How to Recover Lead & Copper from Blast Furnace Matte
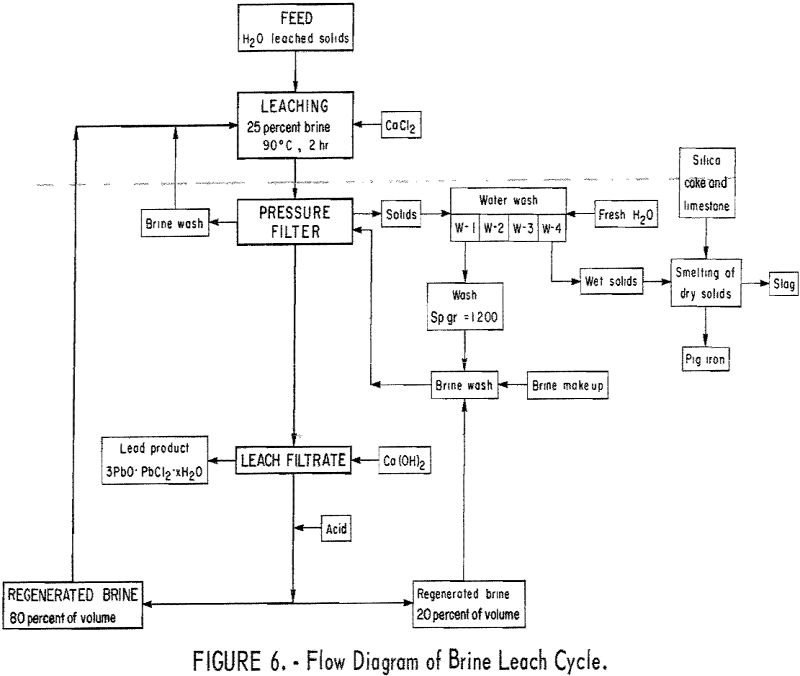
This research has shown that & solid waste byproduct from secondary lead smelters can be successfully processed to recover copper and lead that is lost during smelting. The major steps in the process and the products recovered are as follows: Copper and lead sulfides in blast furnace matte are converted to sulfates and iron sulfide […]
Electrorefining Vanadium Scrap

A molten-salt electrorefining process was developed which provides a practical way for reclaiming vanadium from scrap generated in the processing of ductile vanadium into bar, sheet, wire, and other shapes. Refining produced extremely ductile vanadium with a purity range of 99.93 to 99.95 percent. The process was particularly effective in reducing the interstitial elements, carbon, […]
Ball Mill Pulverizing
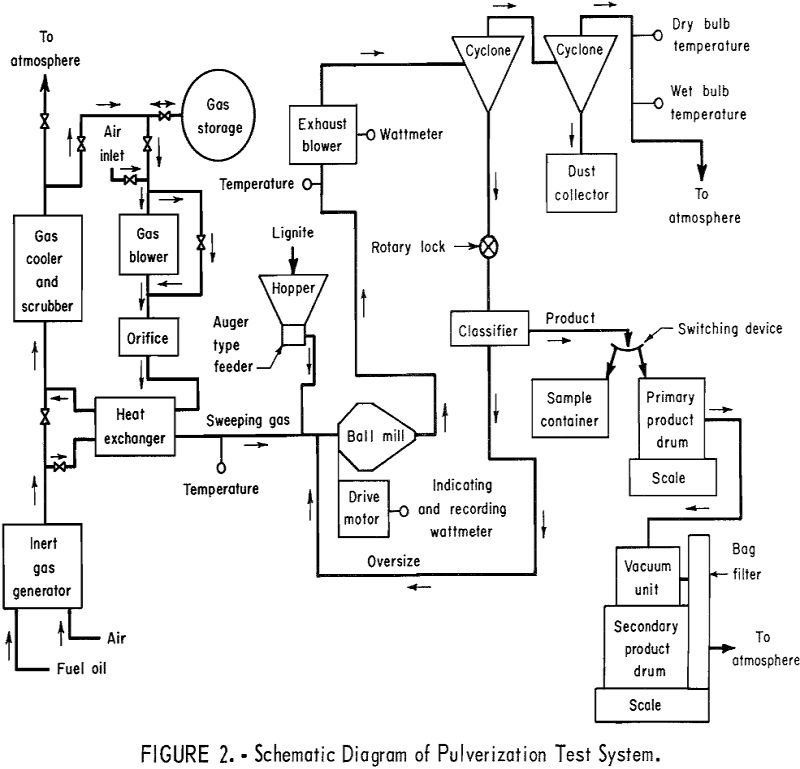
As in a pilot-plant-scale hammermill, the effect of moisture content in the pulverization of lignite in a similar size ball mill was observed to be a highly significant factor with respect to power required and in pulverization capacity. Both predrying before pulverization and drying in the mill were found to be highly beneficial in pulverization […]
Fluorine Determination Method
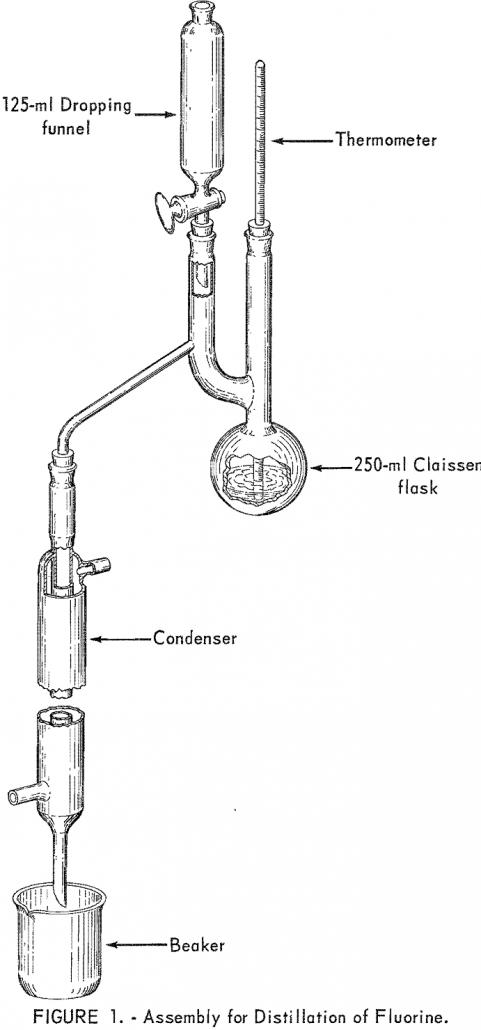
Coal normally contains trace amounts of fluorine ranging up to about 0.02 percent. These small quantities of fluorine generally are volatilized when coal is burned in boiler furnaces. but they may be a transient factor in some types of corrosion and occasionally in deposit formation, and may contribute to atmospheric pollution. A standard method is […]
Vacuum Arc Melting
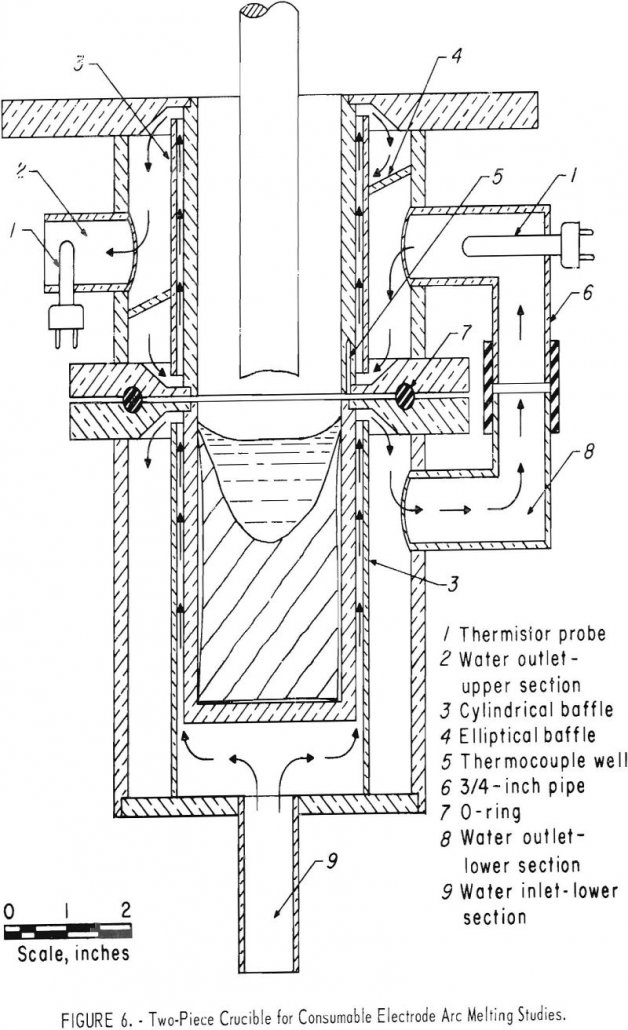
During the past decade, several novel melting and casting techniques including vacuum arc melting, skull casting, Hopkins’ Process or electroslag melting, and electron-beam melting have been developed on an industrial scale. All of these techniques employ a water-cooled crucible. Heat transfer during vacuum-arc melting with water-cooled crucibles has been studied on a theoretical bases, but […]
Mining by Nuclear Explosives Fracturing
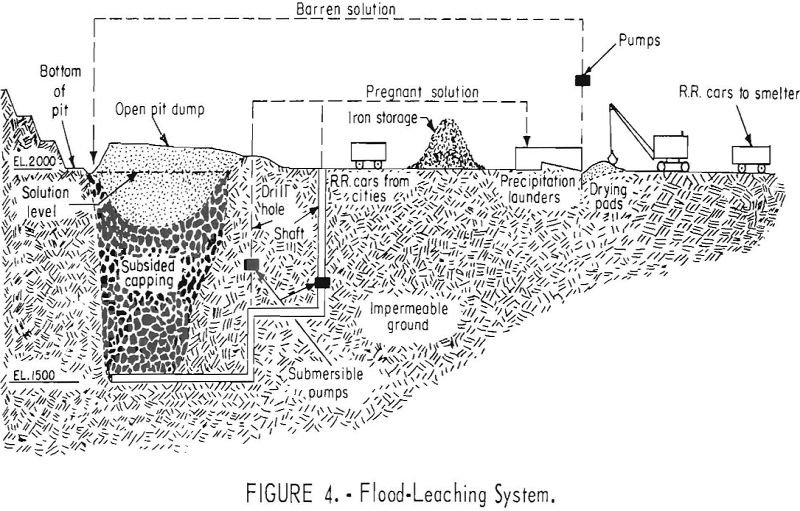
The copper in many large low-grade and small high-grade deposits cannot be economically recovered by conventional methods because the value of the copper content of the large low-grade deposits is less than the cost of recovery, and the tonnage in the small deposits is not enough to amortize a recovery plant. These deposits are suitable […]
Gold Distribution & Variability in Drill Core
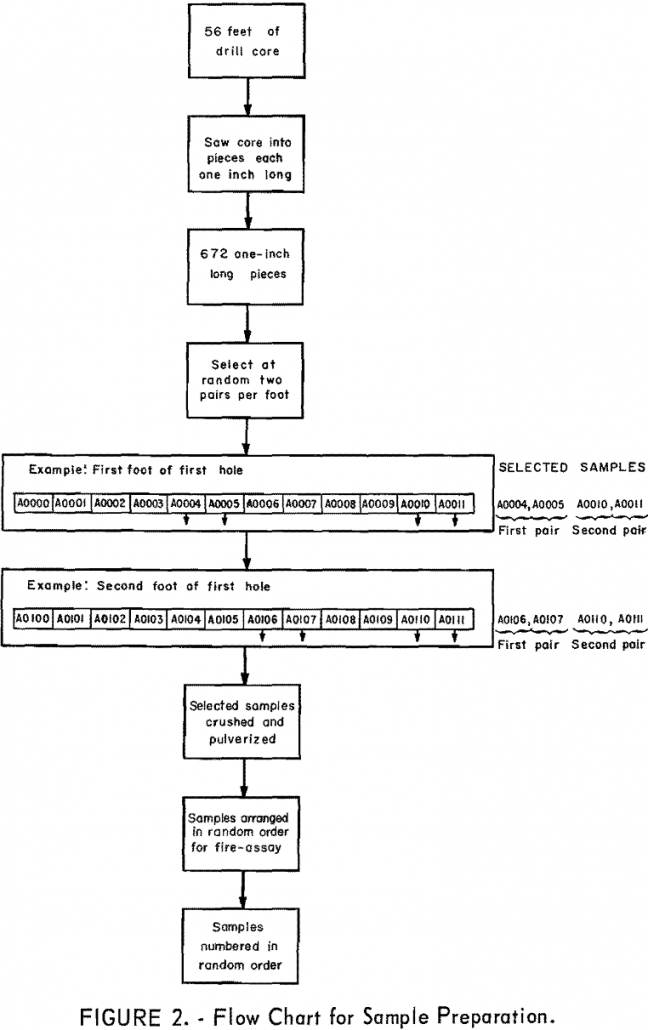
The extreme variability in gold mineralization in drill core is revealed through the detailed sampling experiment. This variability is that naturally present on the smallest scale that can be found by fire assay. With samples of substantially larger volumes, less variability would be found. Most of the variability is associated with among-feet rather than within-feet […]
Electrowinning Rare Earth Elements
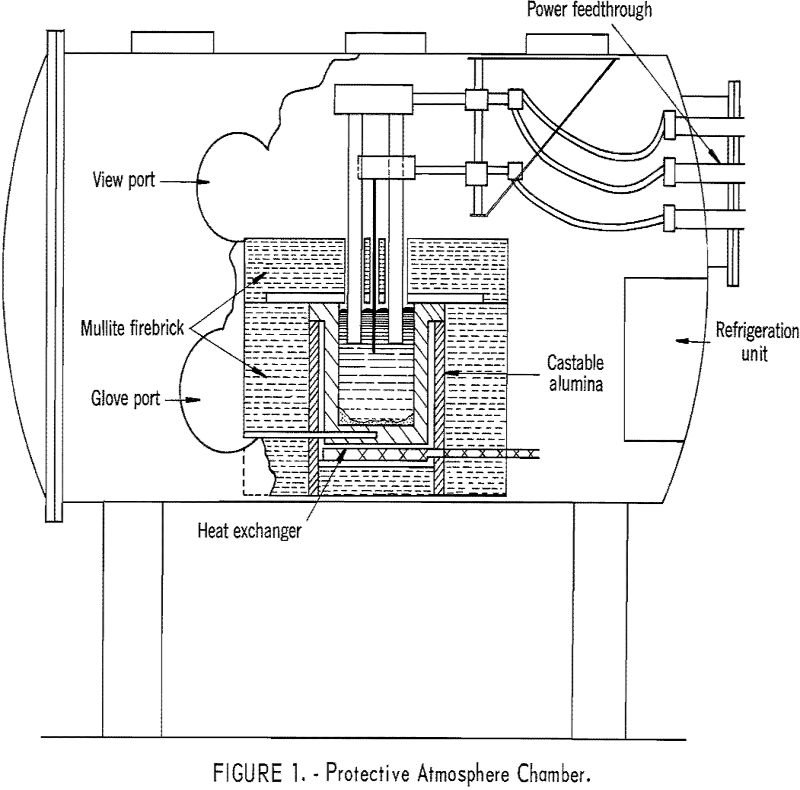
Electrowinning Rare Earth Elements like Neodymium, praseodymium, and didymium, were (obviously) electrowon from their oxides dissolved in fluoride melts. The use of a thermal gradient cell resulted in recovery of nodules of well-coalesced metal with a purity of 99.9 percent. Current efficiencies of up to 83 percent were obtained. Shallow immersion of fluted anodes allowed […]
Electrorefining Vanadium
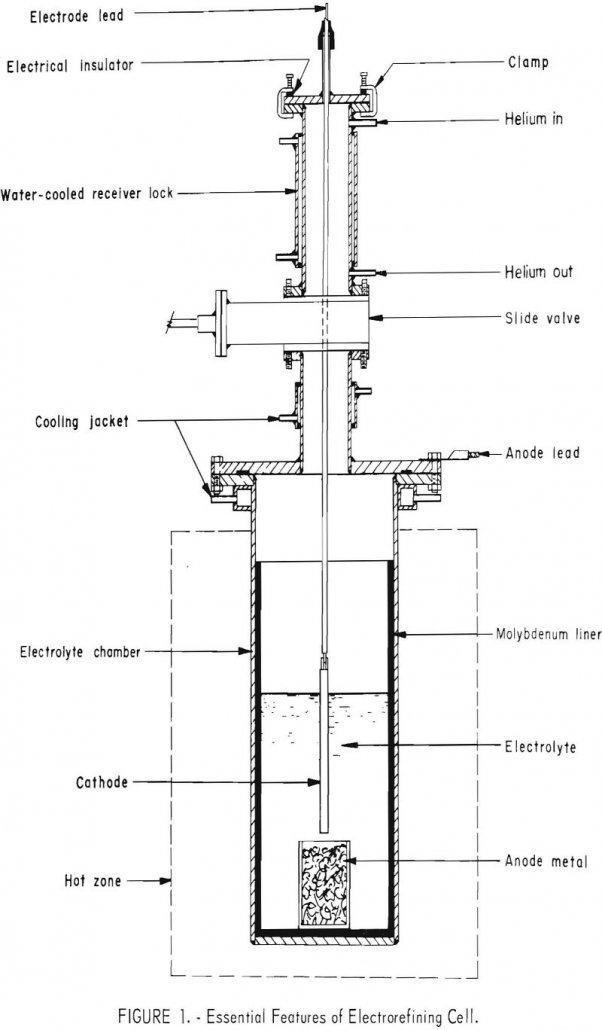
A molten salt, inert-atmosphere electrorefining process was developed for producing ductile vanadium from commercial vanadium. Five different chloride electrolytes were utilized. The chief impurity elements in the commercial vanadium were aluminum, iron, molybdenum, nitrogen, and silicon totaling 8 percent. Refining reduced these elements to produce 99.0 to 99.6 percent vanadium. The process was especially effective […]
Conveyor Belt Fire Hazard
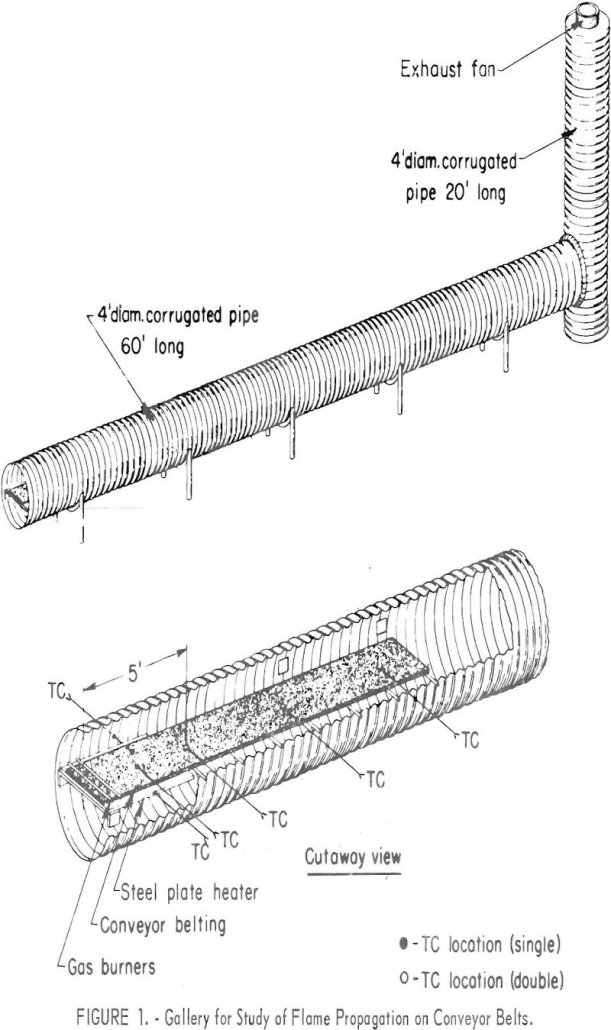
This investigation showed that neoprene, polyvinyl chloride, and rubber belts ignite readily when subjected to an impinging flame. Although pre-heating of the belt is not necessary for ignition, preheating does increase the probability of developing a self-sustaining flame after ignition. The time and total quantity of heat required to ignite neoprene were greater than those […]
