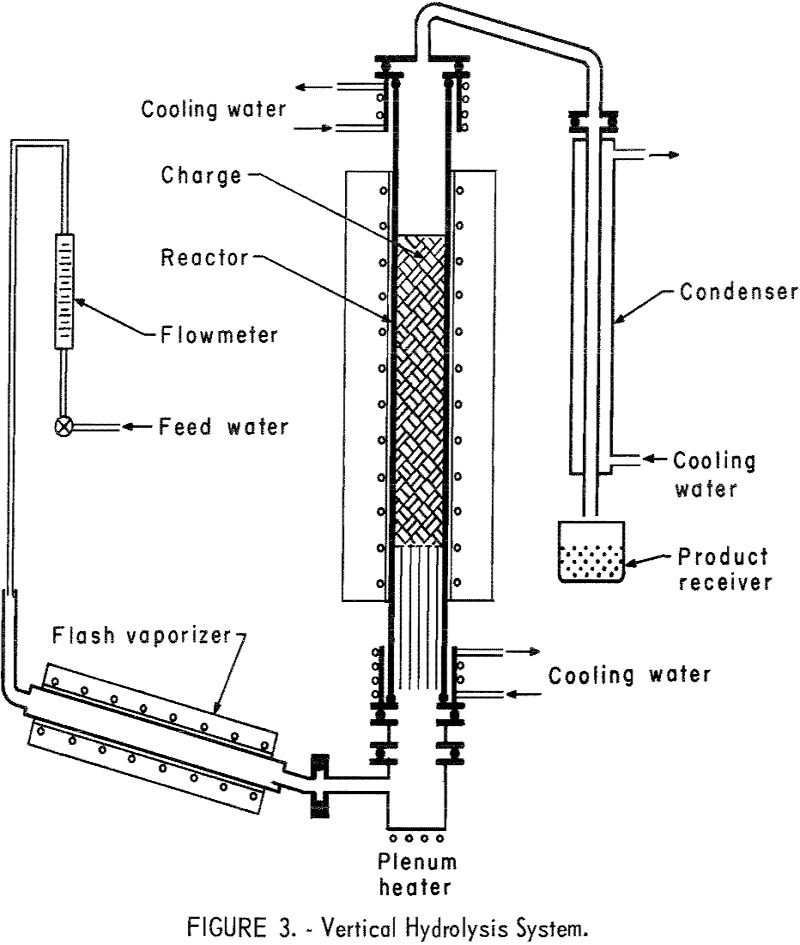
This report describes a preliminary investigation of methods for recovering hydrofluoric acid (HF) from waste byproduct fluosilicic acid (H2SiF6). Fluosilicic acid is generated by plants processing phosphate rock in the manufacture of fertilizer; most phosphate rock contains 3 to 5 percent fluorine in the form of the mineral fluorapatite (Ca3(PO4)3F). When this fluorine-bearing material is […]
Calcium Vanadate Precipitation and Processing
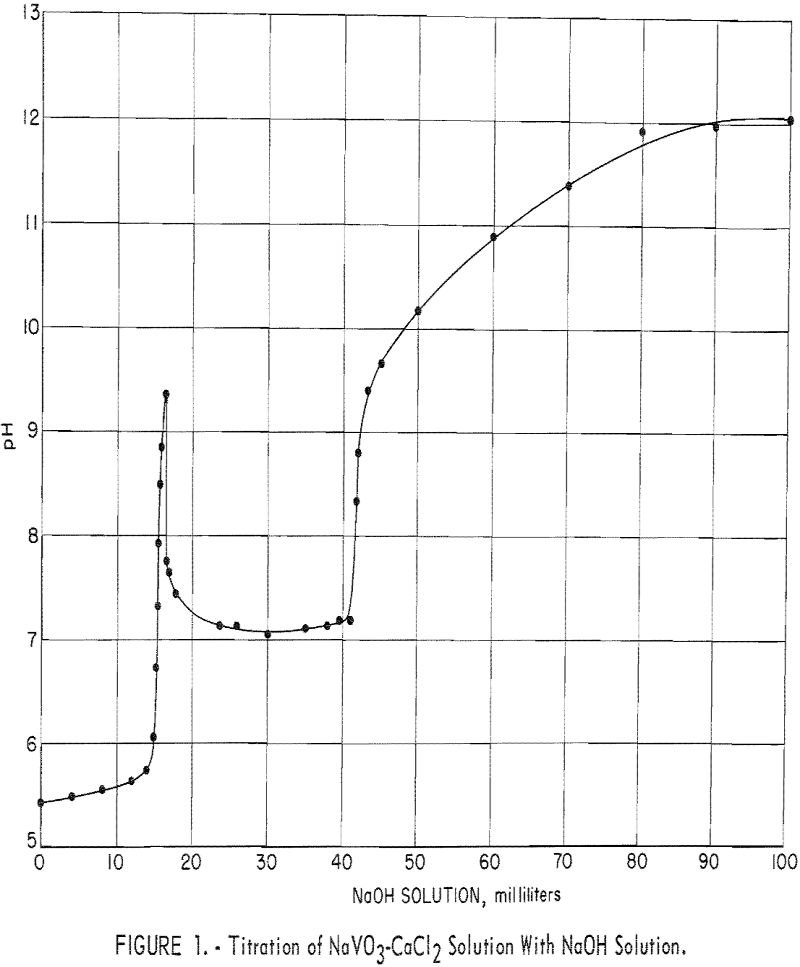
This report presents the results of a Bureau of Mines laboratory investigation to ascertain if the precipitation of calcium vanadate from low-tenor alkaline leach solutions can be practically employed for producing marketable technical-grade oxide (red cake) or ammonium metavanadate (AMV). The research was undertaken during the development of an autoclave process for extracting vanadium from […]
Iridium Electrodeposition
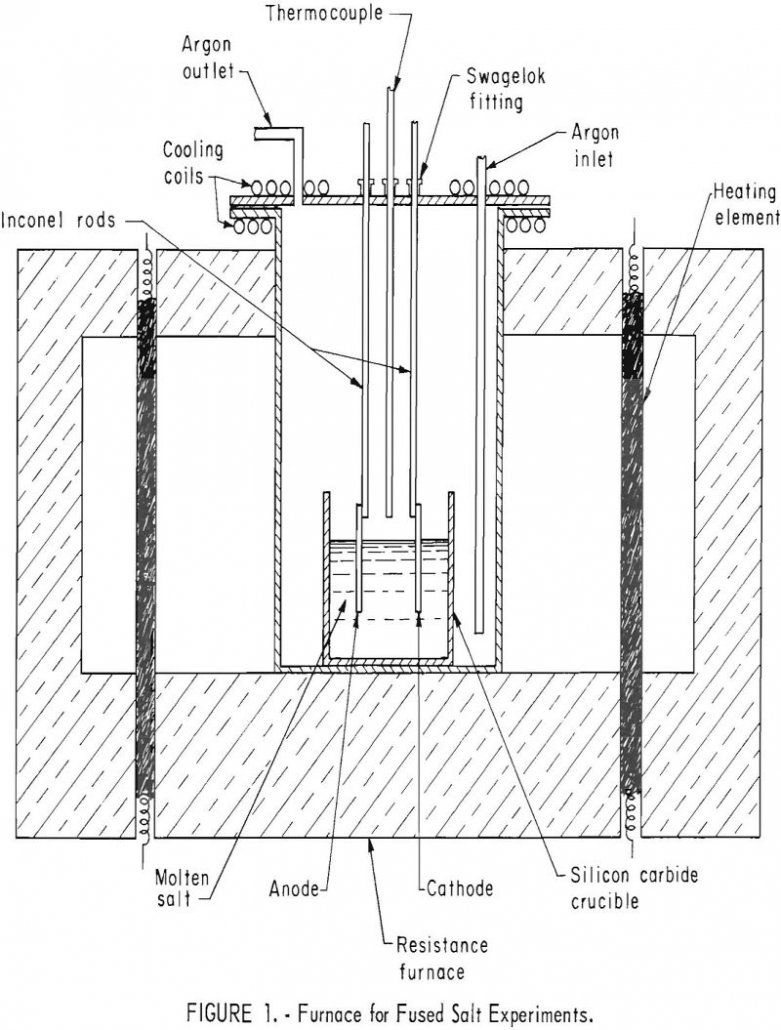
Adherent, coherent electro-deposits of iridium 15 mils thick and alloys of iridium 4 mils thick were formed in argon atmosphere from fused cyanide electrolytes. The use of pure iridium to prevent oxidation appears limited to temperatures under 1,000° C because of volatility of the oxide of iridium. Iridium alloyed with platinum-group metals such as platinum, […]
Magnetic Separation of Pyrite
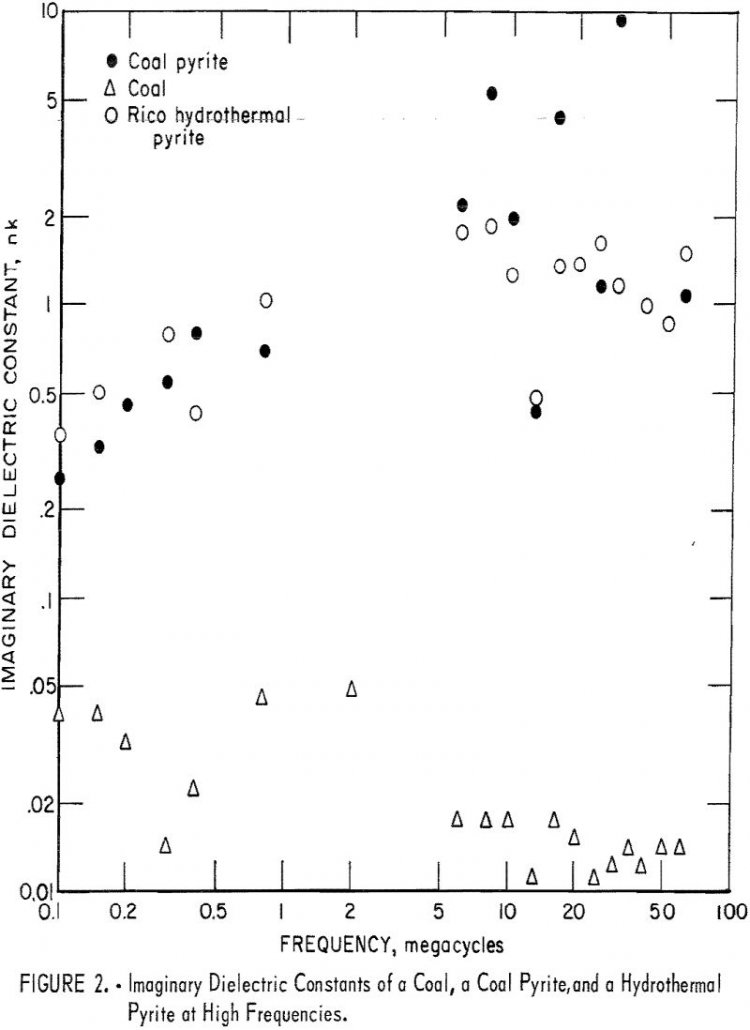
Exploratory measurements of the dielectric constant of coal and pyrite indicate that pyrite in coals can be heated selectively. If about 1 percent of the radiation is absorbed in the process, it would be very attractive from a commercial standpoint. The following recommendations are offered. More precise and systematic measurements of the dielectric properties of […]
Smelting low Pyrite Copper Concentrate
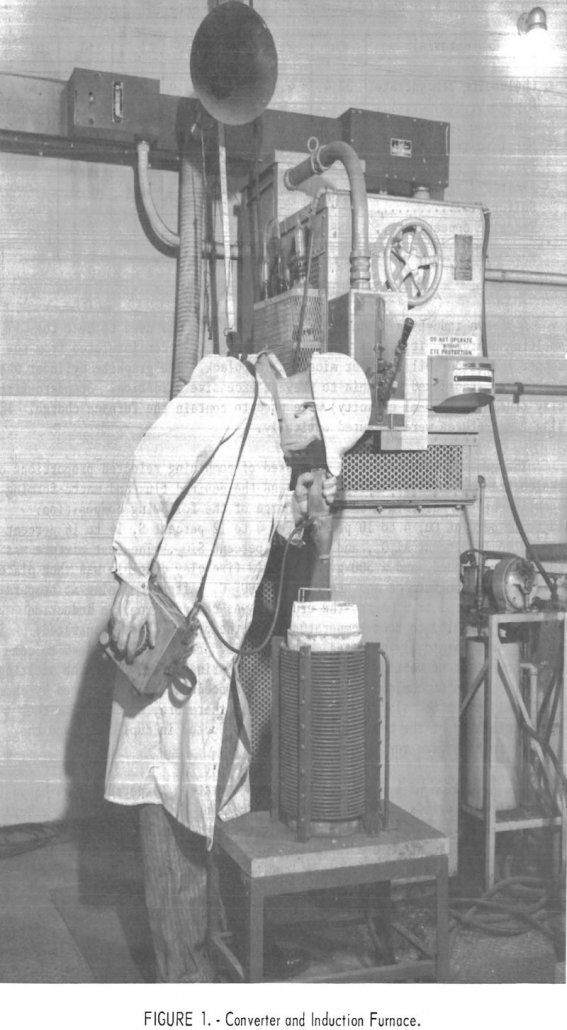

A laboratory smelting study was conducted on a copper ore containing chalcocite and native copper to test the technical feasibility of non-pyritic smelting (low pyrite). The results of this investigation led to the following conclusions, based on sulfur and copper recoveries and matte compositions: The concentrate can be effectively smelted when pyrite is replaced by […]
Columbium Alloys

As a continuing endeavor, the Bureau of Mines is developing columbium and tantalum alloys for high-temperature applications. This investigation was undertaken to improve the high-temperature properties displayed by the more common columbium alloys that are commercially available. In a previous investigation beneficial improvements were realized by alloying columbium with elements such as hafnium, tungsten, titanium, […]
Columbium Tantalum Flotation
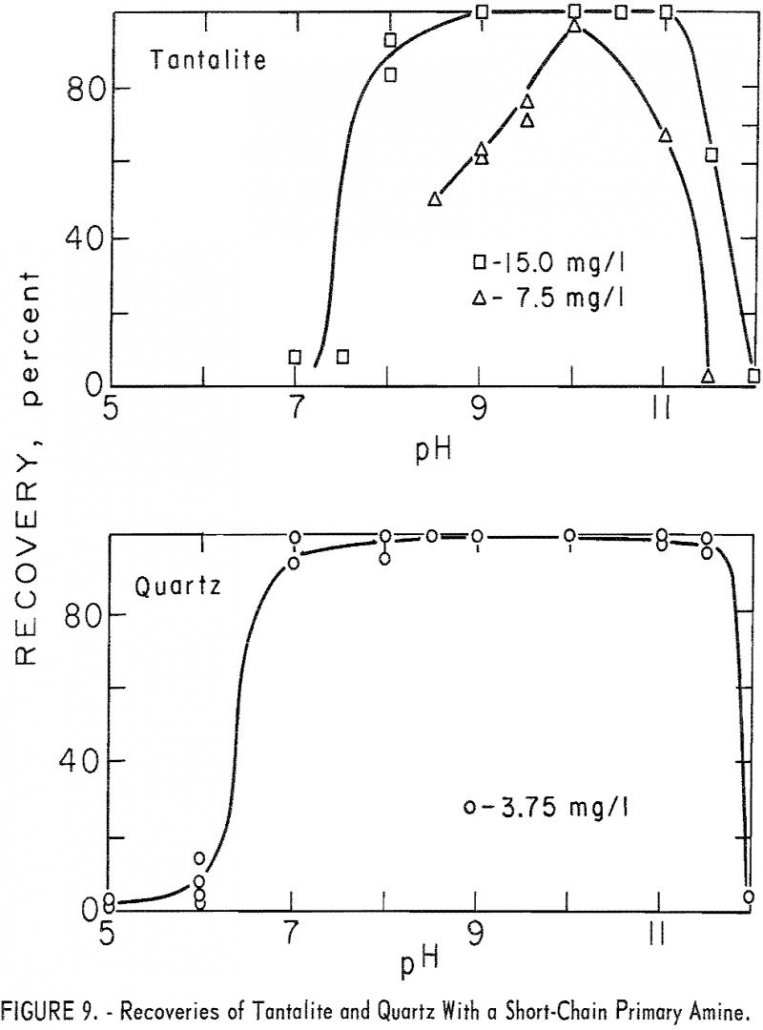
The purpose of this investigation was to determine the flotation characteristics of important columbium / tantalum ore minerals as a guide for the practical concentration of low-grade columbium ores. Placer deposits amenable to gravity concentration have been the major source of columbium; however, these deposits are limited. Therefore, the future of columbium is dependent upon […]
How to Purify & Concentrate a Manganese Leach Solution
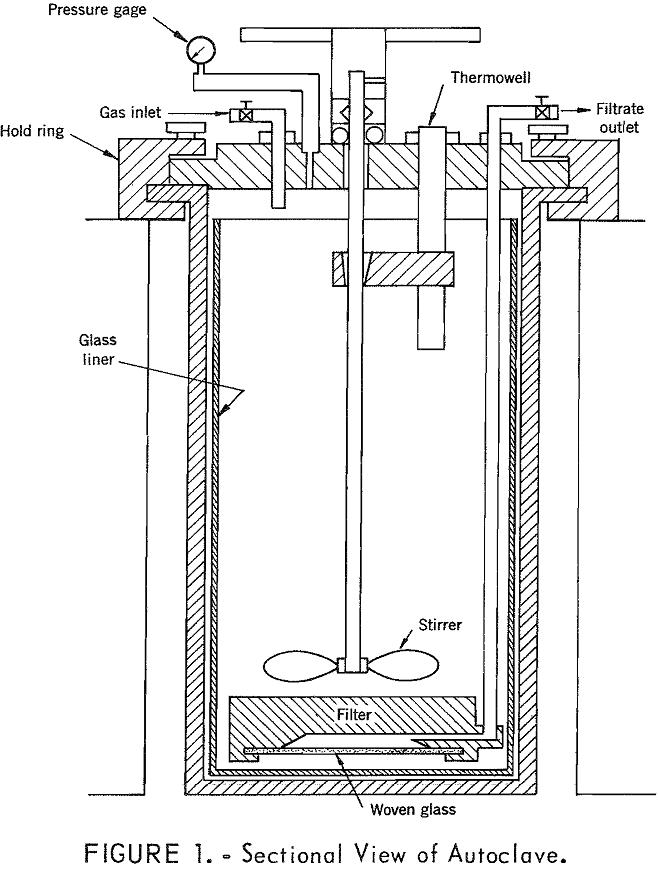
A temperature of 250° to 260° C was found to be satisfactory for simultaneous removal of iron and manganese from the pregnant leach liquor resulting from leaching of low-grade manganese ore. A holding time of about 15 minutes at this temperature was sufficient for maximum iron removal under oxidizing conditions. Using optimum conditions with oxygen […]
