Dry Magnetic Cobbing Separation
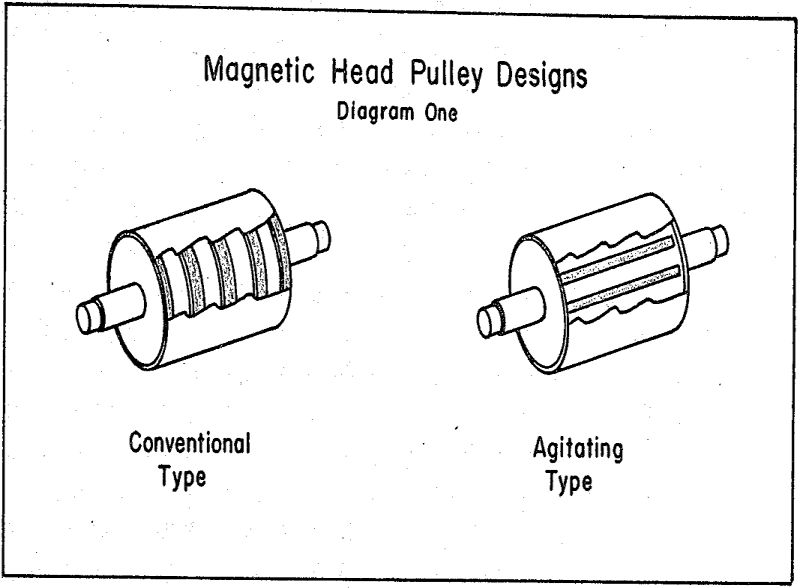
Cobbing, as used in this paper, refers to coarse dry magnetics separation. It is applicable when, by its practice, plant cost can be reduced or the value of its products increased by the removal of a barren or lean reject or a high grade final product. This paper attempts to describe cobbing as it is […]
Contact Angles and Flotation Rate
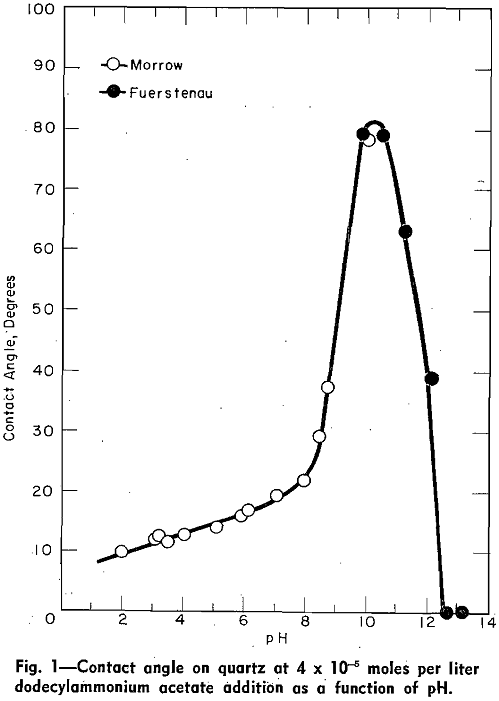
The object of this article is to point out the experimental relationship which exists among contact angle, adsorption density, zeta potential, and flotation rate data. In each of the experiments discussed in this article, the surface properties of quartz, as a function of pH, were measured in solutions to which constant quantities of dodecylammonium acetate […]
Earthquake Design for Metallurgical Plants
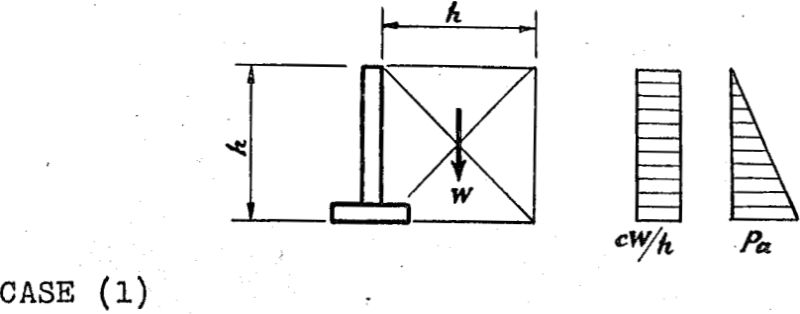
All persons and communities that have experienced strong-motion earthquakes are convinced of the importance and complexity of earthquake problems that must be solved in order to reduce the personal hazards and property losses to a reasonable minimum. It is also clear that absolute elimination of all risks is impossible. Reduction of existing hazards and precautionary […]
Analyzing Ore Reserves: Statistical Method of Calculating

There are certain data handling techniques used by statisticans that can help one to calculate the size of an orebody and to develop some of the relationships between size, cutoff grade, average grade, mining cost, and profit. Knowing the relationships amongst these factors can help determine the most desirable operating conditions. A statistical technique that […]
How to Measure the Tensile Strength of Rocks
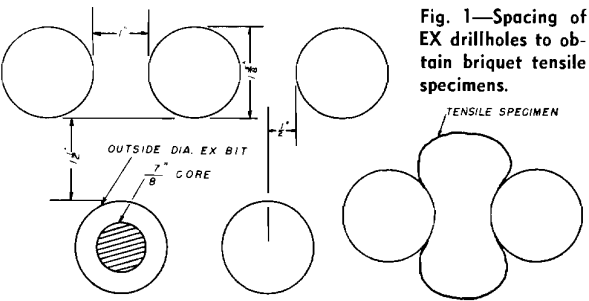
Principle and equipment are the same as for the test for tensile strength of hydraulic-cement mortar. The test specimen has the shape of a briquet. While in the original cement mortar test the briquet is cast in a special mold, it is prepared from rocks in different ways, depending on how easily they can be […]
Cement Grinding Plant Design
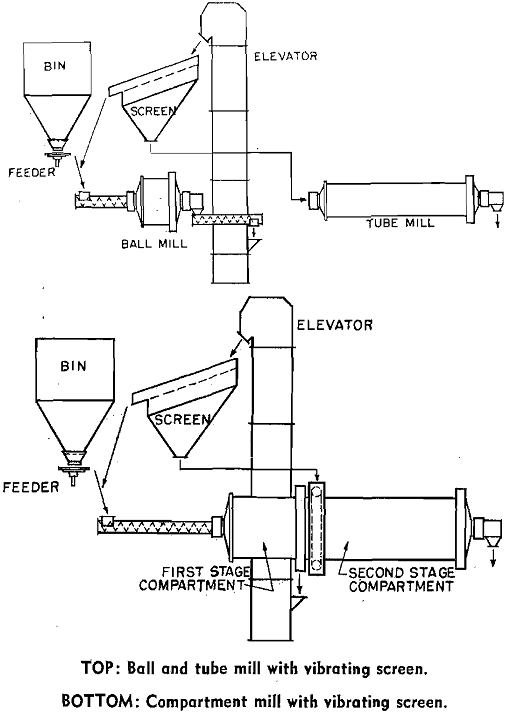
Grinding is a large and costly part of Portland cement manufacture. Prior to clinkering in the rotary kiln, raw materials are ground to a fineness of 80 to 90 pct passing 200 mesh. Then, after burning and cooling, the resulting clinker is ground to about 92 pct passing 325 mesh. Open Circuit Clinker Grinding: Many […]
Molybdenite Leaching Kinetics
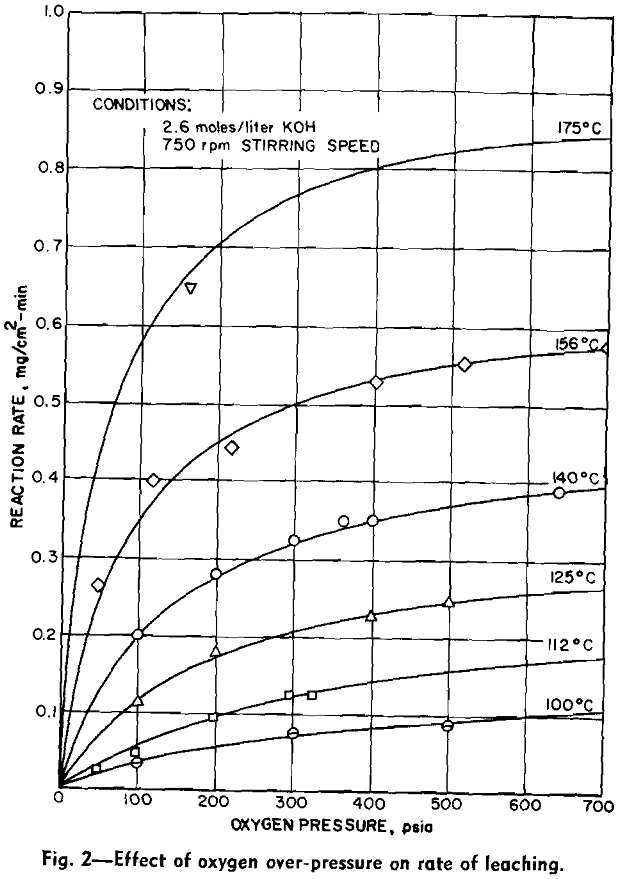
High temperature-high pressure techniques have long been used to great advantage in the organic chemical industry, the petroleum industry, and the paper industry. Only recently, however, have these methods been used to extract metals from their ores on a commercial scale. The Chemical Construction Corp., together with interested producers of nickel and cobalt, has done […]
Comminution: Energy-Size Reduction Relationships
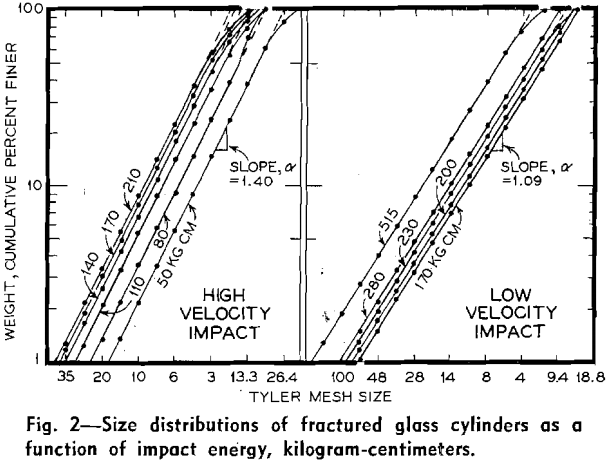
Search for a consistent theory to explain the relationship between energy input and size reduction in a comminution process has accumulated, over the years, an enormous amount of plant and laboratory data. Although some correlation of these data has been possible for purposes of engineering design and for the advancement of research in fracture, there […]
Lime Burning Operation Heat Energy Requirements
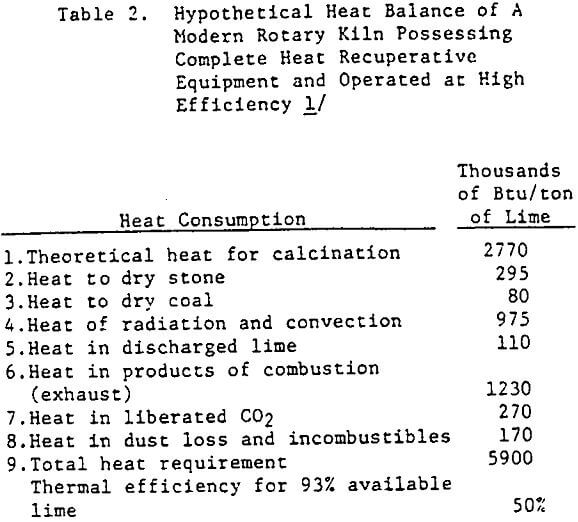
There are two types of lime, high calcium and dolomitic lime. Typical analyses of these materials are shown in Table 1. This discussion is concerned only with high calcium lime. Lime is produced from naturally occurring limestone by subjecting the limestone to a temperature in the range of 2200°F for sufficient time to drive off […]
Phosphate Rock
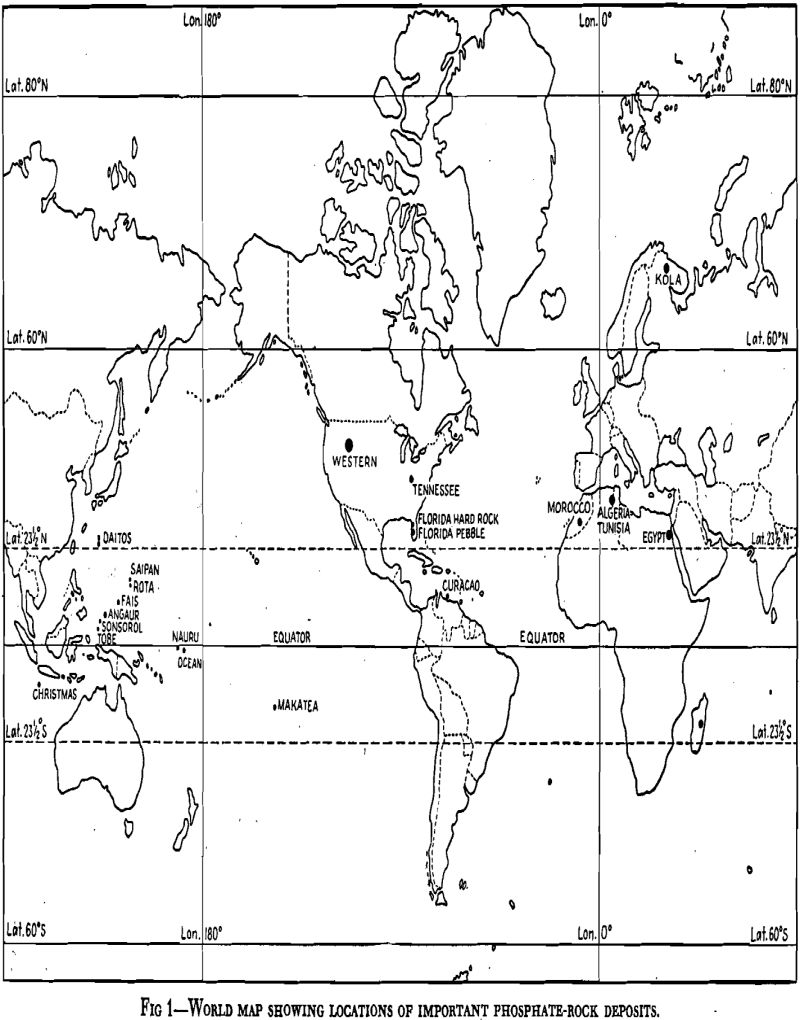
Apatite, the most abundant crystalline phosphate mineral, is found in igneous rocks and probably is the primary origin of all other phosphates, whether mineral or organic. Its chemical formula may be expressed as Ca5(Cl,F) (PO4)3. The chlorine may be replaced almost entirely by the fluorine. It is found in large or small hexagonal prisms, usually […]
